When you search on Google, an ad may appear at the top of the results, like this:
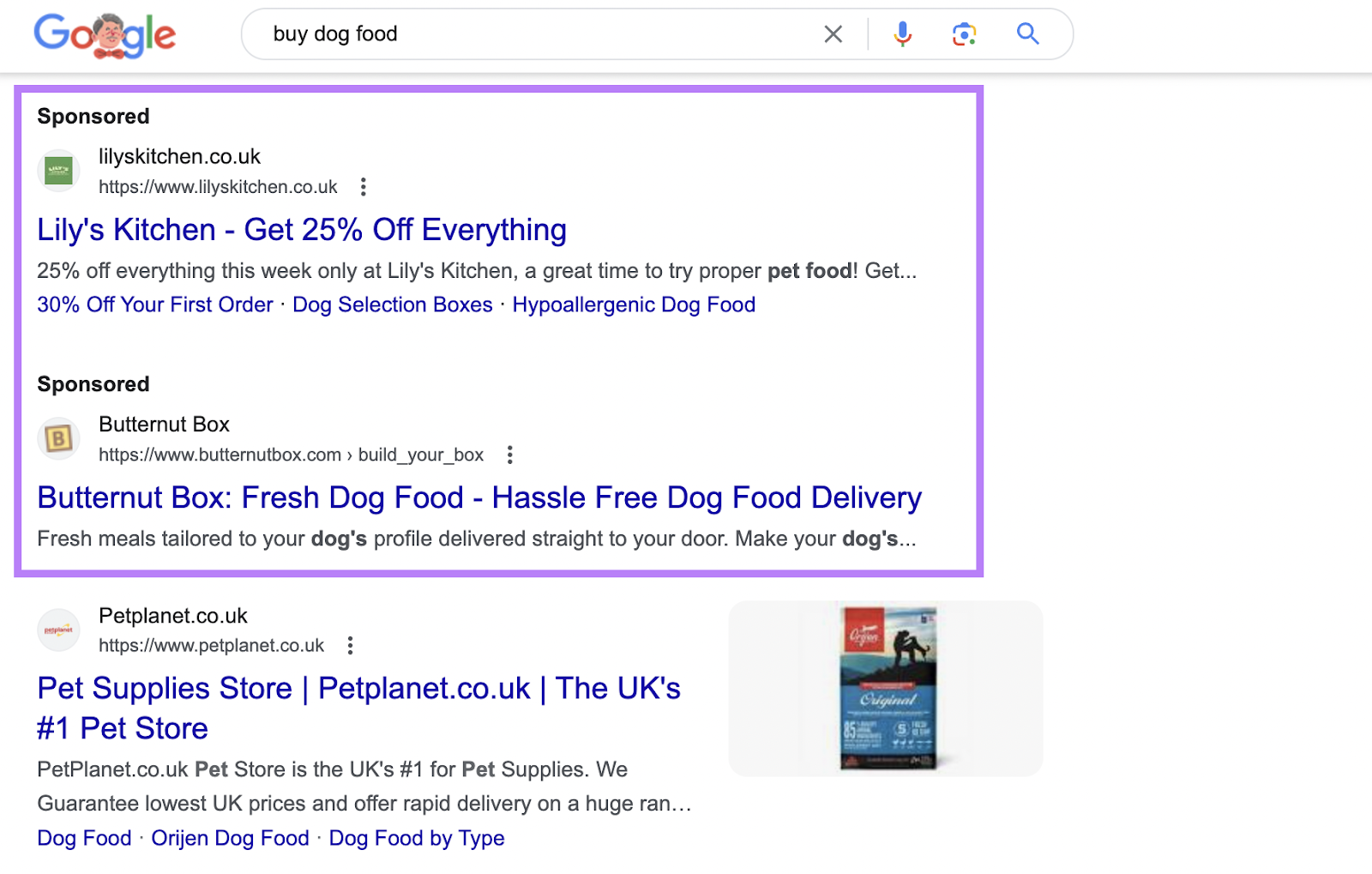
That’s a Google ad.
However, it’s only one type of Google advertising. In this article, we discuss the different types of Google ads, how each ad works, and how you can start your own campaign.
What Is Google Ads?
Google Ads (previously Google AdWords) is an online advertising platform that lets you advertise your products or services on Google’s online properties. These include the search engine, partner websites, and YouTube.
Here’s the Google Ads overview dashboard:
You pay a fee for your ads to appear on Google. A process called “bidding” determines that cost. Bidding acts like an auction in which a business sets the maximum amount it’s willing to pay when someone clicks its ads.
But why pay if there are free listings on Google?
Those free listings are organic results, which appear based on relevance to a search query. Google uses hundreds of factors to rank them. That ranking differs from how Google decides which ads to show.
Why Use Google Ads?
Here are six reasons why you should use Google Ads.
1. Immediate Visibility
Google Ads makes your advertisement visible quickly. Ads appear prominently based on factors like your bid and ad quality. This is useful if you have a new product launch or a special promotion and want immediate attention.
2. Flexibility
Google Ads provides a variety of ad formats—such as text, images, and videos. You can choose the format that best conveys your message.
3. Precise Targeting
Precise targeting allows you to target specific audiences by age group, interests, or geographic location. Here’s an example of targeting your audience by interest:
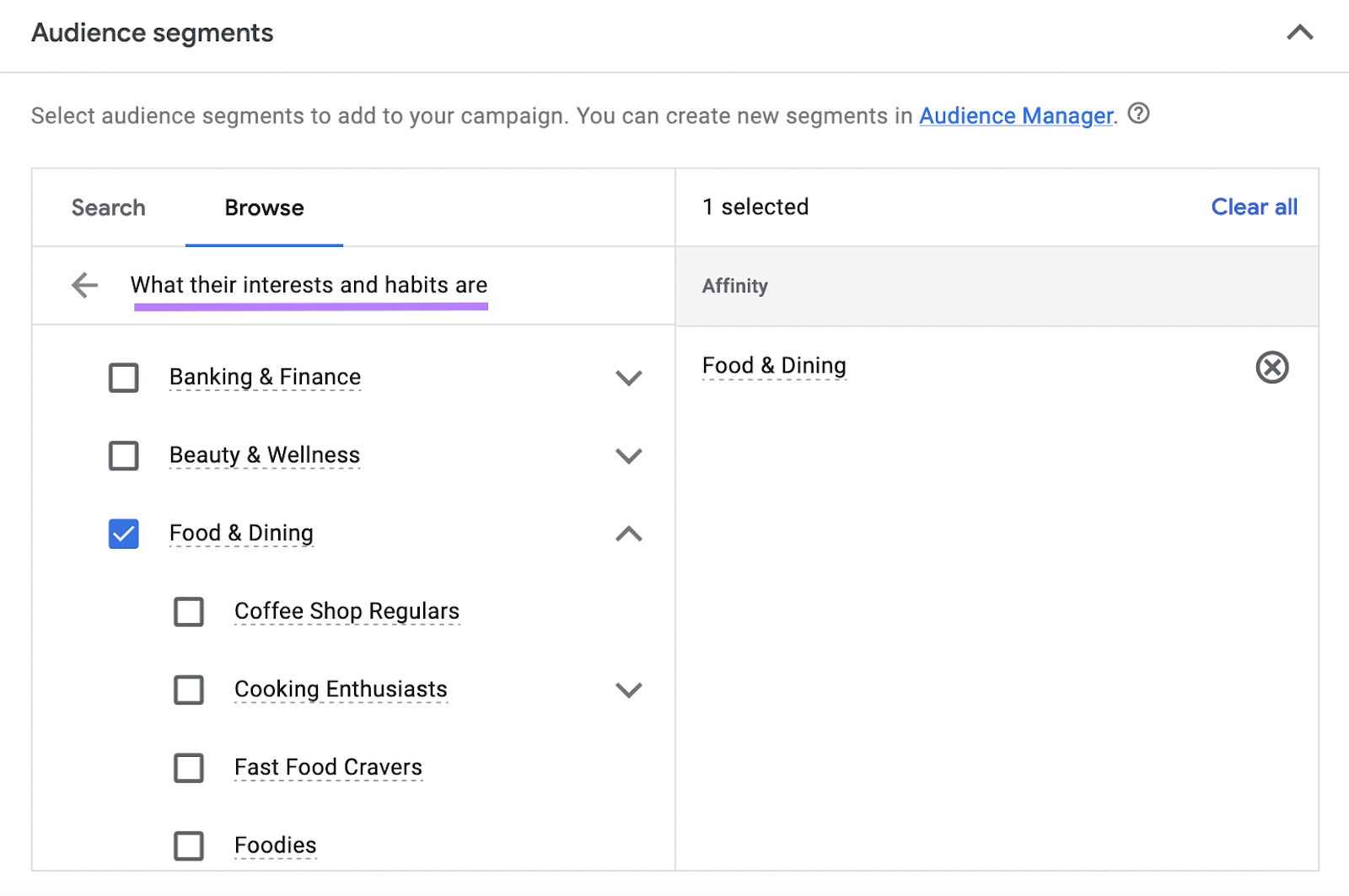
For example, a local restaurant might target people interested in “Food & Dining.” Google identifies this interest from users’ search history, visited websites, and apps.
