What Is a 301 Redirect?
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirection from one URL to another, used to maintain search engine rankings and user access when a webpage's URL changes. It signals to search engines and browsers that the original URL has been permanently replaced with a new one.
For example:
We updated a blog post and redirected it to a new URL.
From https://sem.vipacademictools.com/blog/wordpress-seo/ to https://sem.vipacademictools.com/blog/wordpress-seo/.
(If you click on the old URL, you’ll be automatically redirected to the new page).
We did this because we wanted the page to follow URL best practices.
But that’s far from the only reason to use a 301 redirect.
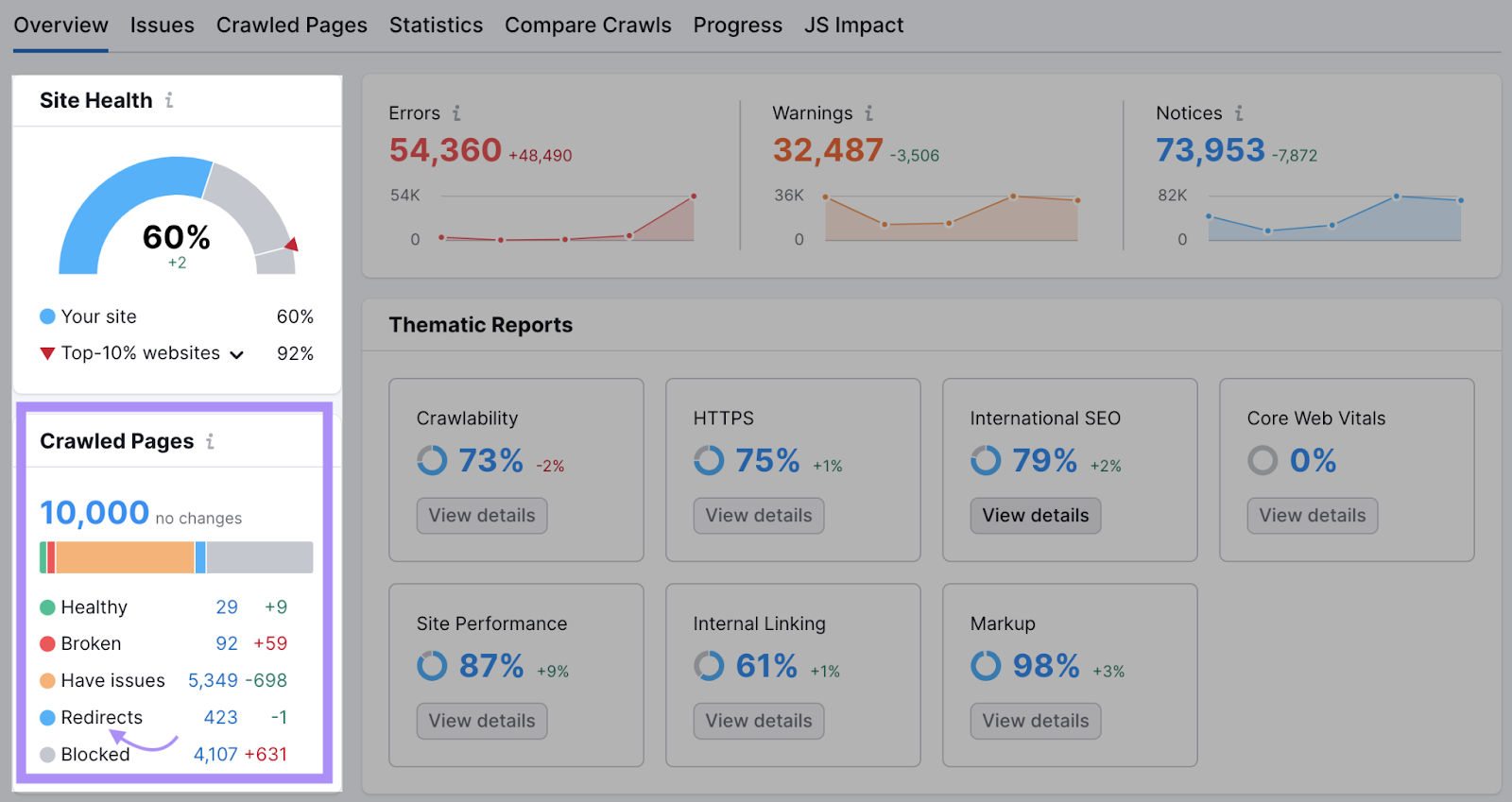
Tip: To quickly find redirect issues on your site, run a quick audit with Site Audit. And you’ll see it right there on the dashboard:
301 vs 302 Redirect
The main difference between a 301 and a 302 redirect is that 301 redirects are permanent and 302 redirects are temporary.
301 is the most common type. It takes visitors to the new URL and tells search engines the redirect is permanent.
A 302 redirect, on the other hand, also takes visitors to the new URL but tells search engines the redirect is only temporary.
When Should You Use a 301 Redirect?
There are different types of redirects (301, 302, meta refresh, etc.). And each has its own specific use case.
Here’s when (and why) you should use a 301 permanent redirect versus another type.
Permanently Moving a Page to a New URL
For example, from https://www.website.com/old-page-name/ to https://www.website.com/new-page-name/.
Sometimes, you need to change the URL of a page on your site.
Maybe a product name has changed slightly and you need to update the URL. Or want to better categorize your site's pages. The reasons are endless.
Implementing a 301 redirect will ensure that users and search engines are redirected to the new URL. And help search engines pass the SEO power of the old URL to the new URL.
Deleting a Page
If, for any reason, you want to delete a page on your site, you should redirect it to another relevant page if at all possible.
Why?
It creates a better user experience. And gives people an alternative.
For example, if you simply delete the page, users who click on a link to the page in search or on another webpage will land on a page like this:
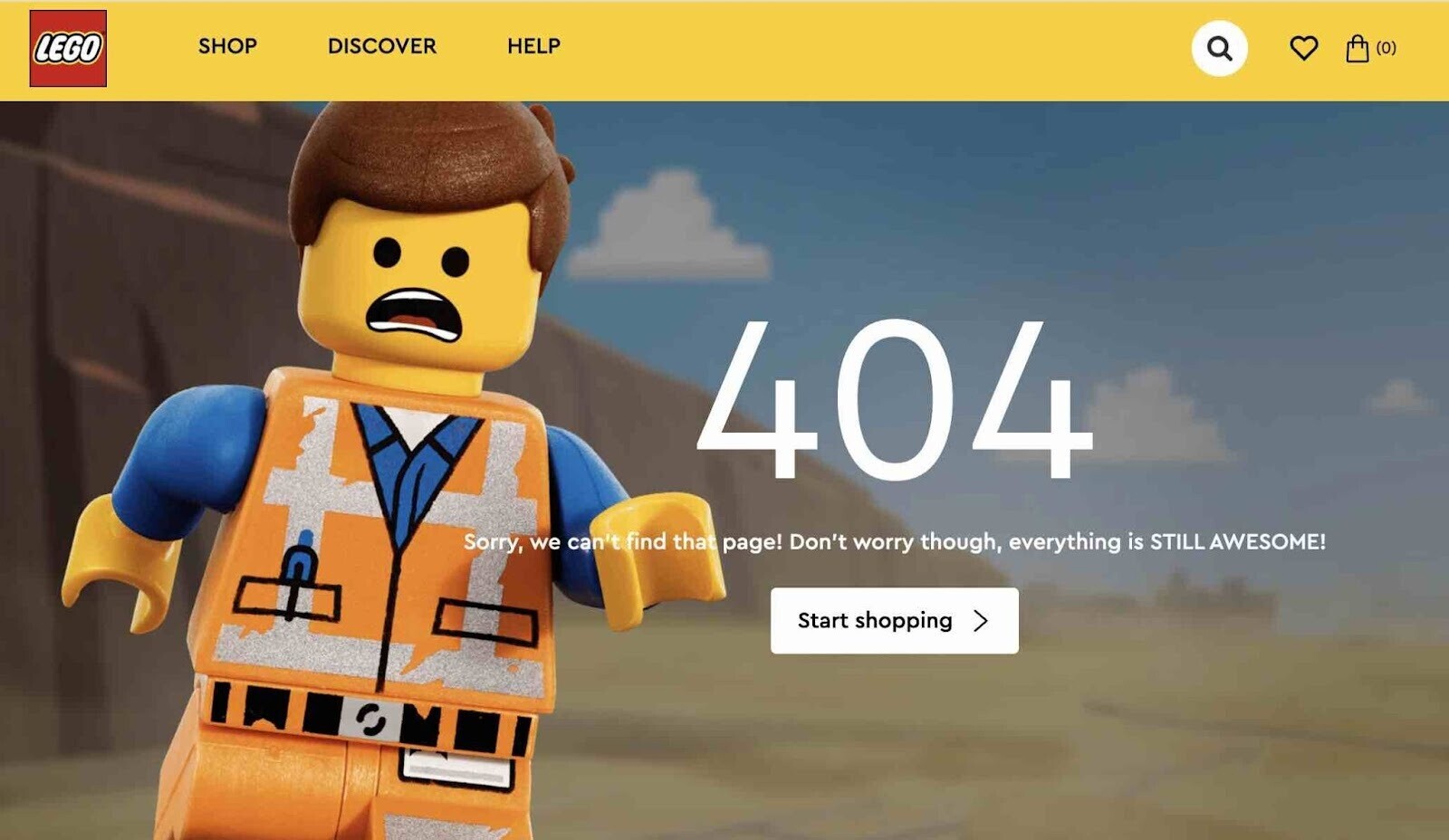
Without an alternative, the user will likely bounce.
Your best bet, in most cases, is to use a 301 redirect to send the user to a similar page with the same intent on your site.
Migrating Your Site to a New Domain
For example, from https://www.website.com to https://www.newwebsite.com.
You may also want to migrate your site to a new domain entirely.
Say you’re migrating from a .net to a .com. Or maybe you’ve rebranded and need to move to a different domain name.
A 301 redirect is the best way to do that. And notify Google using Google Search Console's Change of Address tool.
Changing Your Site Structure
For example, from https://www.website.com/old-category/post/ to https://www.website.com/new-category/post/.
If you want to change your site's structure to make it easier to organize your content and for Google to understand how your pages are related, opt for 301 redirects.
The same applies to changing any subfolder structure on your site.
Whether that’s blog categories, ecommerce categories, or other folders. A permanent redirect is the best way to implement the change.
Moving From Non-WWW to WWW URLs (or Resolving Duplication Issues)
For example, from https://www.website.com to https://website.com.
You need to make sure the main version of your site is either non-www or www.
Doing so will make your site appear more consistent to users and search engines. And avoid duplication issues.
The best way to make this clear is to use a 301 redirect to indicate which is the main version. And redirect users and search engines to your preferred version.
Switching From HTTP to HTTPS
For example, from http://www.website.com to https://www.website.com.
If you want to switch from HTTP to HTTPS (because it’s more secure and one of Google’s ranking signals), use a 301 redirect.
Doing so will ensure Google properly indexes the new protocol. And that users are redirected to the right pages.
Merging Two (or More) Domains
For example, from https://www.website.de to https://www.website.com/de/.
Sometimes, companies will need to merge one domain with another. This is common after business mergers and acquisitions.
This process requires exhaustive planning. But, for simplicity’s sake, if we’re talking about merging, the way to keep as much SEO power as possible is to merge using a 301 redirect.
Resolving 'Trailing Slash' Issues
For example, from https://www.website.com/page-name to https://www.website.com/page-name/.
Variants of a URL with and without a trailing slash are actually different pages. And Google will see them that way.
You need to make sure your site uses a consistent approach to handling trailing slashes on page URLs. The correct way to do this is to 301 redirect one to the other.
Resolving Upper-Case vs. Lower-Case Issues
For example from https://www.website.com/Page-Name/ to https://www.website.com/page-name/.
Just as with trailing slashes, upper- and lower-case URLs can be considered different pages.
Even one capitalized letter in a URL can make it different from its lower-case counterpart. And search engines may see it as a duplicate.
Using 301 redirects is usually the best way to resolve these issues.
Note: Generally speaking, it makes sense to use lower-case for your URLs and not to mix upper-case and lower-case.
How to Do a 301 Redirect
The way you implement a 301 redirect depends on your server and the content management system (CMS) you use.
Here’s how to do a 301 redirect across some of the common setups.
Tip: Remember to run a site audit after implementing redirects to make sure everything is running smoothly.
301 Redirects on WordPress Sites
Implementing WordPress redirects is relatively simple and straightforward, compared to other available redirect methods.
If you have a WordPress website, consider using a plugin before trying any of the other redirect methods on this list.
If you’re using the Yoast SEO Premium plugin, you’ll find a built-in redirects manager you can use to implement redirects.
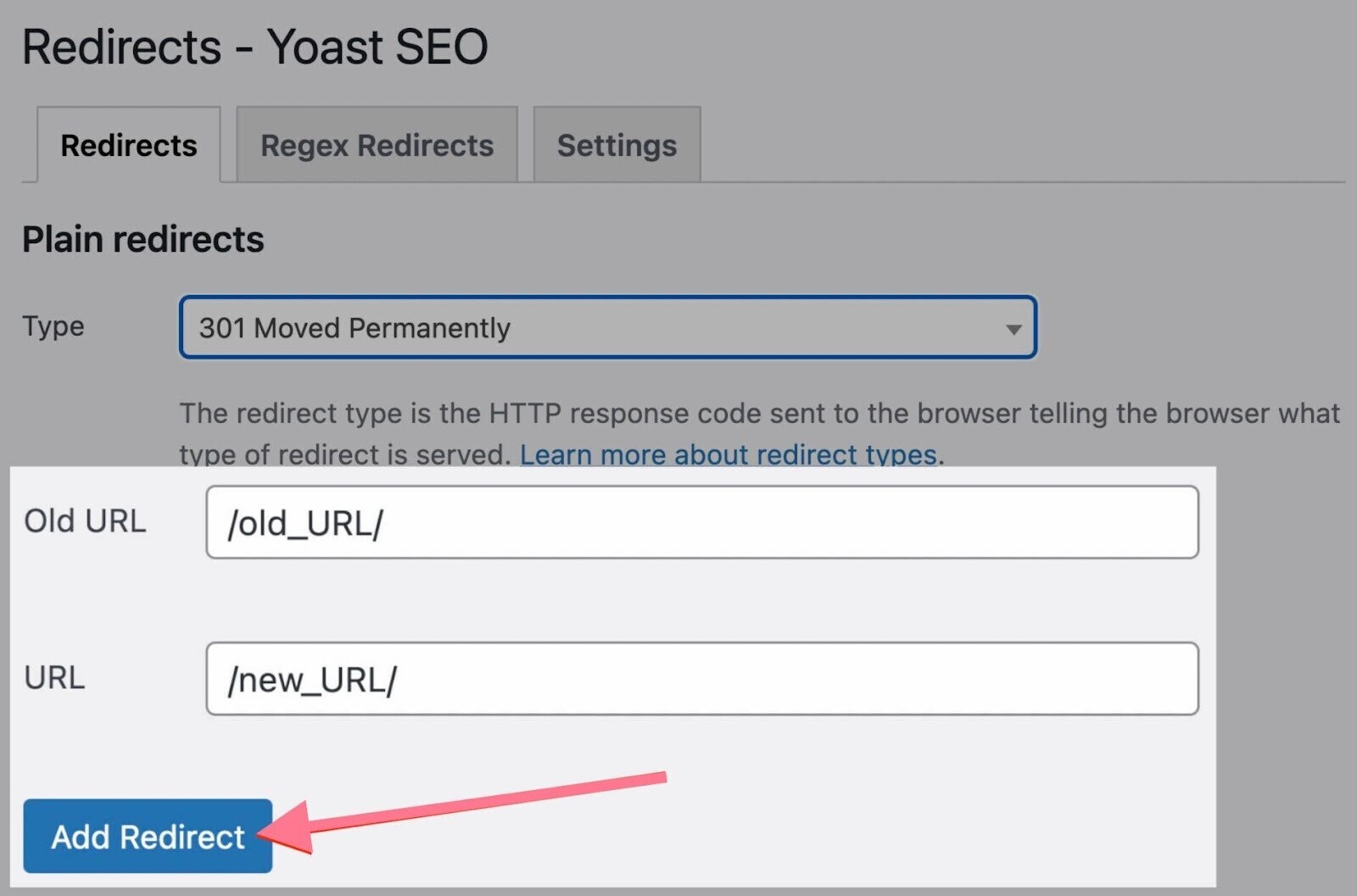
If you’re using the free version or another plugin that doesn't offer redirects, you’ll need to install a dedicated redirects plugin.
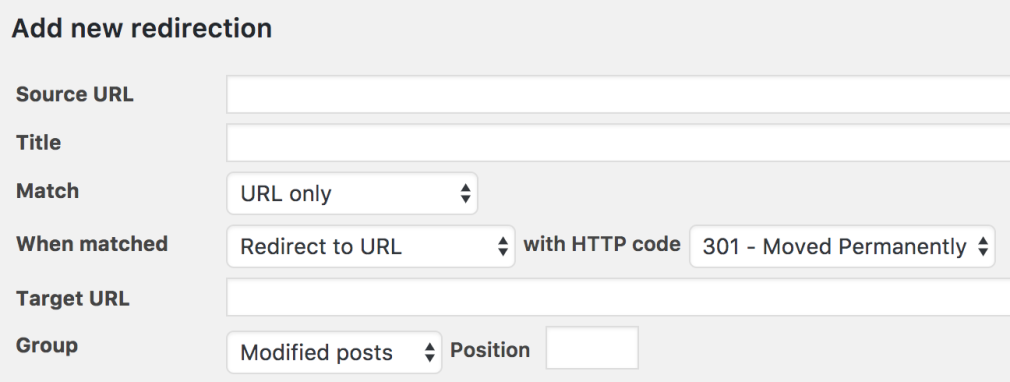
Redirection is among the most popular redirect managers for WordPress. You can add your redirects in minutes.
Like so:
If you’re using an alternative like Rank Math, you'll find a redirect manager included within the plugin.