4. Remarketing
Google Ads lets you show ads to users who have visited your website but didn’t complete a desired action, such as a purchase. These users will see your ads on other sites, reminding them of your offer and increasing the chances shoppers return and convert.
5. Cost-Effective
Google Ads usually uses a cost-effective pay-per-click (PPC) model, charging you only when someone clicks your ad. You can also choose cost per thousand impressions (CPM) and cost per action (CPA) pricing. These options let you select the best model for your goals.
6. Measurable Results
Google Ads provides detailed performance reports for measurable results. You can track metrics like views, clicks, and conversions. These insights help you improve your campaigns by identifying which ads work best and how to optimize your budget and targeting.
With Google Ads, you can increase website traffic, generate leads, and drive sales. Success depends on several factors, including the type of Google paid ads you use.
Types of Google Ads
Here are five types of Google ads:
1. Google Search Ads
Google search ads show up on Google’s search engine results pages (SERPs) when users search for certain keywords. Here is an example of a search ad for “buy firm mattress online:”
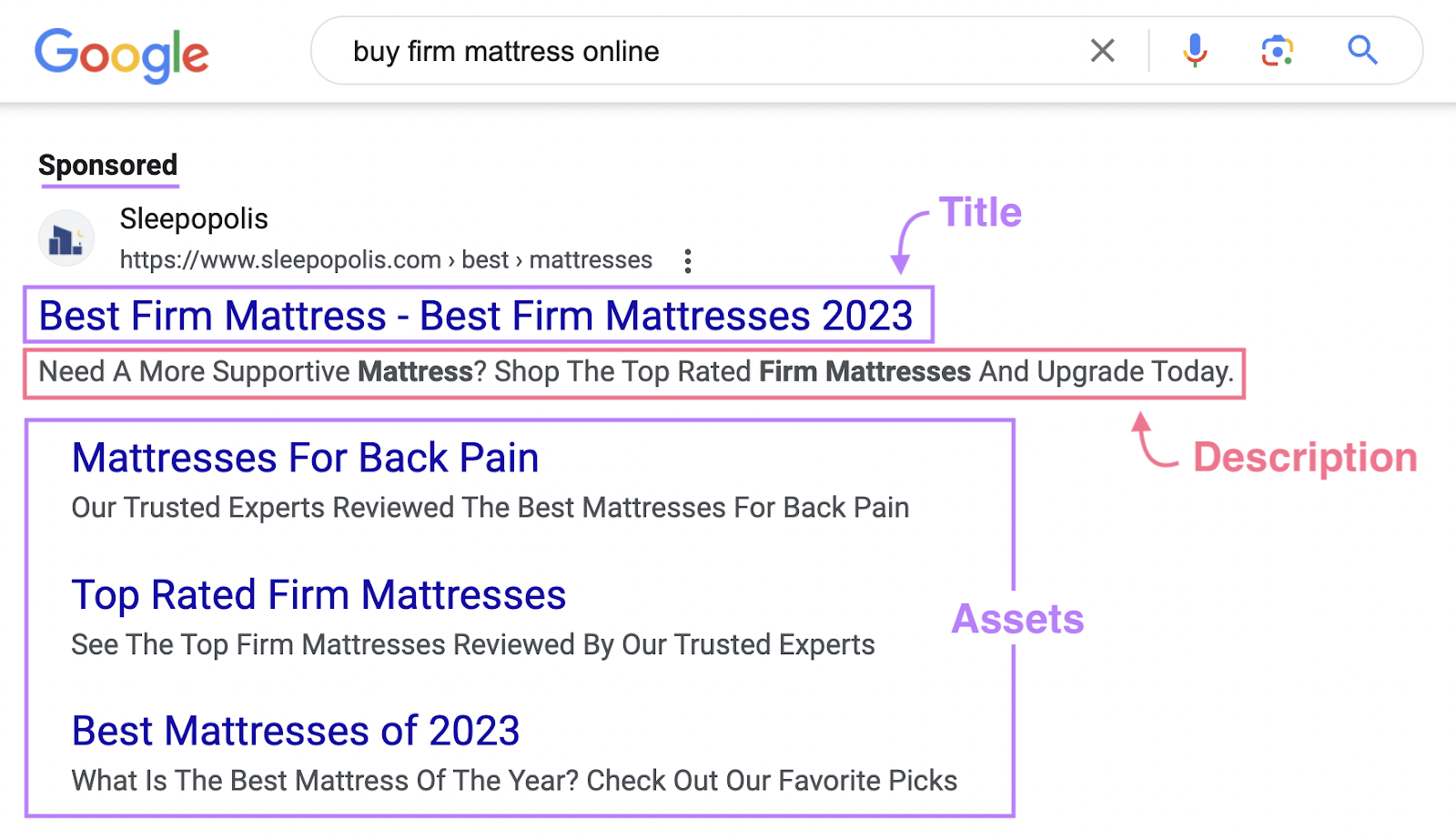
This ad contains three main parts:
-
Title & description: The headline and text summarizing the product or service
-
Ad Assets: Additional details such as page links, selected during setup
These ads typically appear at the top or bottom of the SERP.
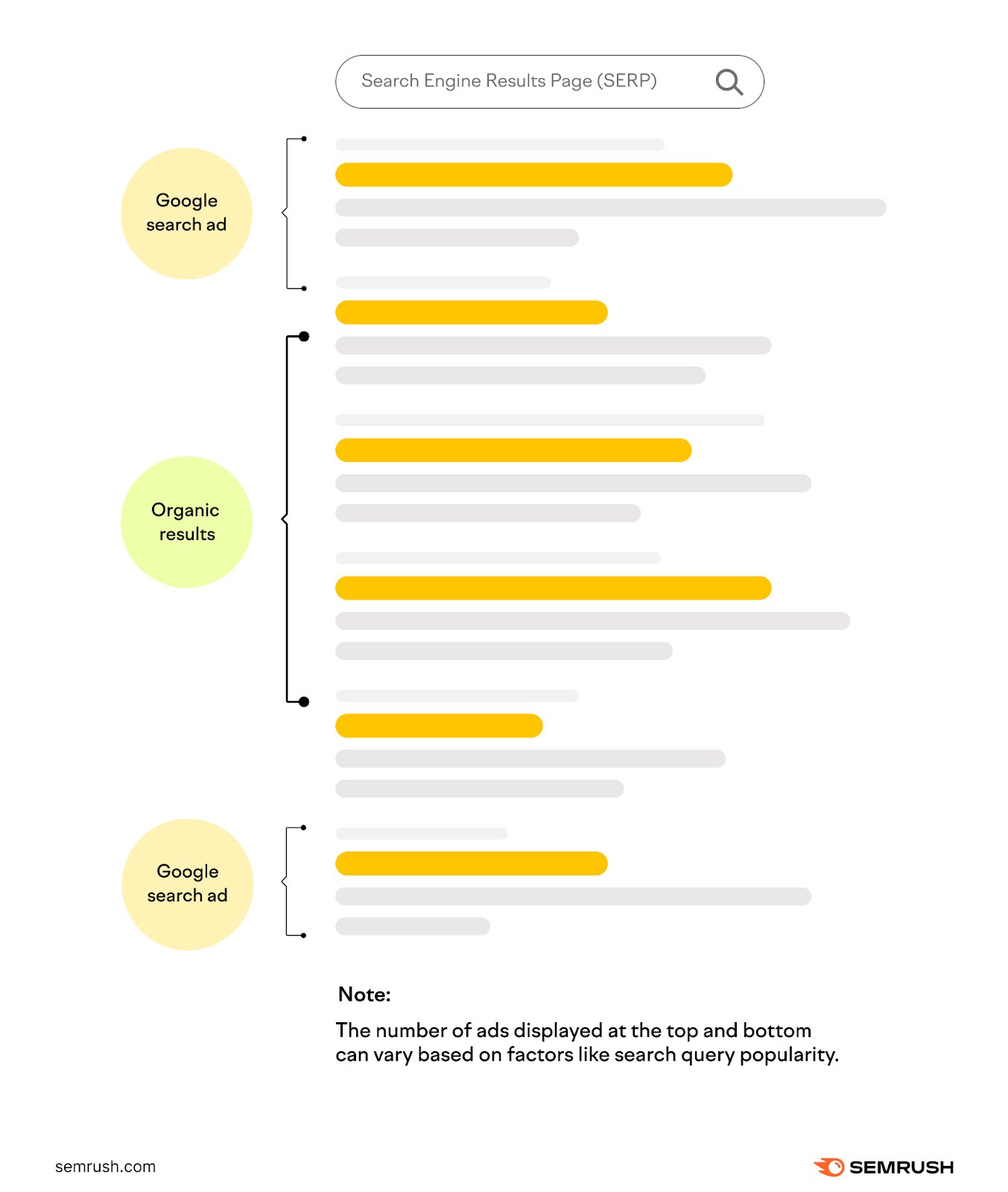
Search ads match user intent. Ads can help you connect with potential customers at the moment they’re searching for products or services related to your business. For instance, if someone searches “best running shoes,” a shoe store can place its ad at the top of the results page.