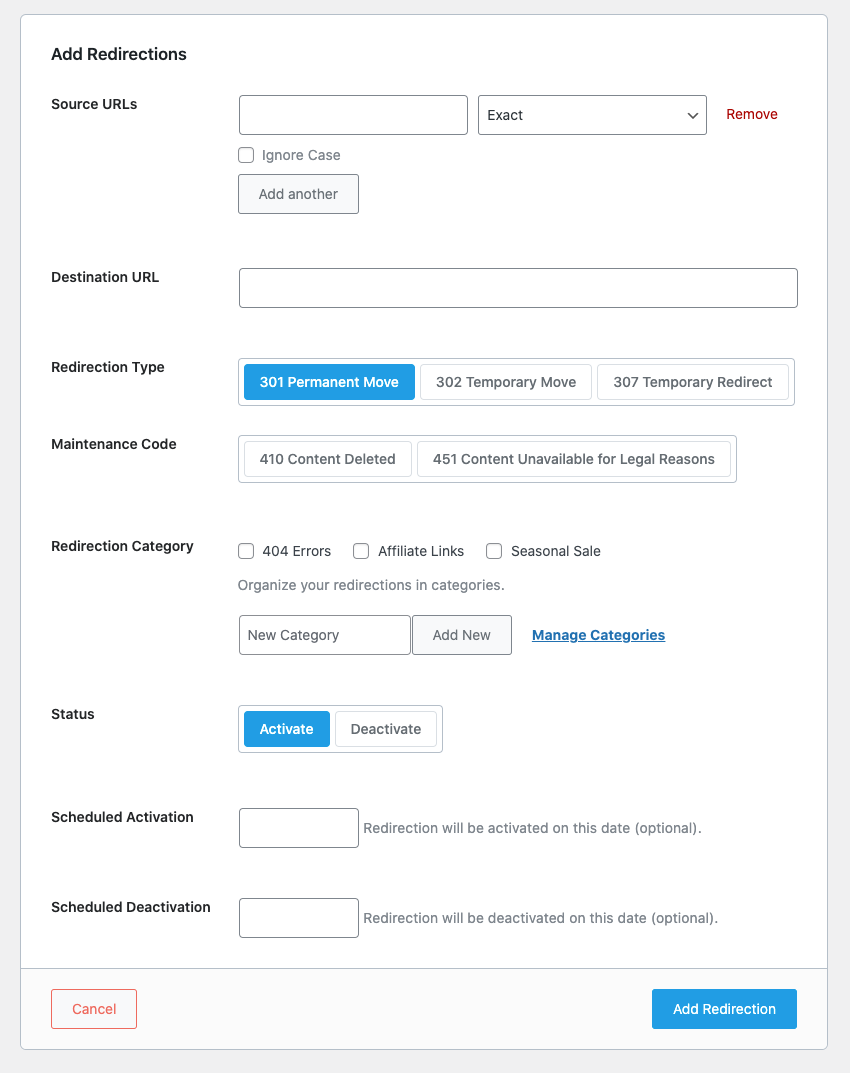
301 Redirects on Shopify Stores
As with WordPress, implementing 301 redirections on a Shopify store is relatively simple and straightforward.
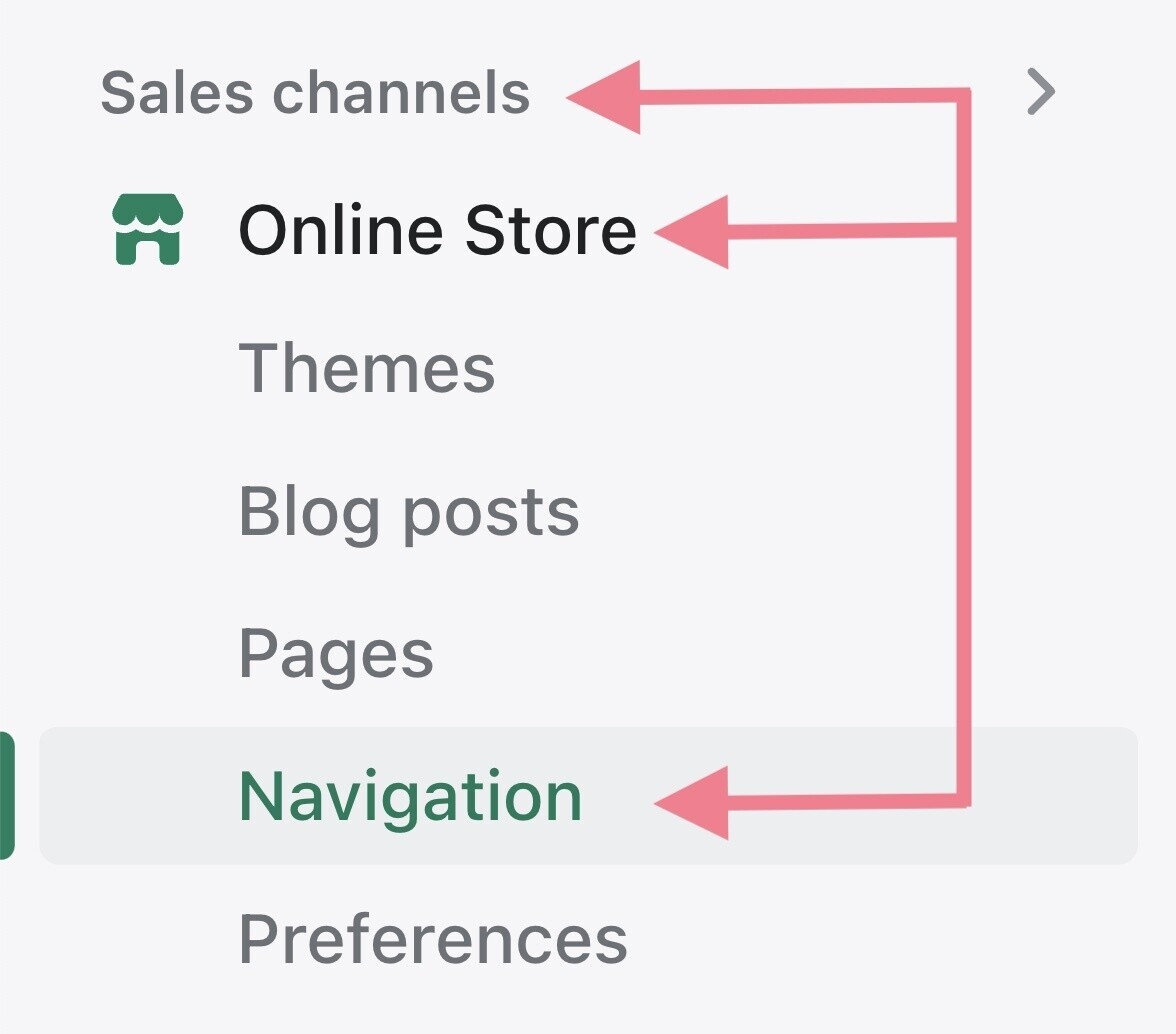
To do so, head to Sales channels > Online Store > Navigation
You’ll see a discreet “View URL redirects” link in the top-right corner. Go ahead and click it.
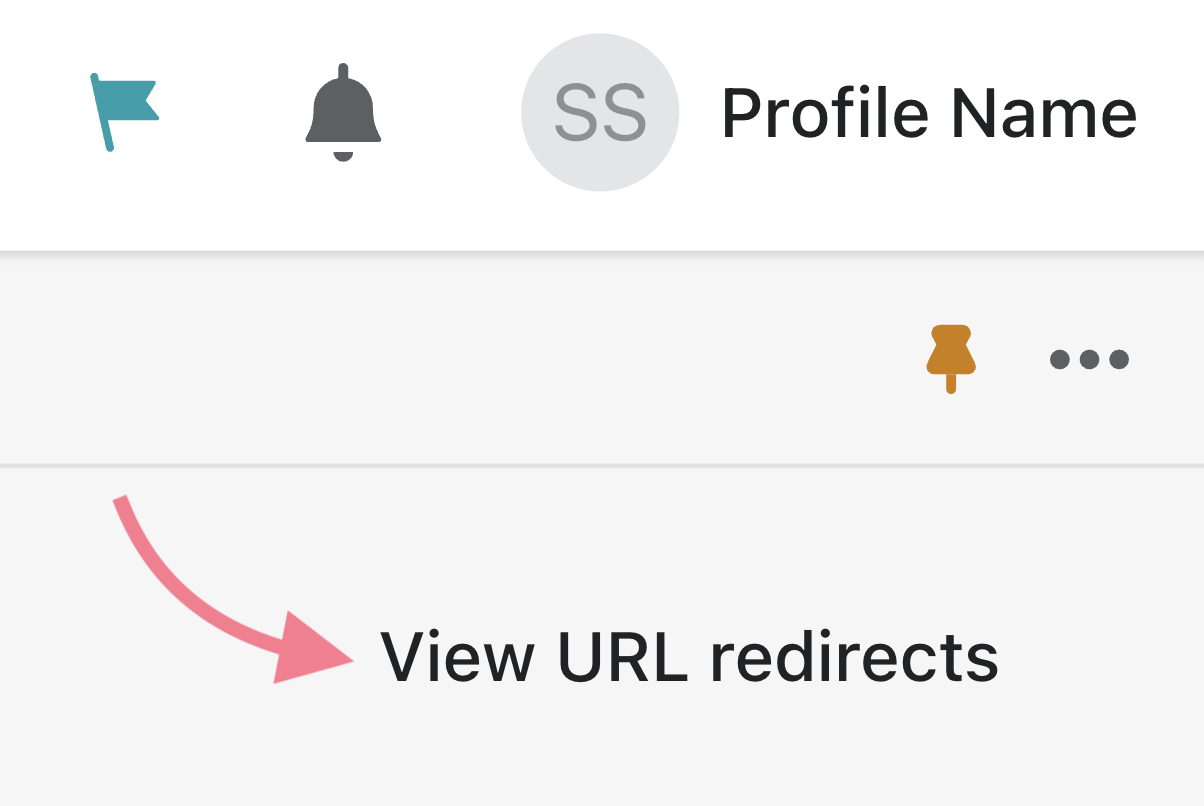
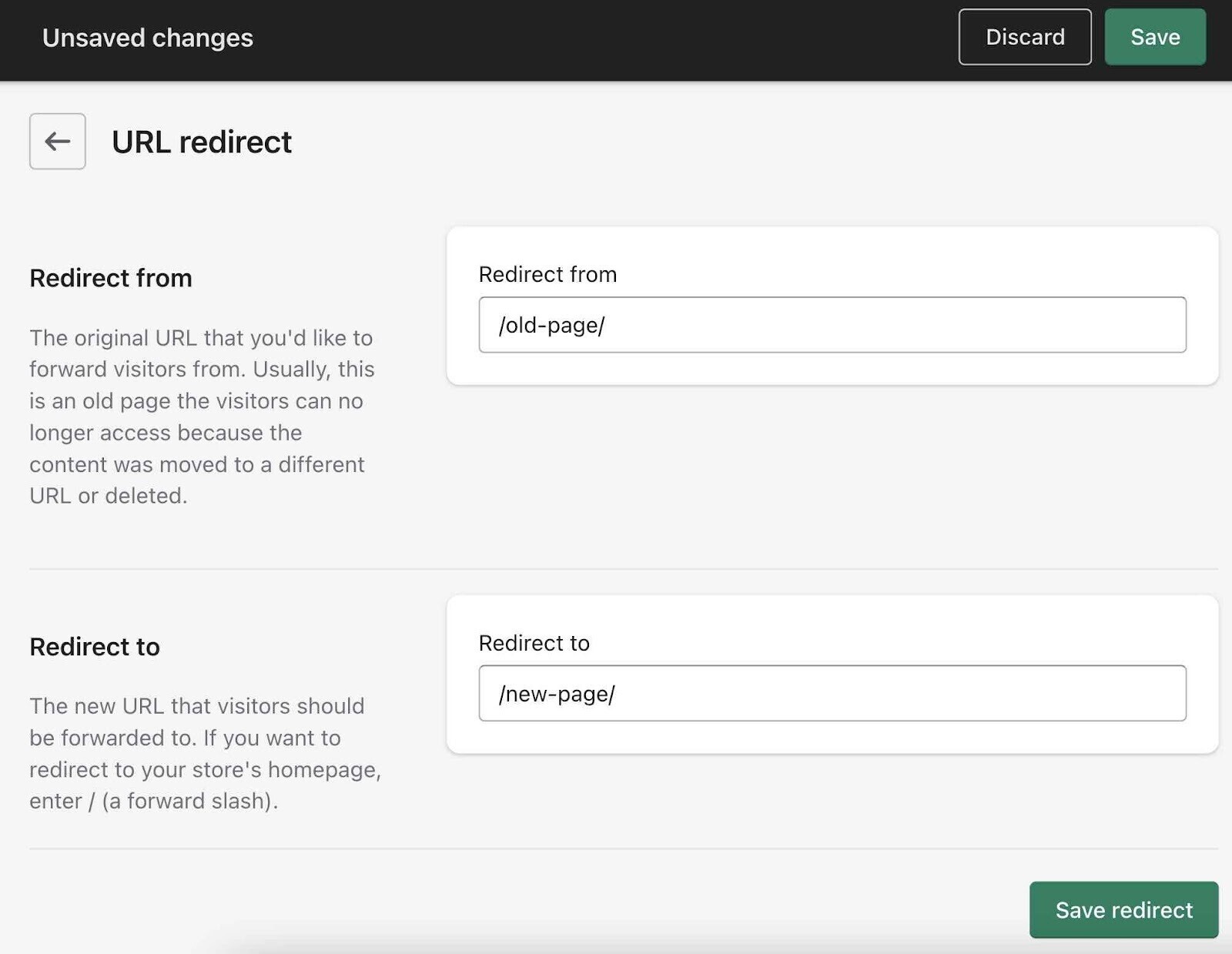
Next, click “Create URL redirect.”
It is then as simple as adding your “from” and “to” URLs and saving the redirect.
301 Redirects on BigCommerce
If you’re running a store on BigCommerce, here is how to add 301 redirects:
Navigate to Settings › 301 Redirects.
And add a redirect, including your old URL.
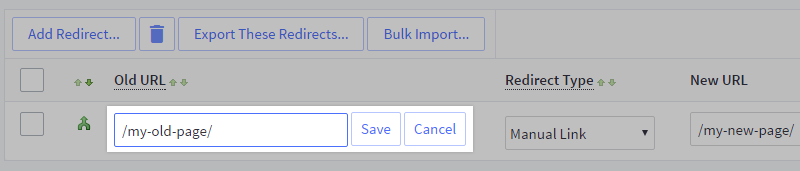
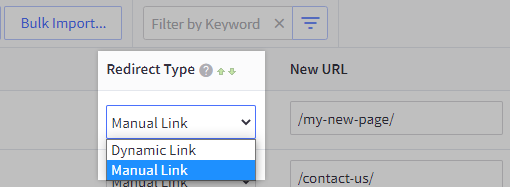
Choose a manual link, where you enter the new URL to redirect to.
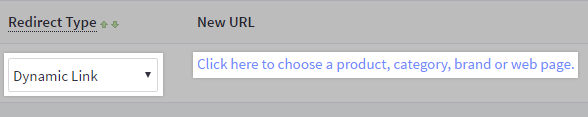
Or dynamic link, where you select a page or category, and the redirect will automatically update if you change this page later.
Enter your new page's URL or choose a page to redirect to if you selected the dynamic link option above.
301 Redirects on Magento Stores
If your ecommerce store runs on Magento, the functionality to add 301 redirects is built right into the platform.
Here is how to create them:
Magento 1
If you are running Magento 1, navigate to Catalog > URL Rewrite Management
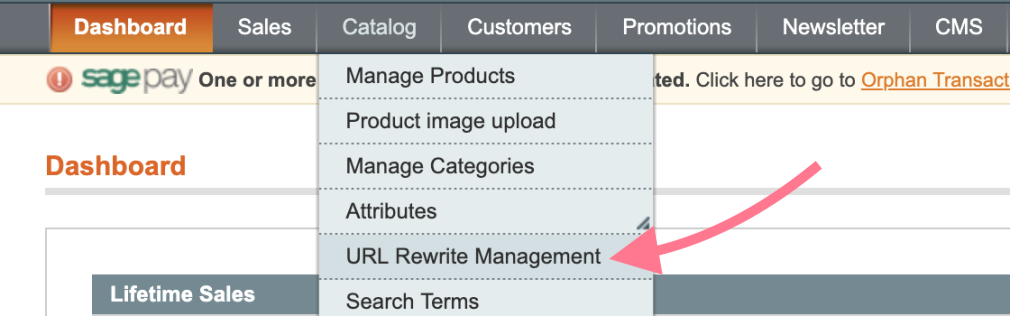
You’ll see any redirects that have previously been created.
Go ahead and “Create URL Rewrite.”
And select “Custom” rewrite.
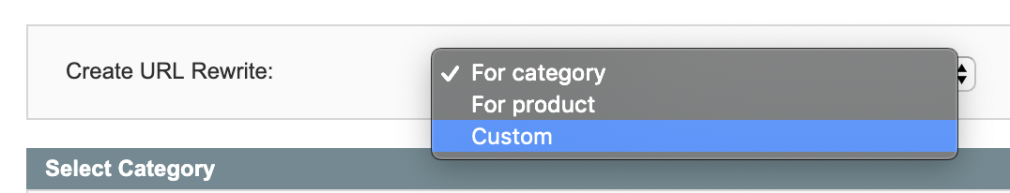
Then, fill out the required URL rewrite information.
Like so:
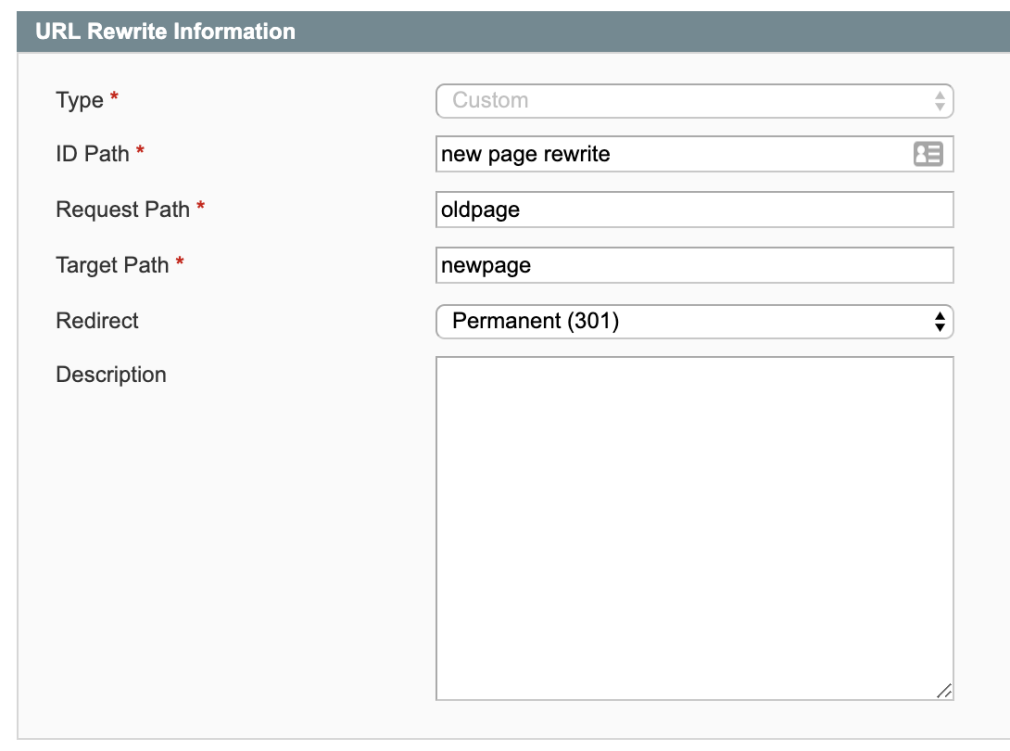
ID Path = The name of your rewrite that's used for admin purposes only.