For easy setup, you can use the Ads Launch Assistant app. The app lets you manage Google Ads campaigns from start to finish with AI and Semrush data.

Enter your URL, language, and location to get keyword suggestions and AI-generated ad copy. Then confirm your campaign, set a budget, and launch your Google Ads campaign.
2. Google Display Ads
Google Display Network (GDN) ads are visual ads placed on websites, apps, and platforms that partner with Google through AdSense. Here’s an example of a display ad on the Washington Post website:
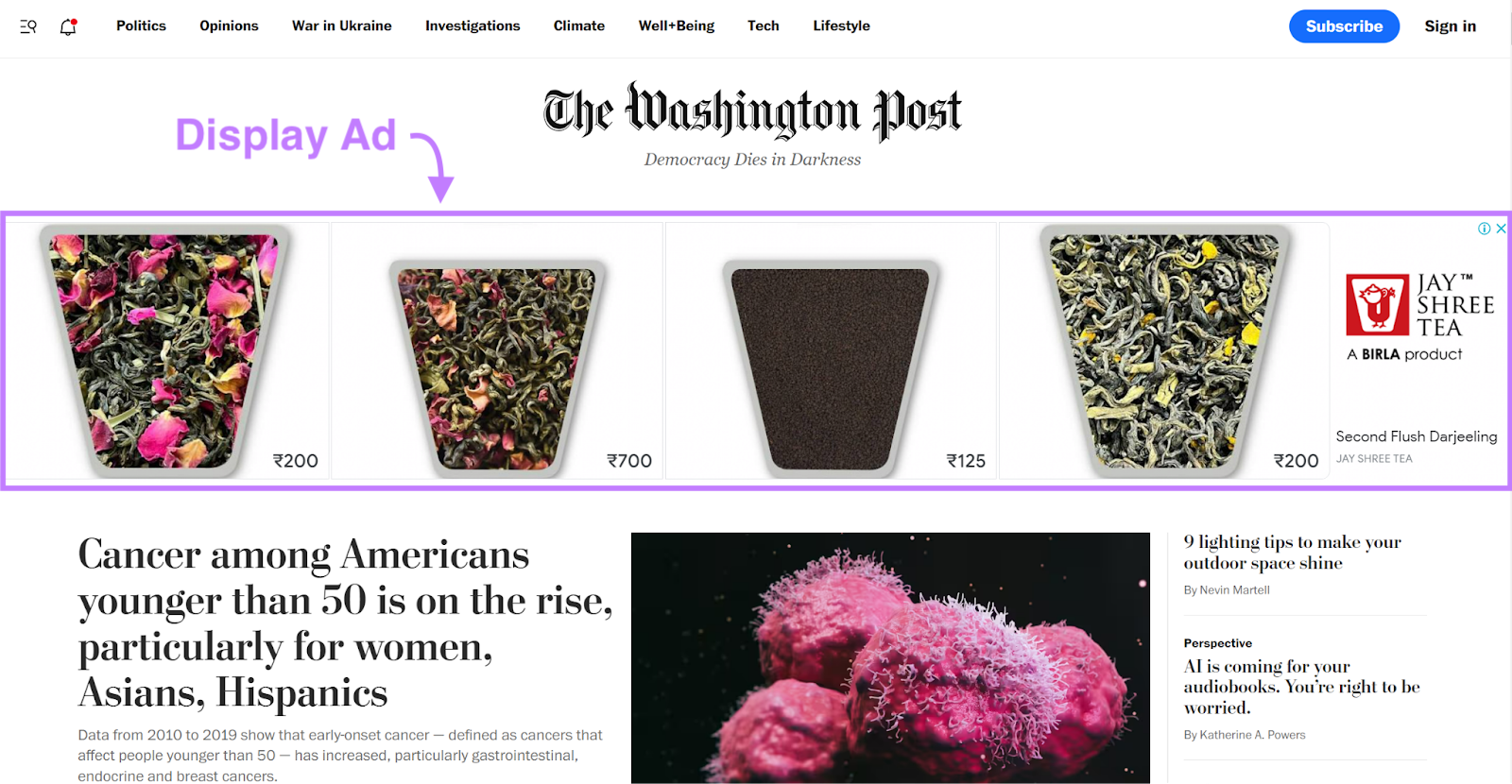
These ads can appear in the banner, sidebar, or footer. Display ads are shown to users based on their interests and browsing behavior, rather than specific search queries. If you often read fitness articles, you may see ads for running shoes on a news website.

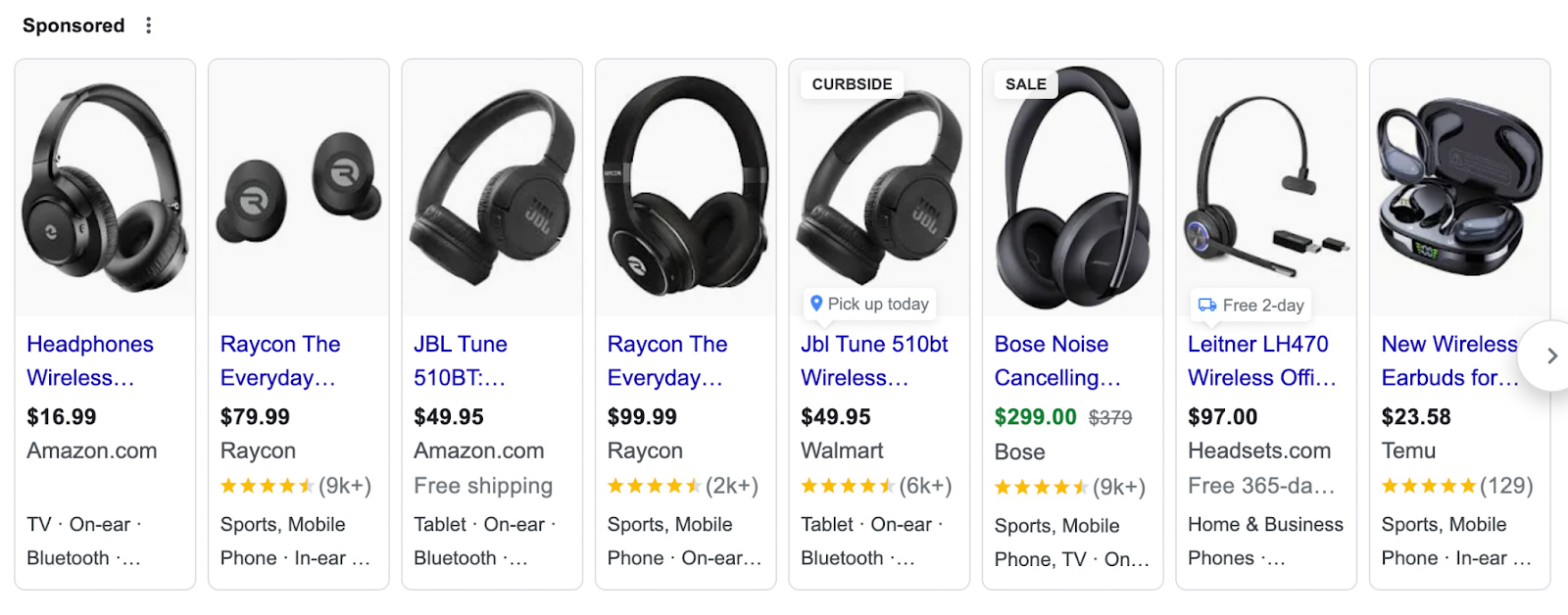
3. Google Shopping Ads
Google Shopping ads present products directly in search results, complete with images, prices, and store names. These ads appear when users search for specific products. Here’s an example:
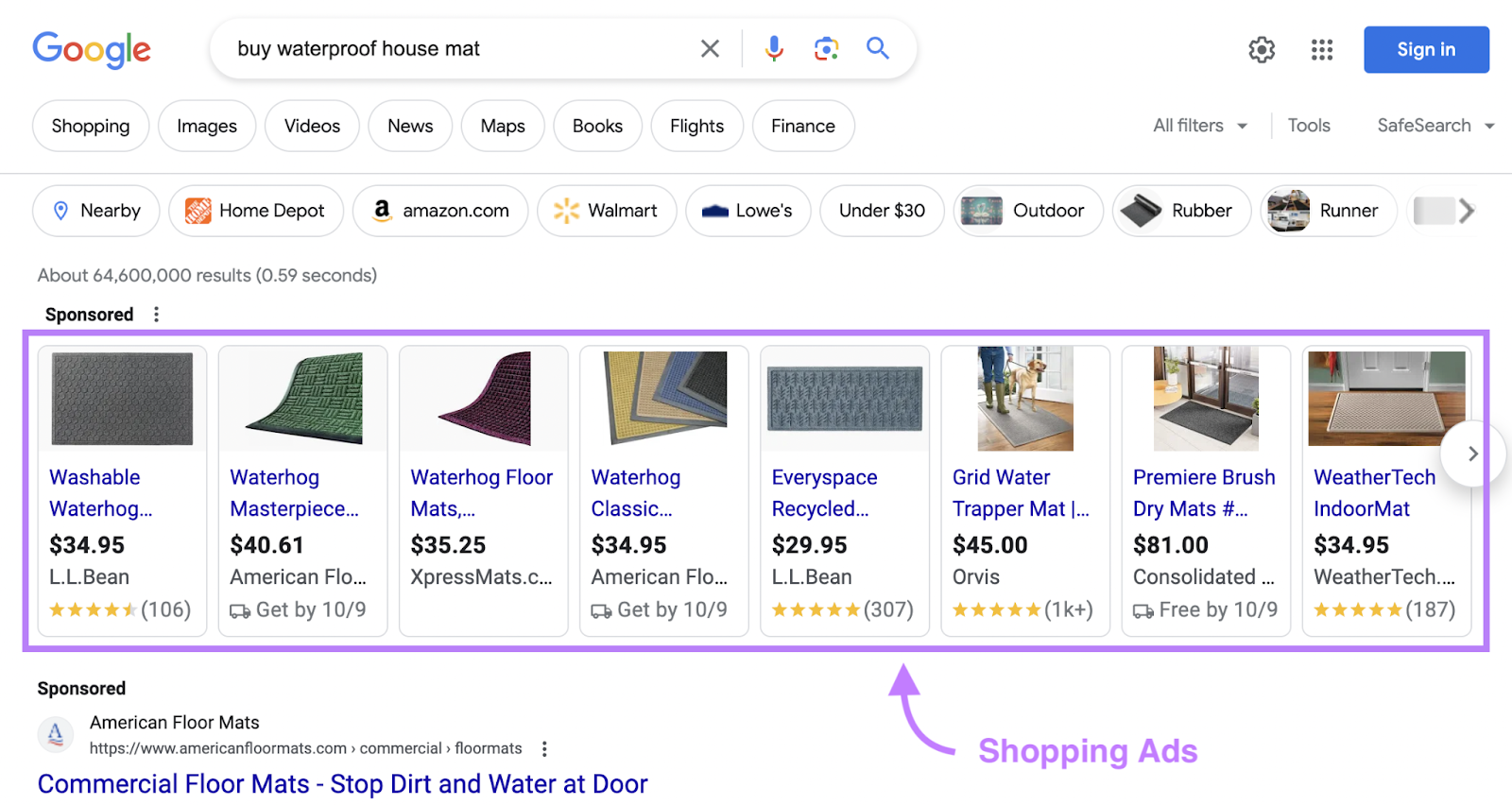