Request Path = The original / from URL
Target Path = The new / target URL
Redirect = Permanent (301)
Description = Any description you want to add for the redirect
Magento 2
For Magento 2, first navigate to “URL Rewrites”:
Marketing > SEO & Search > URL Rewrites
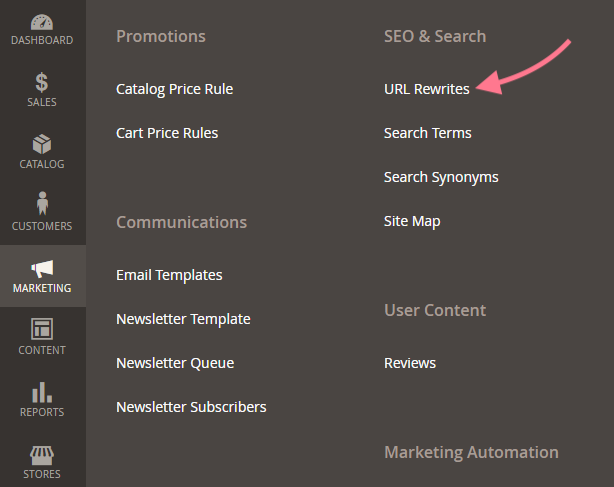
Go ahead and “Add URL Rewrite” and fill out the required information.
Like this:
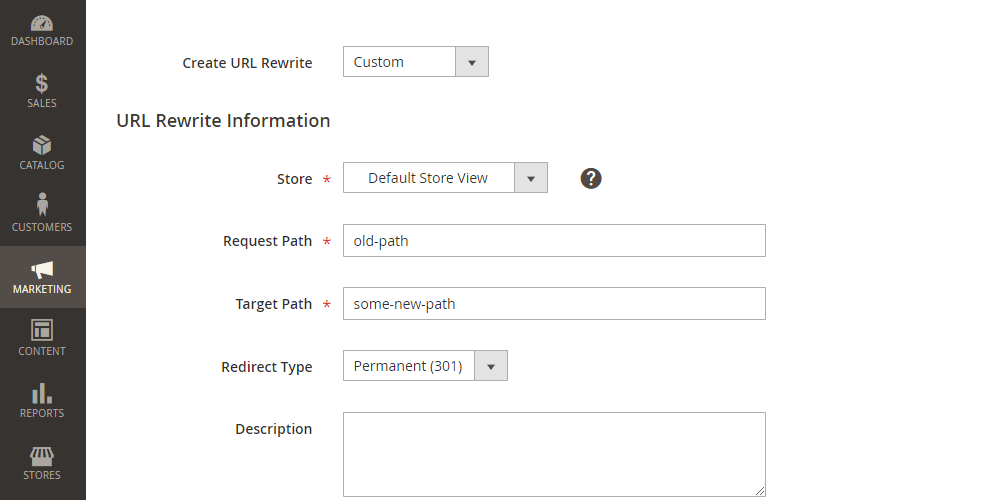
Create URL Rewrite: Custom
Store = The store you want to add the redirect for
Request Path = The original / from URL
Target Path = The new / target URL
Redirect Type = Permanent (301)
Description = Any description you want to add for the redirect
301 Redirects on Apache Servers
Warning: This 301 redirect method is only meant for experts. Mistakes here can cause big problems for your website. If you’re not an expert, proceed with extreme caution or reach out to an expert who can help.
If your site runs on an Apache server, you can edit your site's .htaccess file to implement redirects.
To add a redirect to the file, add a line that tells the server what to do. You’ll add your new rules immediately under “RewriteEngine On,” which you can find in the mod_rewrite module in Apache.
Once you’ve located the right place to add a new rule, use the following examples to do the following:
Redirect a Single Page
RRedirect 301 /oldpage/ https://www.example.com/newpage/Redirect an Entire Domain to Another
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.example.com/$1 [R=301,L]Redirect an Entire Site to a Subfolder
Redirect 301 / https://www.website.com/subfolder/Redirect a Subfolder to a Different Domain
Redirect 301 /subfolder https://www.newwebsite.com/Redirect a Site Directory After a URL Change
Options +FollowSymLinks RewriteEngine On RewriteRule
^(.*)/old-category/(.*)$ $1/new-category/$2 [R,L]Redirect From Non-WWW to WWW
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^www\. [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.%{HTTP_HOST}/$1 [R=301,L]Redirect From HTTP to HTTPS
RewriteCond %{https} off
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://www.example.com/$1 [R=301,L]Redirect to Trailing-Slash URLs
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !(.*)/$
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.website.com/$1/ [R=301,L]301 Redirects on Nginx
Warning: This 301 redirect method is only meant for experts. Mistakes here can cause big problems for your website. If you’re not an expert, proceed with extreme caution or reach out to an expert who can help.
To create a permanent 301 redirect on Nginx, you need to add a line to your .conf file that is typically found in the root of your server.
Some of the common lines you might need to use are as follows:
Redirect a Single Page
server {
# Permanent redirect to an individual page
rewrite ^/old-page$ http://www.website.com/new-page permanent;
}Redirect an Entire Domain to Another
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name devisers.in www.devisers.in;
return 301 $scheme://www.devisers.com$request_uri;
}Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS
server {
listen 80;
server_name website.com www.website.com;
return 301 https://website.com$request_uri;
}Redirect From Non-WWW to WWW
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name devisers.in;
return 301 $scheme://www.devisers.in$request_uri;
}301 Redirects on a Windows Server
Warning: This 301 redirect method is only meant for experts. Mistakes here can cause big problems for your website. If you’re not an expert, proceed with extreme caution or reach out to an expert who can help.
If your site runs on a Windows server in ASP.NET, you need to add redirects into the web.config file in the site root.
Here’s how to implement the most common 301 redirections:
Redirect a Single Page
<configuration>
<location path="old-page">
<system.webServer>
<httpRedirect enabled="true" destination="http://www.website.com/new-page/" httpResponseStatus="Permanent" />
</system.webServer>
</location>
</configuration>Redirect An Entire Domain to Another
<system.webServer>
<httpRedirect enabled="true" destination="http://www.newwebsite.com/" />
</system.webServer>Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name="HTTP to HTTPS redirect" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="(.*)" />
<conditions>
<add input="{HTTPS}" pattern="off" ignoreCase="true" />
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" redirectType="Permanent" url="https://{HTTP_HOST}/{R:1}" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>Redirect from Non-WWW to WWW
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name="Redirect http://website.com to http://www.website.com HTTP" patternSyntax="ECMAScript" stopProcessing="true">
<match url=".*"></match>
<conditions>
<add input="{HTTP_HOST}" pattern="^website.com$"></add>
<add input="{HTTPS}" pattern="off"></add>
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" url="http://www.website.com/{R:0}" redirectType="Permanent" appendQueryString="true"></action>
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite> How to Use 301 Redirects to Boost Your SEO Performance
301 redirects can help you overcome issues that hold back your site's organic visibility. Or make the most out of opportunities to drive growth.
Here are some of the most common ways 301s can be used to boost your SEO performance:
Migrate Your Blog From a Subdomain to a Subfolder
This is one of the most common ways to use 301 redirects for quick SEO wins.
A subdomain is like a child of the parent domain. And is often used to host blogs and stores.
For example, blog.yourdomain.com
And a subfolder is part of your main domain. Like any other page.
For example, yourdomain.com/blog/
The thing is:
Google can treat your subdomain as a separate entity from your main domain.
Which means Google might not take into account all the valuable content on your subdomain and its valuable assets (like backlinks) when evaluating your primary domain.
So, to help you potentially rank better and drive more traffic, it might make sense to redirect your blog from a subdomain to a subfolder.
Note: Every website is different, so don’t redirect a subdomain to a subfolder without first doing your research to make sure that would be a beneficial move.
Resolve Keyword Cannibalization Issues
Keyword cannibalization is when two (or more) pages are showing up in Google for the same or highly similar keywords and competing against each other. Google doesn’t know which pages should rank higher for which keywords.
You don’t want that.
And the simplest way to fix cannibalization issues is often to redirect the lowest-performing page to the other.
By low-performing, we mean the one with fewer backlinks, lower ranking, lower traffic, etc.
You can quickly find cannibalization issues using Semrush’s Position Tracking tool. Under the cannibalization tab.