The main advantage is the detailed product display. For example, users who search for “wireless headphones” see a list of products with images and prices. A Shopping ad allows them to compare and choose without leaving the search results page.
4. Google Video Ads
Google video ads appear on YouTube. Video ads can play before (pre-roll), during (mid-roll), or after (post-roll) a user’s video. Here’s an example of a video ad:
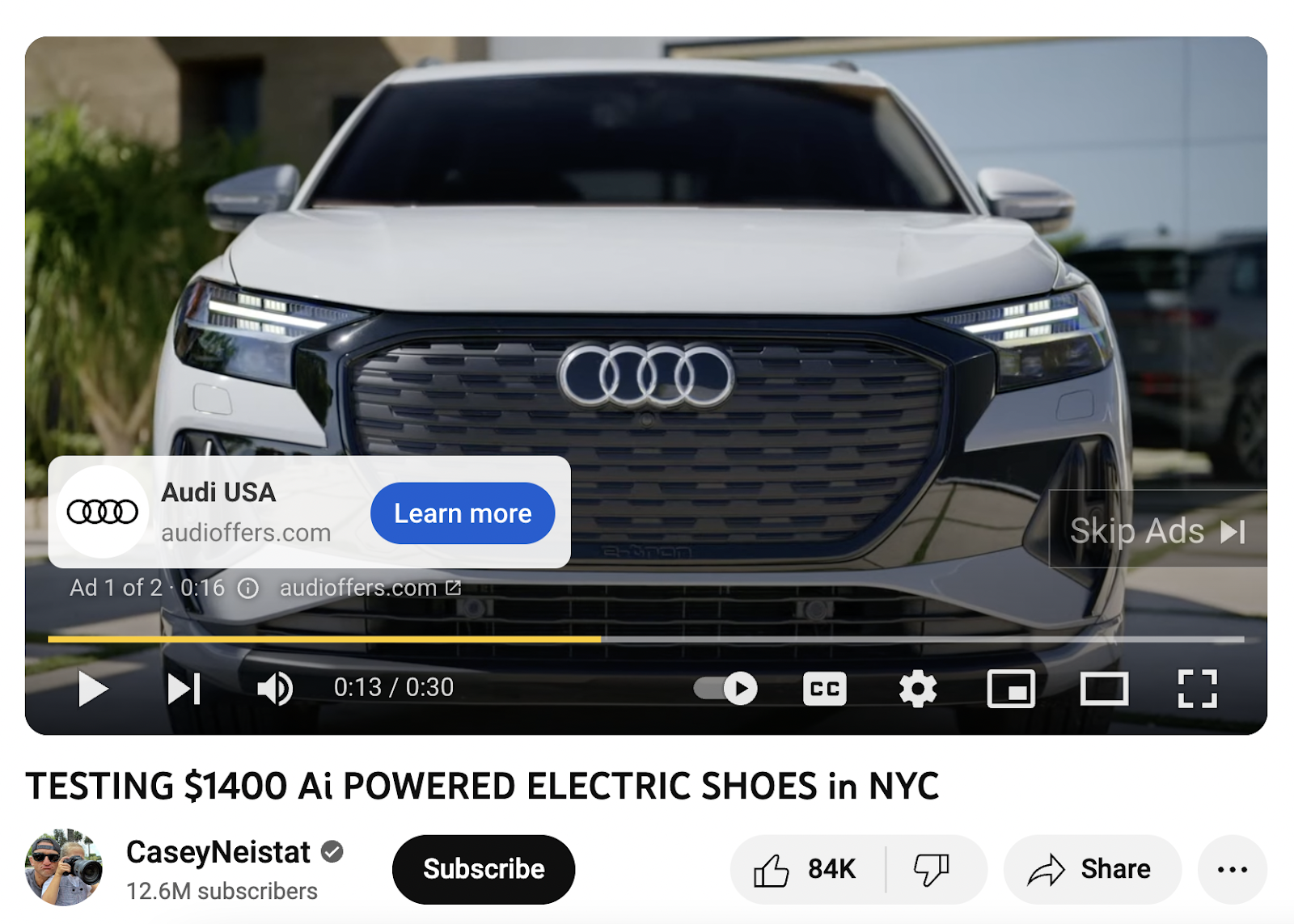
YouTube is one of the largest search engines, so you can reach a wide audience with video ads. Video ads use visuals and sound to convey your message. You can display your online advertisements based on viewer interests, demographics, or the content users are watching. For instance, a travel agency might target viewers watching travel vlogs or destination reviews.
5. Google App Ads
Google App ads help you promote your mobile application. You provide text and images, and Google automatically creates multiple ad formats. These ads appear across Google Search, Google Play Store, YouTube, and the Display Network. Here’s an example of a Google App ad on YouTube:

App campaigns can focus on:
-
App installs: Increase downloads
-
App engagement: Encourage users to return
-
App pre-registration: Let Android users sign up to get notifications when your new app launches
How Does Google Ads Work?
Google Ads works by displaying advertisements based on your bid, the ad’s relevance, and its quality. Users see ads that match their interests, and advertisers reach audiences likely to convert.
Google Ads Auction
When someone searches on Google or visits a website in the GDN, an auction occurs automatically in the background. You and other advertisers bid to have your ads shown.
In your Google Ads account, you set the maximum amount you are willing to pay-per-click or impression:
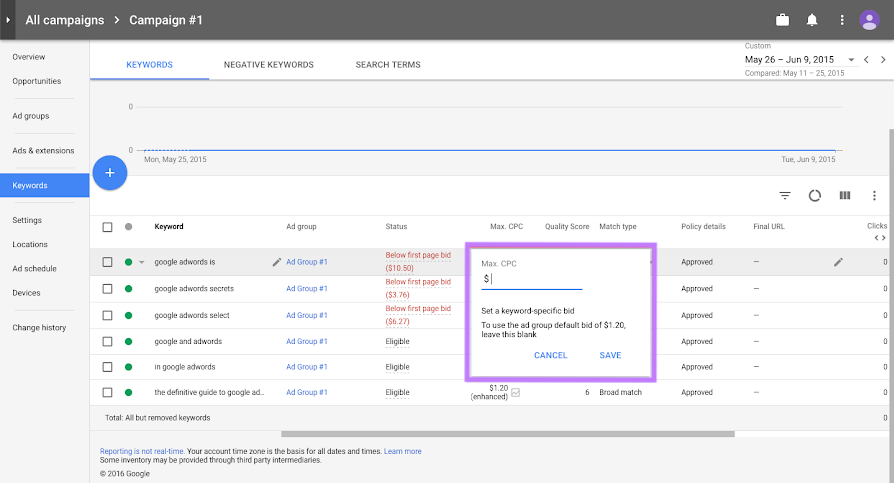
This auction decides which ads show up and in which position.
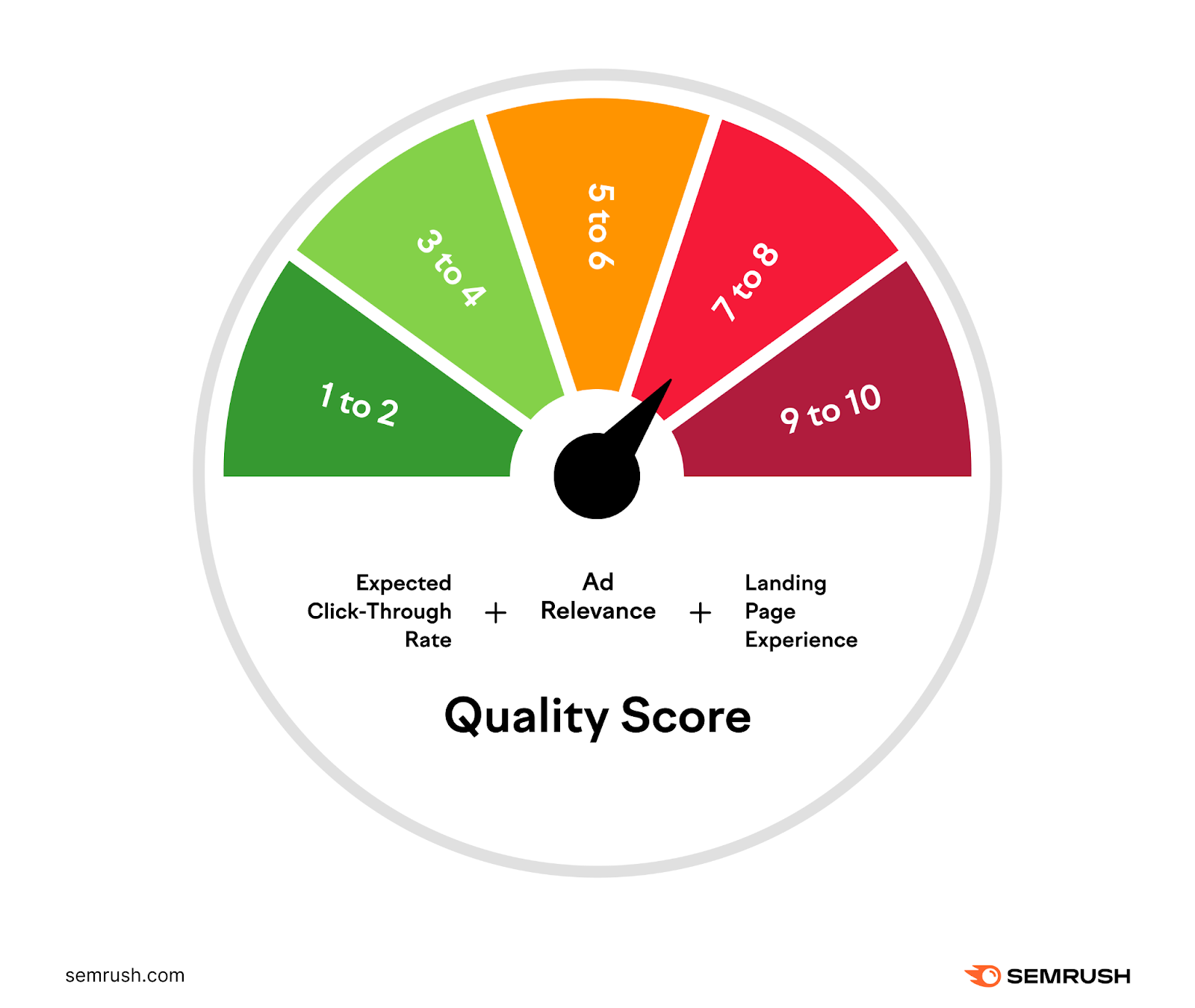
Relevance and Quality
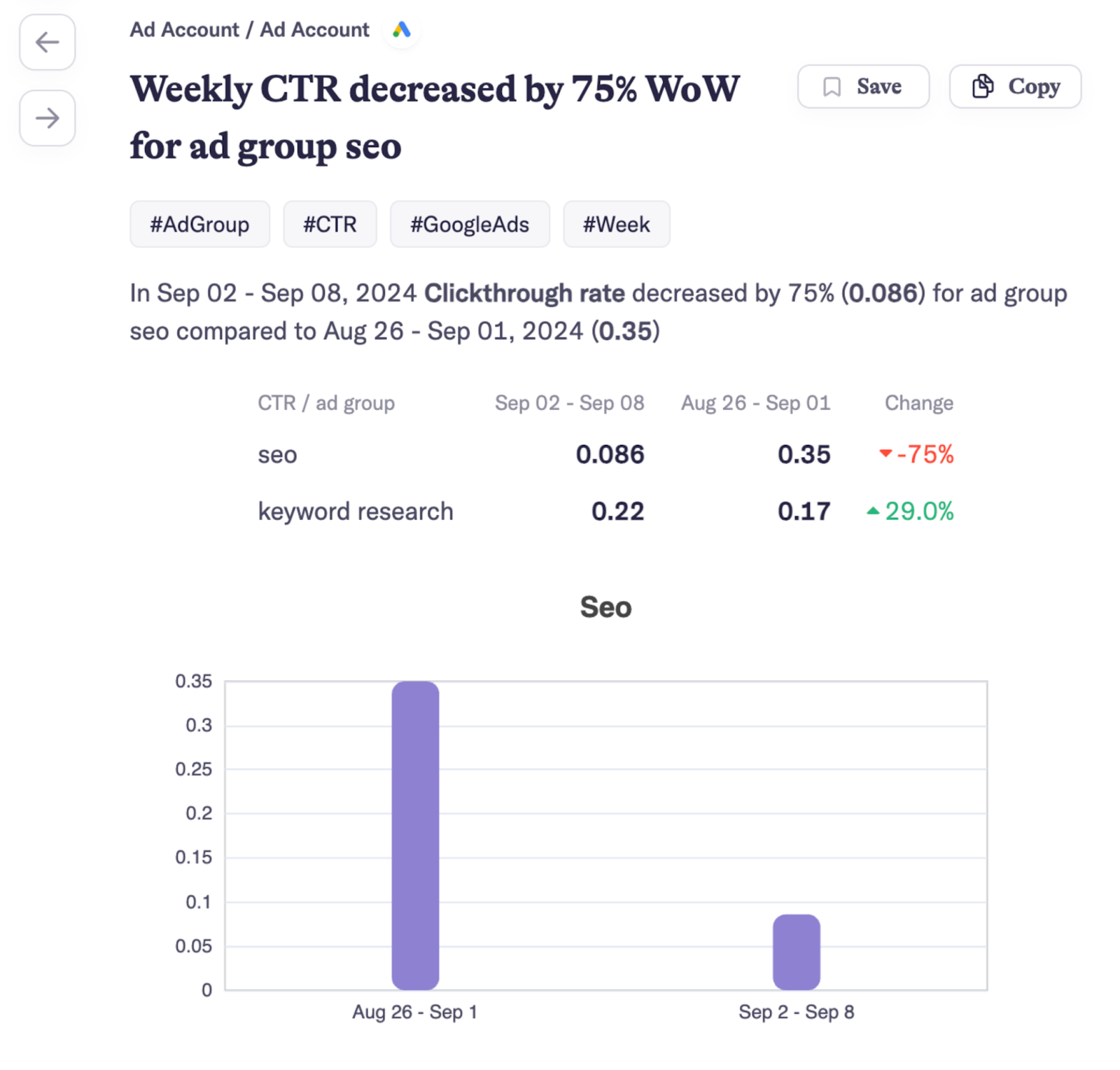
“Relevance” refers to how closely your ad matches a user’s search or the content they’re viewing. Google also checks ad “quality.” The Quality Score evaluates your ad’s expected click-through rate (CTR), ad relevance, and landing page experience. Quality Score is scored out of 10.