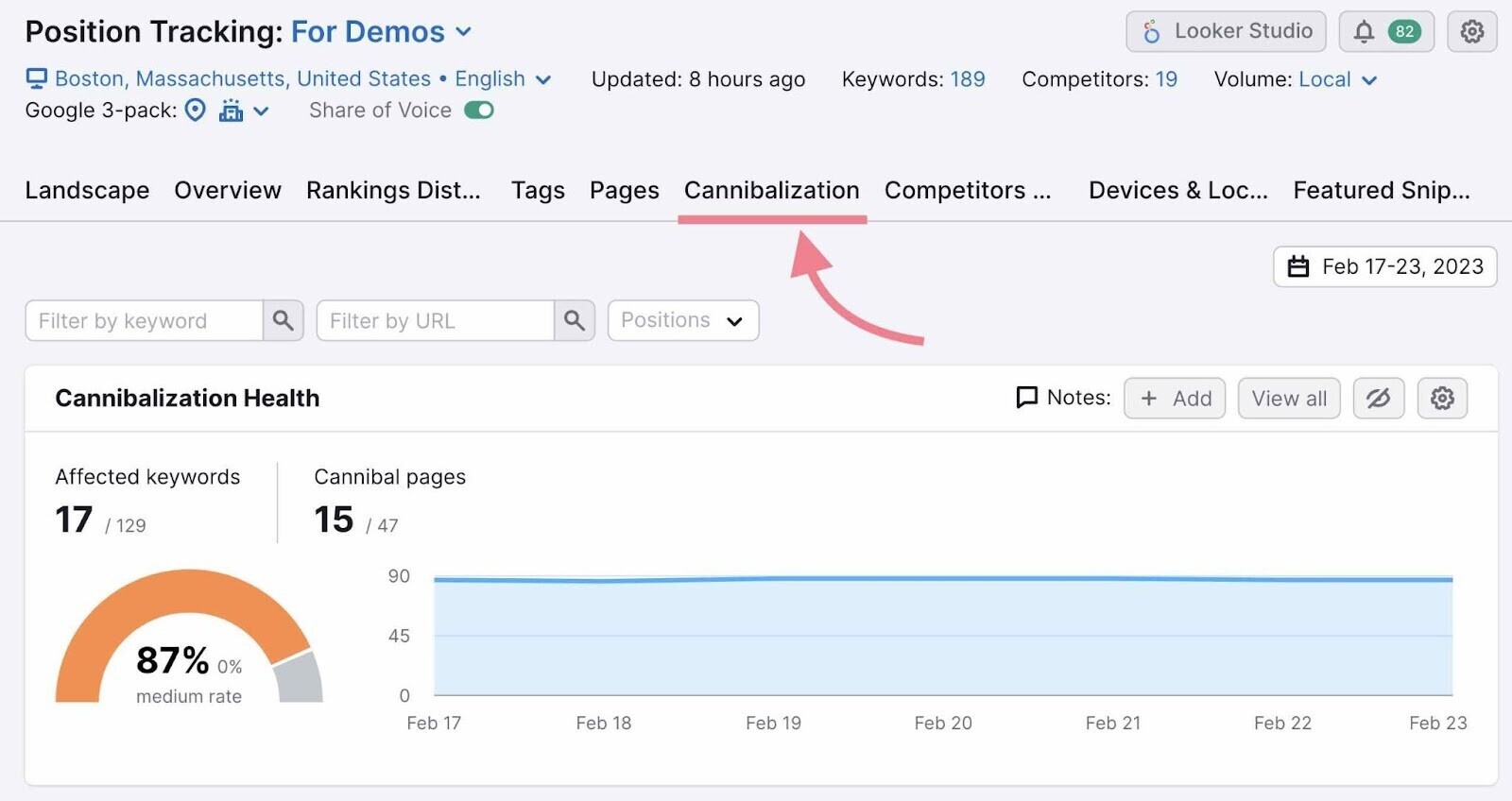
Merge Multiple Websites Into One
Sometimes businesses run on multiple sites.
Let's say you run a hotel chain and have a different website for each hotel. It might make sense to merge these all into one.
Just like Marriott does.
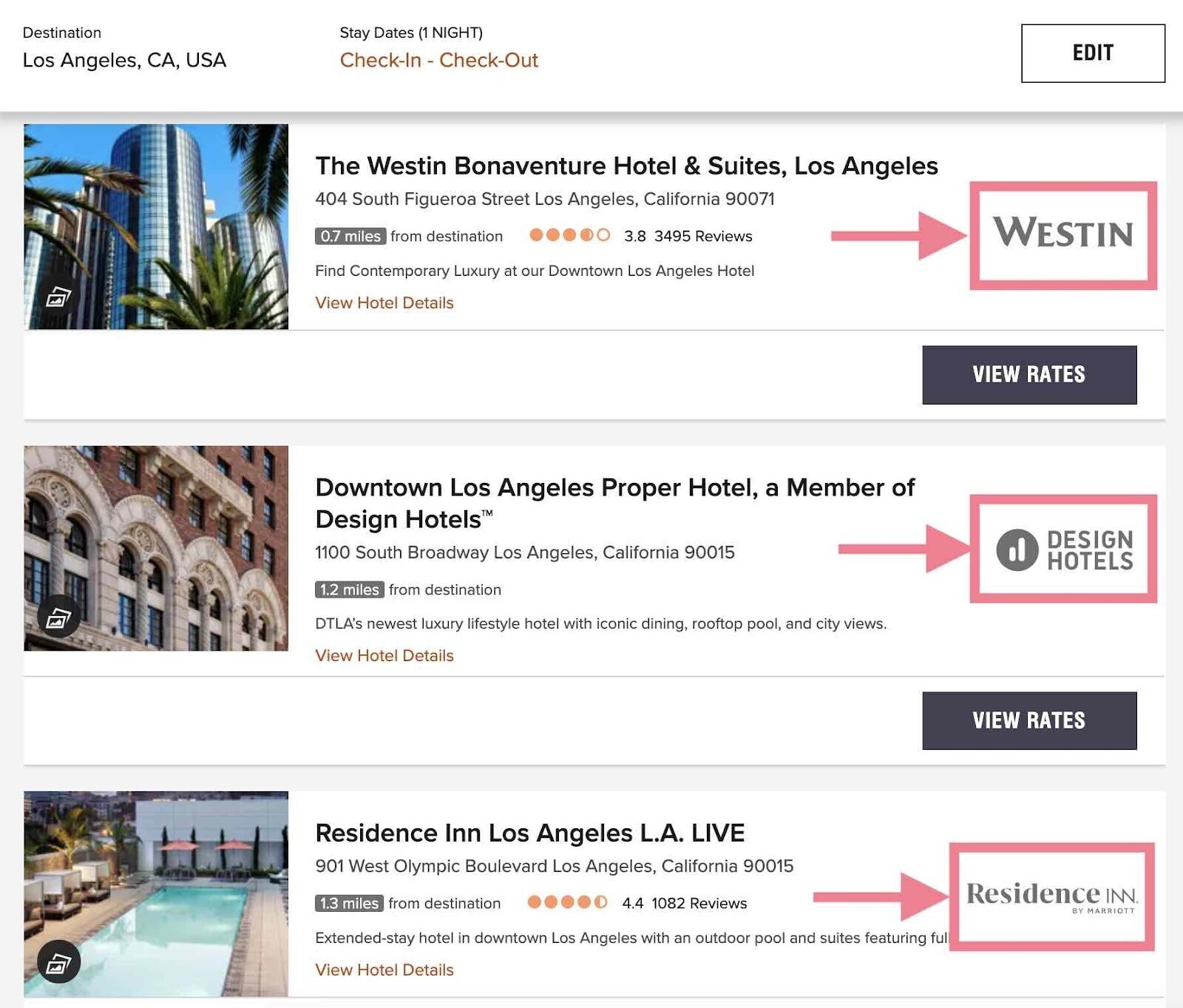
Again, the goal is to combine the authority and equity of multiple domain properties into one, resulting in a stronger site that drives quick wins.
Note: This solution may not work in the same way for every website or business. Do your own research before moving forward with a website-merging or redirecting project.
Common 301 Redirect Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Here’s how to find and fix the most common issues with 301 redirects.
Allowing Pages to 404
Don’t let pages return a 404 error if you can reasonably avoid it. It creates a terrible user experience. And can hurt your SEO performance.
To avoid running into this issue, run an audit on your site every month.
If you use Semrush’s Site Audit, you’ll see pages returning a 4XX status code under the “Issues” tab.