Ad Rank
Ad Rank determines where your ad appears on Google’s SERP or the GDN. Your bid, Quality Score, competition, and the user’s location decide your Ad Rank. A higher Ad Rank can help your ad appear in more prominent positions.

How Do Different Types of Google Ads Work?
Here’s how different types of Google ads work.
Google Search Ads
When a user enters a query, Google reviews all ads targeting that keyword. You can set a “match type”—Exact, Phrase, or Broad—that specifies how closely the user’s query must match your keyword. The algorithm then ranks ads based on bid, relevance, and Quality Score.
Keyword research is crucial to ads ranking well. Use Semrush’s PPC Keyword Tool to create, manage, and optimize keyword lists for your ad campaigns.
Enter your domain and click “Setup.”

Select “Manually.”
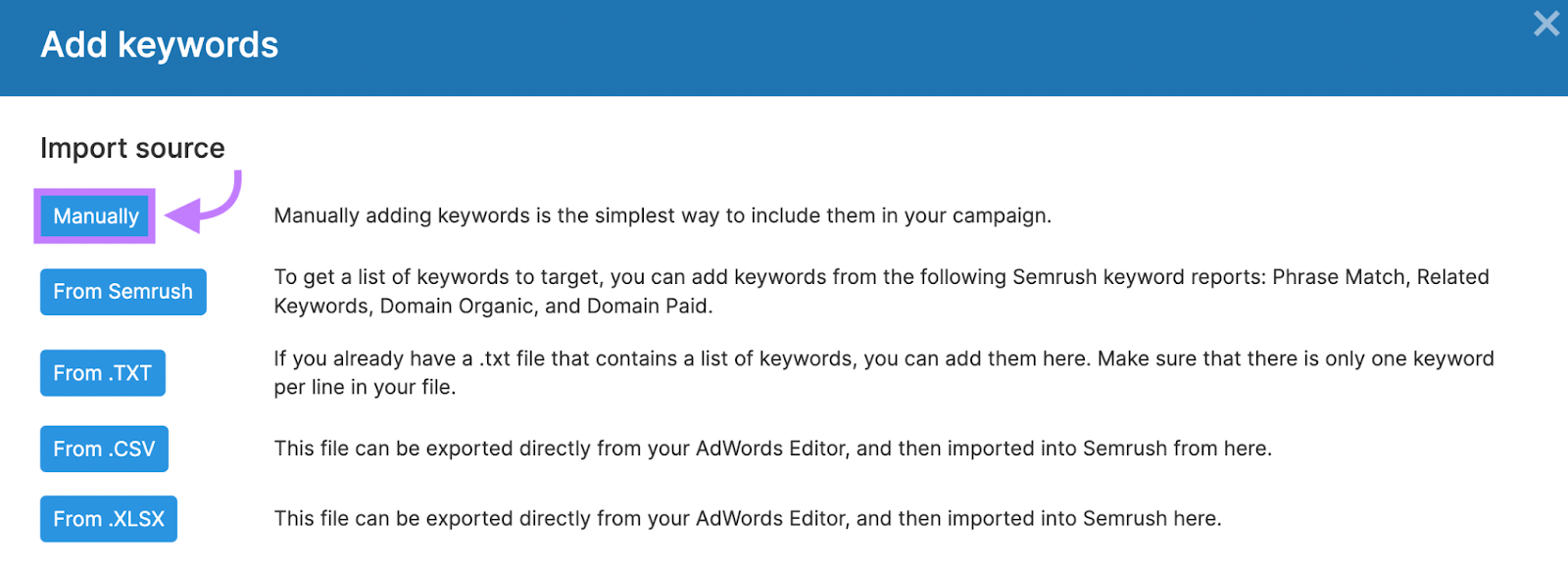
Enter your keywords and add your target location. Then, click “Start PPC Keyword Tool.”
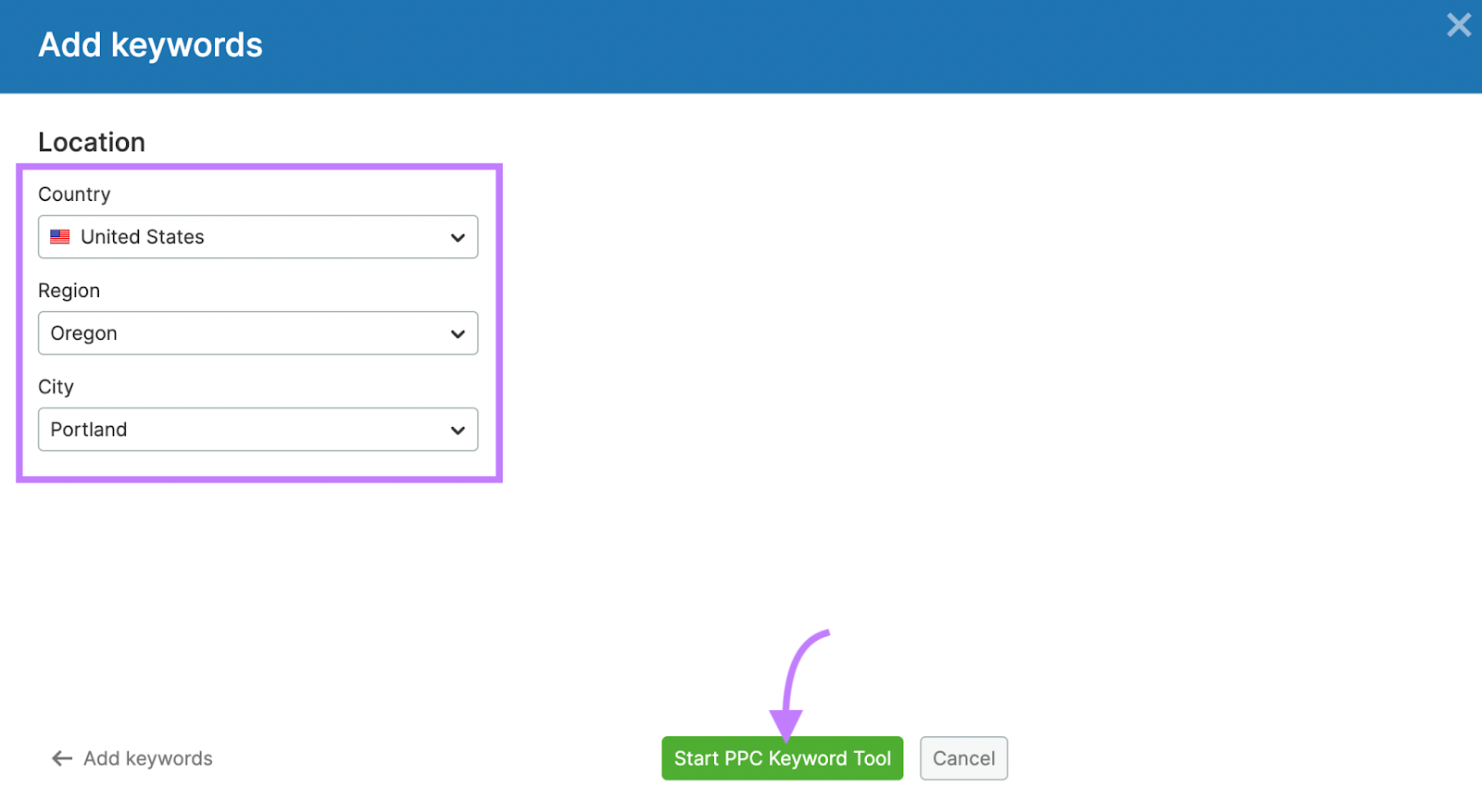
Clean and organize your keywords for your Google paid search ad campaign from the main dashboard.