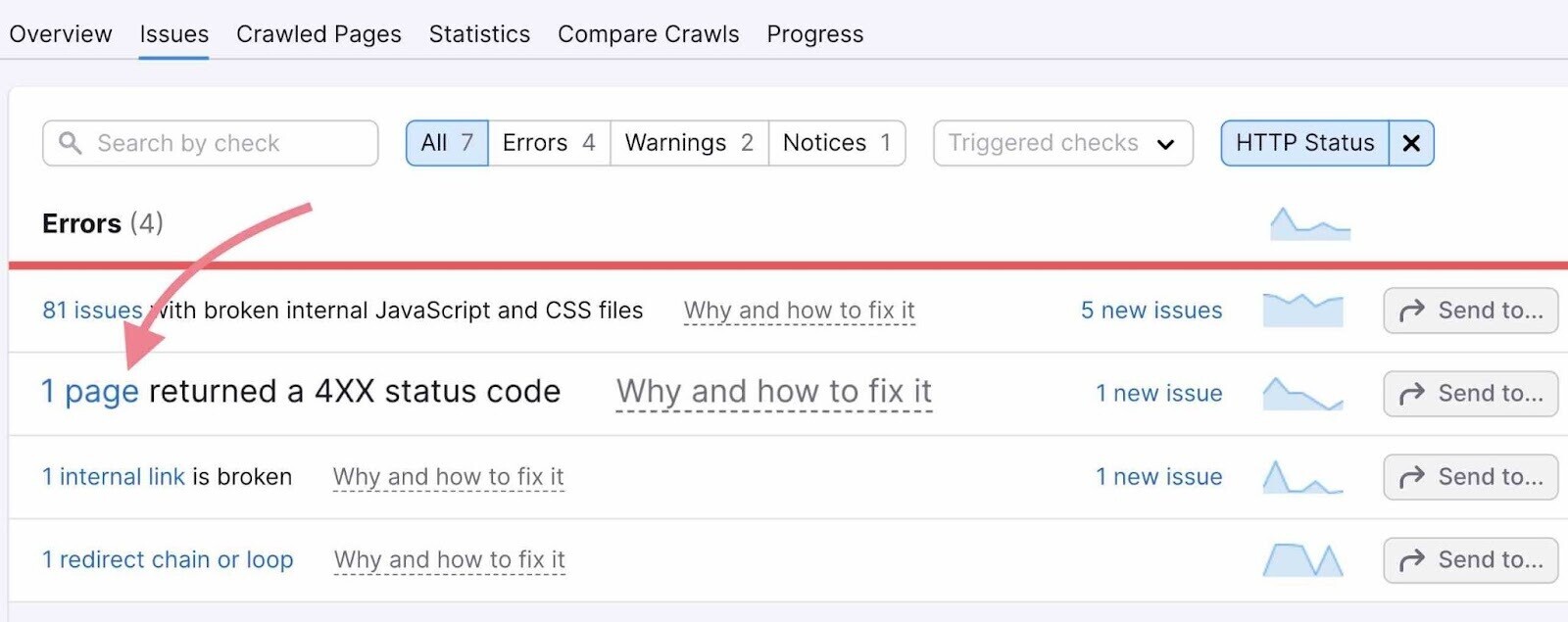
Redirect all 404 pages to other pages that are related and/or serve the same or a similar purpose.
Using 302 Instead of 301 Redirects
A common issue among SEOs is not knowing whether you should apply the 301 redirect vs. 302.
301 redirects should be used when the change is permanent. And 302s when the change is only temporary.
Again, Site Audit can help you find these. You’ll see them as “URLs with a temporary redirect.”
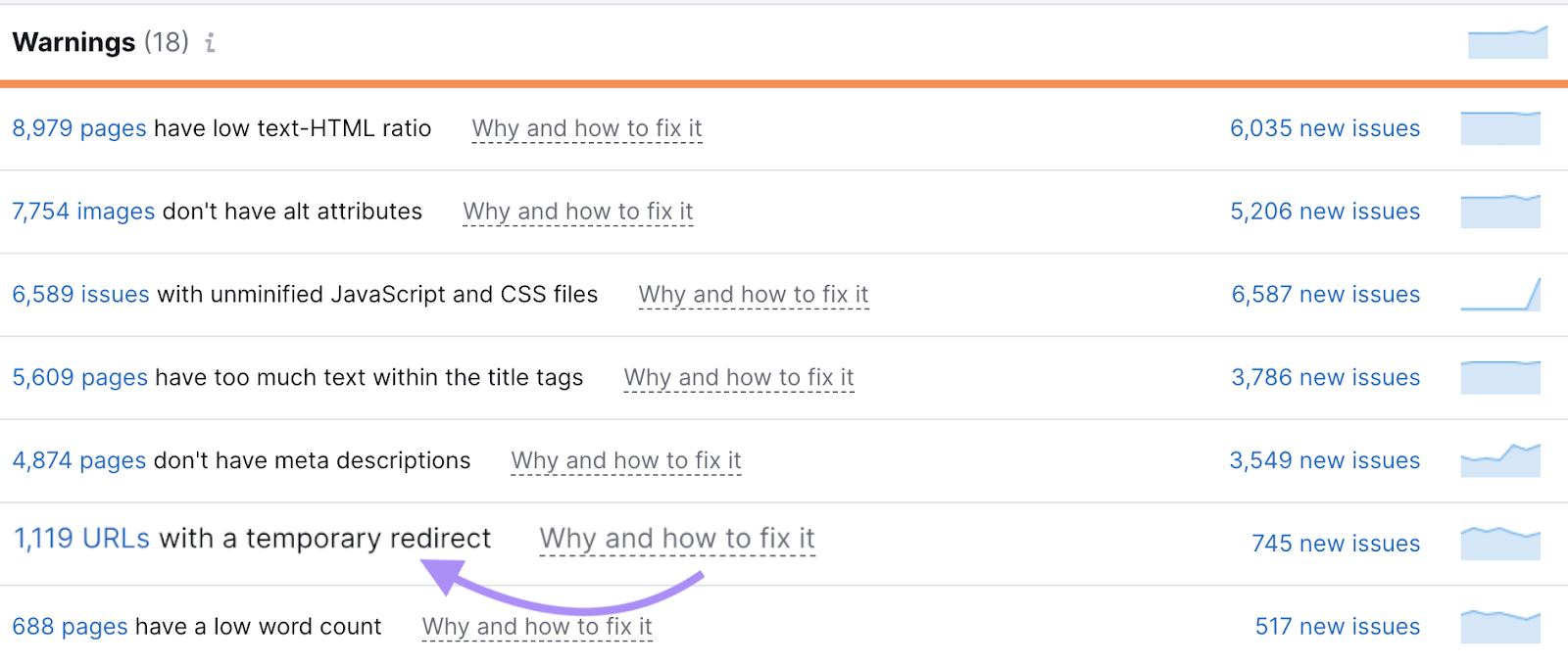
Unless they’re really temporary, update these redirects to 301s.
Using JavaScript for Redirection Without a Proper Setup
301 redirects are server-side. And JavaScript redirects are client-side. Meaning they tell the browser to get the content from a different location.
You might want to use JavaScript for redirects if you don’t have access to your server configuration or .htaccess file, are running an A/B test, or have other specific needs.
But do note that they aren’t the optimal choice.
Search engines need to render a page to find the redirect. And if, for example, Google can’t crawl a site’s JS file, the page can’t be rendered.
Using a 301, 302, or 307 redirect instead of a JavaScript redirect is typically recommended to avoid any issues.
Using Redirects Rather Than Updating Broken Internal Links
It can be tempting to fix broken internal links by redirecting the link to another page. But over time, this can create another issue: a redirect chain. (More on that later.)
Instead, update the target of the broken link first. Then, and only then, add a redirect to the correct page.
You can find broken internal links in Site Audit, under the “Issues” tab.
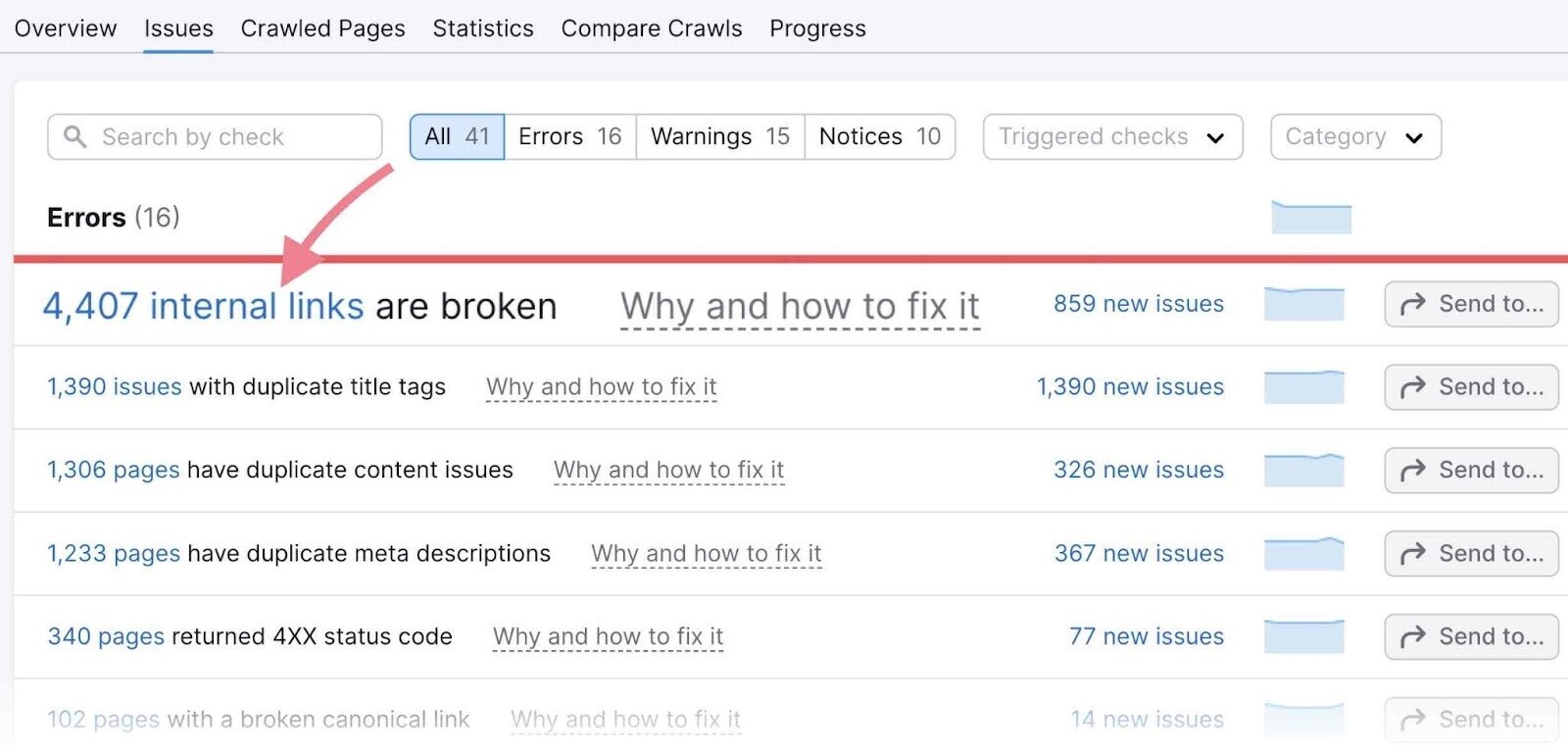
Redirect Chains & Loops
A redirect chain happens when there are two or more redirects between the first URL and the final URL.
And a redirect loop is when a URL is redirected to another, which in turn redirects back to the initial URL. Leading to an infinite loop of redirects.
Both of these issues are detrimental to your site’s user experience and, potentially, your SEO performance.
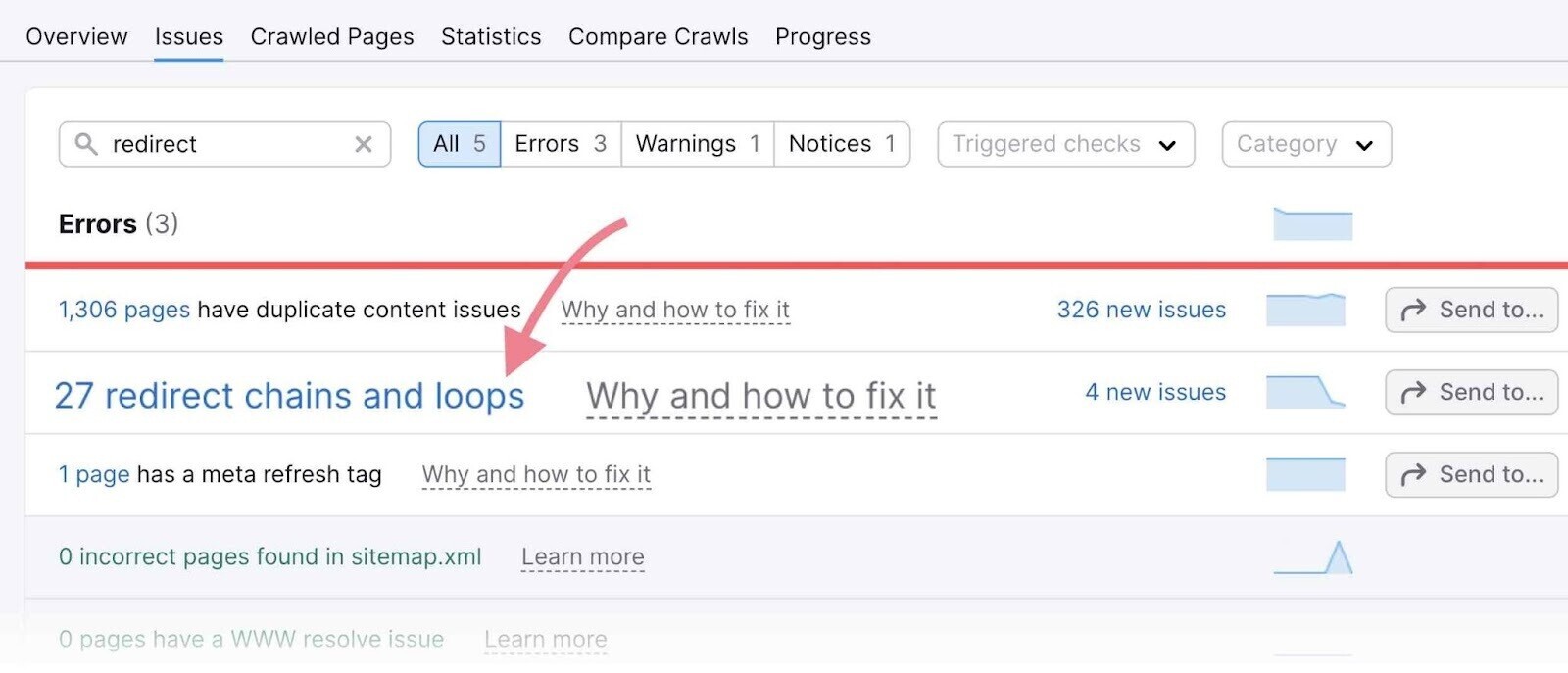
To fix them, first find any chains and loops.
Then, replace the internal links to redirected pages with links to the final URL. And update existing redirects to point directly to the final, most current URL.
Again, you can easily find redirect chains and loops in Site Audit, under the “Issues” tab.
Like so:
Monitor Your 301 Redirects and Technical SEO
Finding and fixing 301 redirect issues is just one of the many steps to improve your technical SEO.
But, if you start addressing the items above, you’ll be on your way to higher rankings. And one step ahead of your competition.
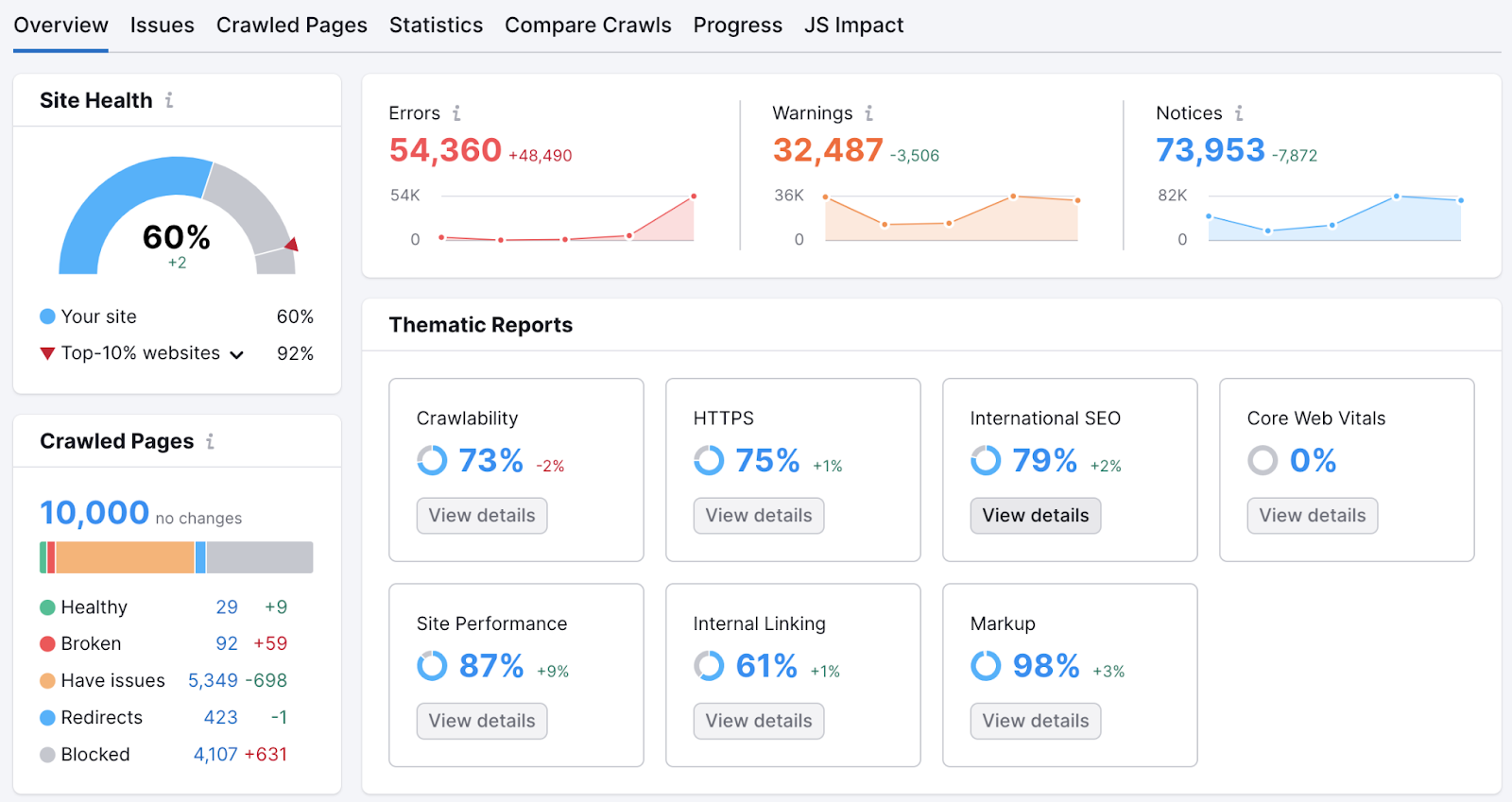
Sign up for a free Semrush account and you can crawl up to 100 URLs.
You’ll get:
- An overall SEO health score for your site
- Thematic reports to help you get a better idea of how your site is performing
- Detailed reports about the issues the tool finds (including redirects)
- A description of each issue and tips on how to fix them
Plus, you can recrawl these pages daily. And schedule audits to run automatically.