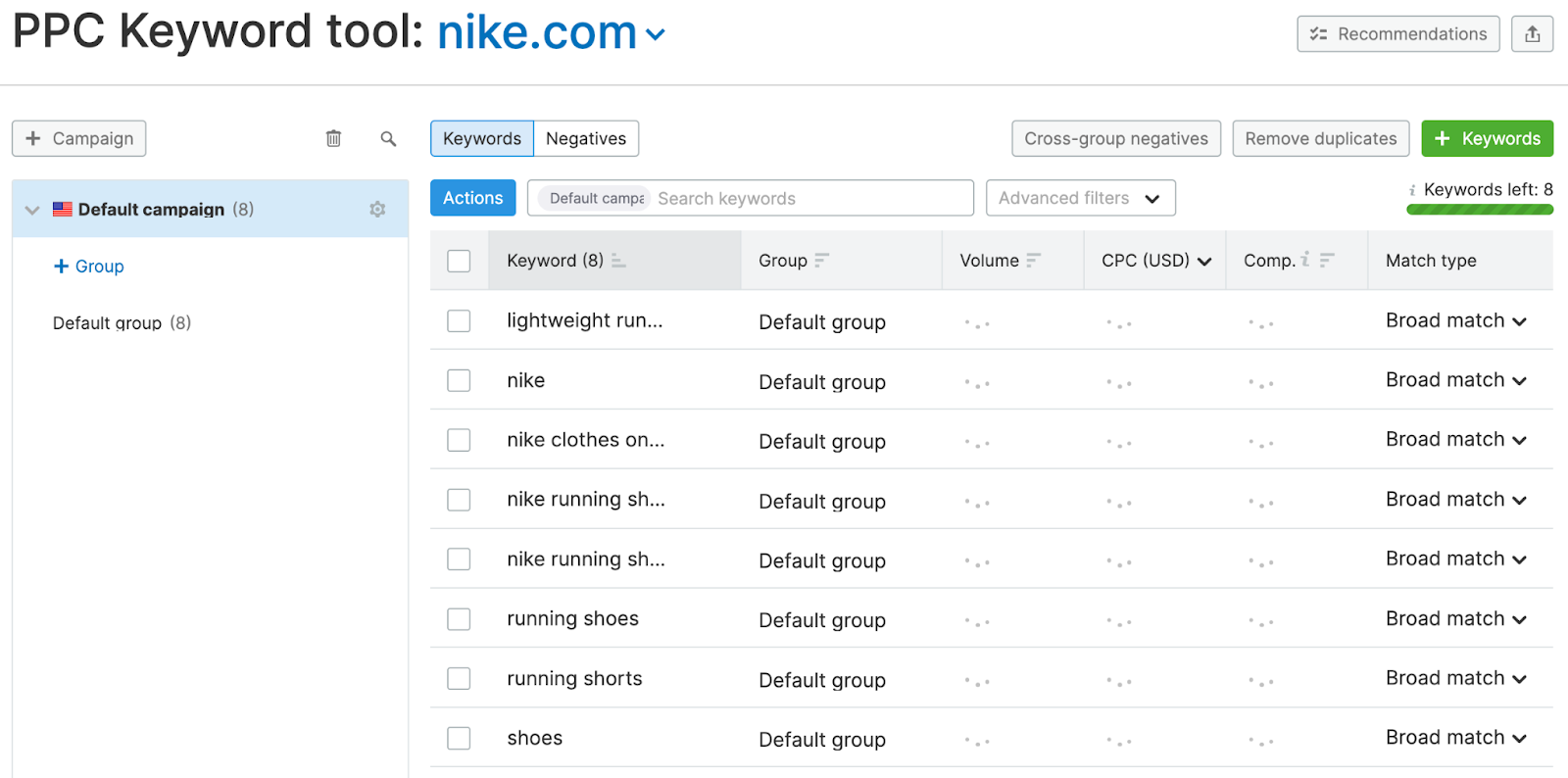
Analyze the potential traffic and the estimated cost per click (CPC) for the keywords in your list.
Further reading: Follow our in-depth setup guide for more information on configuring the PPC Keyword Tool.
Google Display Ads
Google display ads target users by interests, demographics, or topics—rather than specific keywords. When a user visits a website in the Display Network, Google examines the page’s content, the user’s history, and your targeting criteria to show relevant ads.
Google Shopping Ads
Google uses the product data you submit through Merchant Center to display Shopping ads.
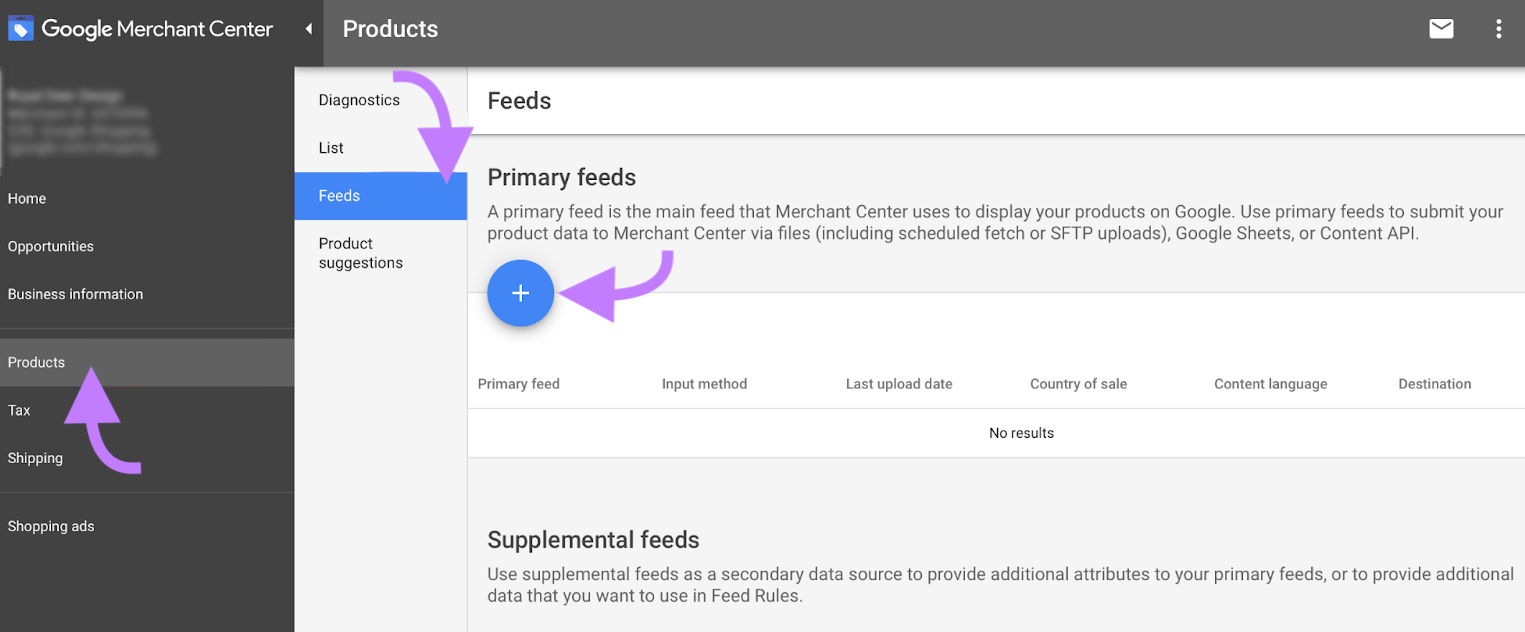
When a user searches for a product, the algorithm matches that search to your product data, factoring in bid amount and relevance.
Google Video Ads
Video ads target demographics and viewer interests. Google checks the viewer’s current video content and previous interactions to decide if your ad is suitable. The user’s bid and Quality Score also matter.
Google App Ads
Google automatically creates ads in multiple formats based on the text, images, and videos you provide. Targeting is based on user behavior, search history, and other data. The algorithm tests different asset combinations to find the most effective approach.
Are Google Ads Worth It?
Google Ads are worth it when you look at the numbers. Google’s economic impact report estimates that for every $1 spent on Google Ads, businesses see $8 in profit through Google search and Ads. Google and YouTube process billions of searches per day, and the Google Display Network reaches over 90% of internet users globally. Numerous case studies show the success of Google advertising:

Linking Google Ads to Google Analytics provides deep insights into performance. You can then optimize ads in real time to boost results. Although you need an initial investment, Google Ads often pays off by driving profit and growth.
How Much Does Google Ads Cost?
Google Ads costs vary by industry, location, and competition. On average, businesses pay $1 to $2 per click for search ads and under $1 for display ads. Competitive industries like insurance or legal services may see costs over $50 per click.
Monthly budgets can range from $50 to thousands of dollars, depending on your goals and resources.
Ready to Launch Your Google Ads Campaign?
Set up your Google Ads account and create a campaign to show ads in Google search. You’ll define your goals, select keywords, write ad copy, and set your budget.
Before you begin, outline a strategy backed by competitive research:
-
Which keywords are your competitors bidding on?
-
What ad copy do competitors use?
-
How much do competitors pay-per-click?
Use Advertising Research to find answers.
Open the tool, enter a competitor’s domain, and click “Search.”

You’ll see tabs like “Positions,” “Position Changes,” “Competitors,” “Ads Copies,” “Ads History,” “Pages,” and “Subdomains.”
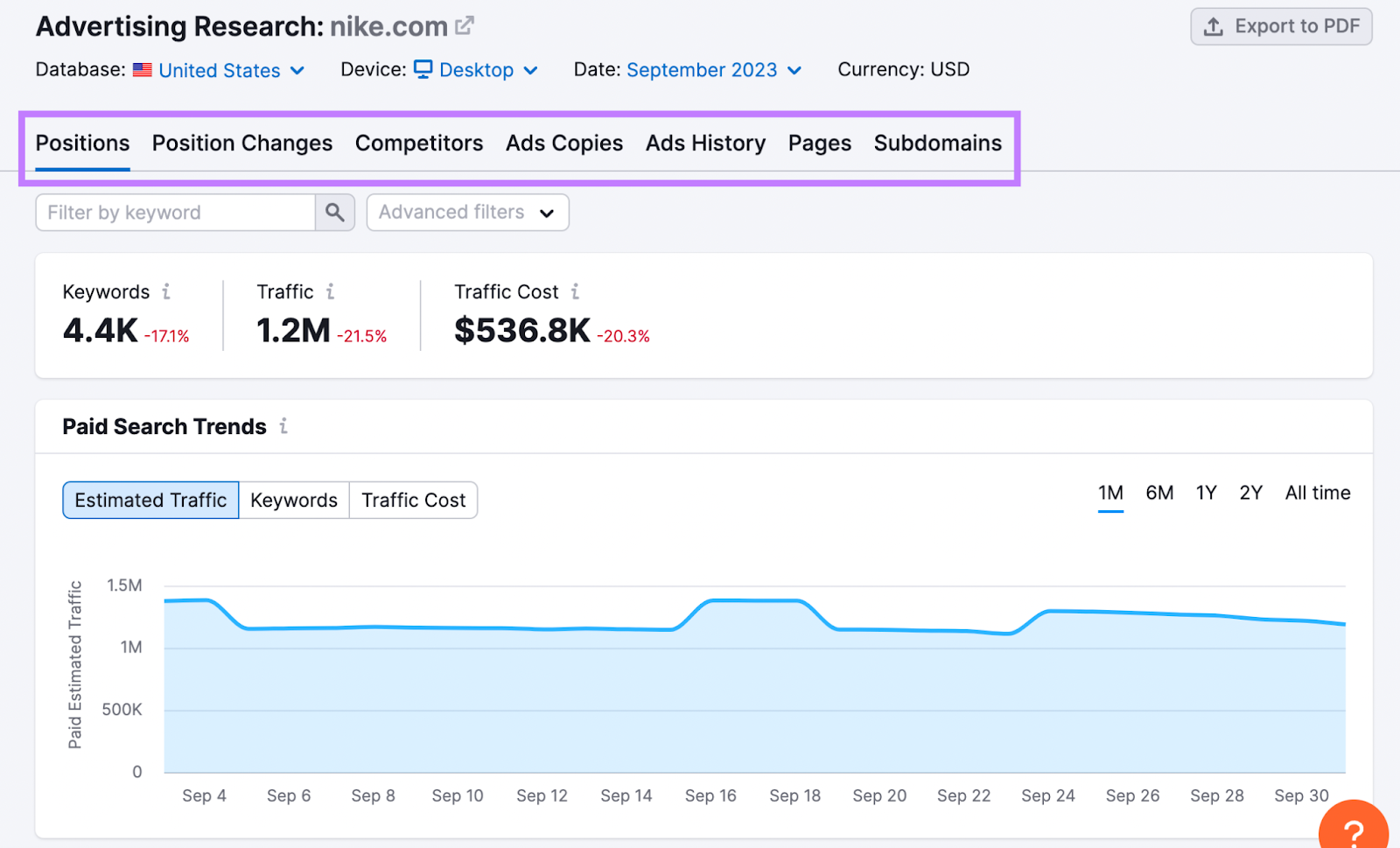
Under the “Positions” tab, you can see the keywords your competitor targets in paid search.
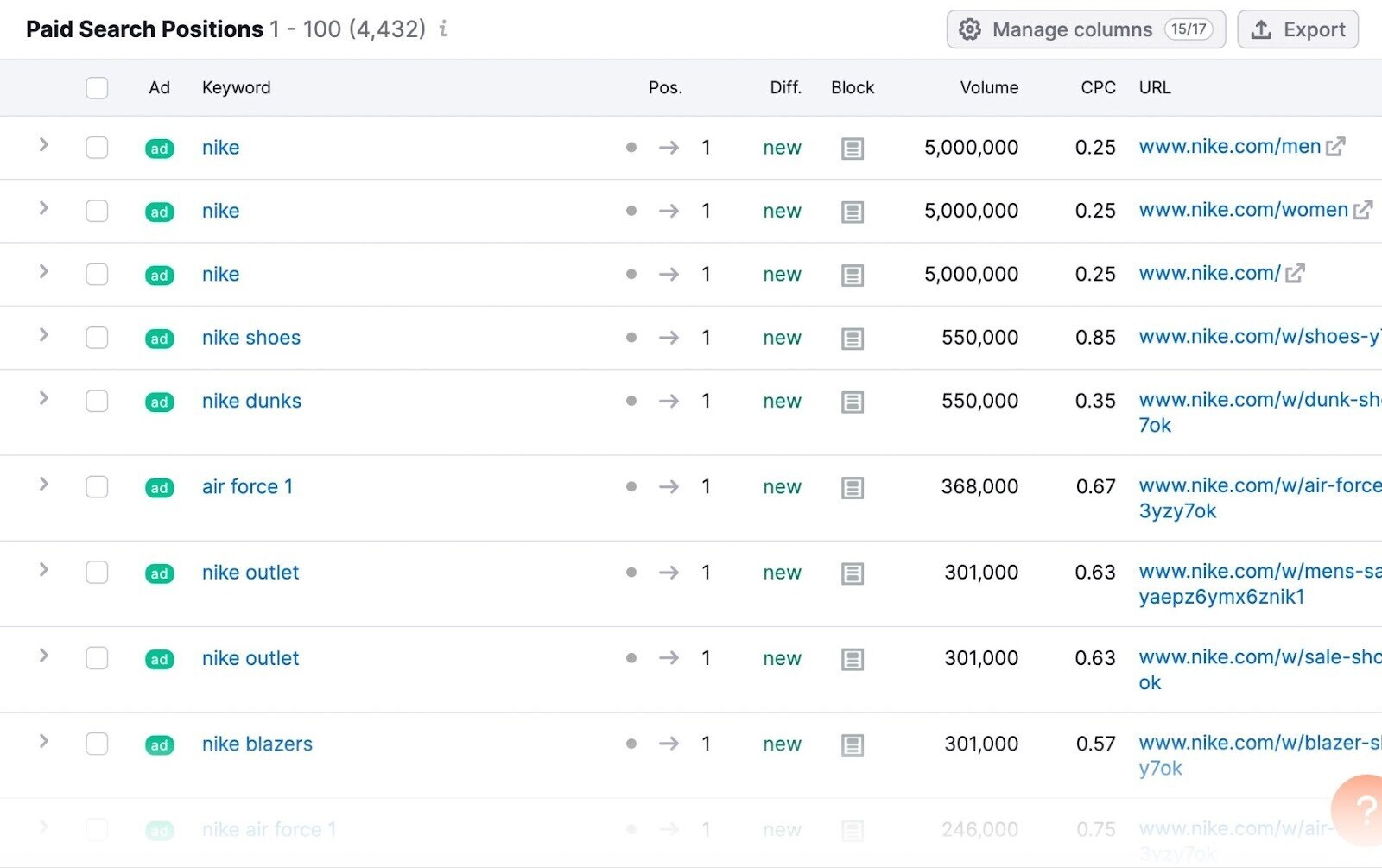
Analyze these keywords to find new opportunities. Then, check the “Ads History” tab.
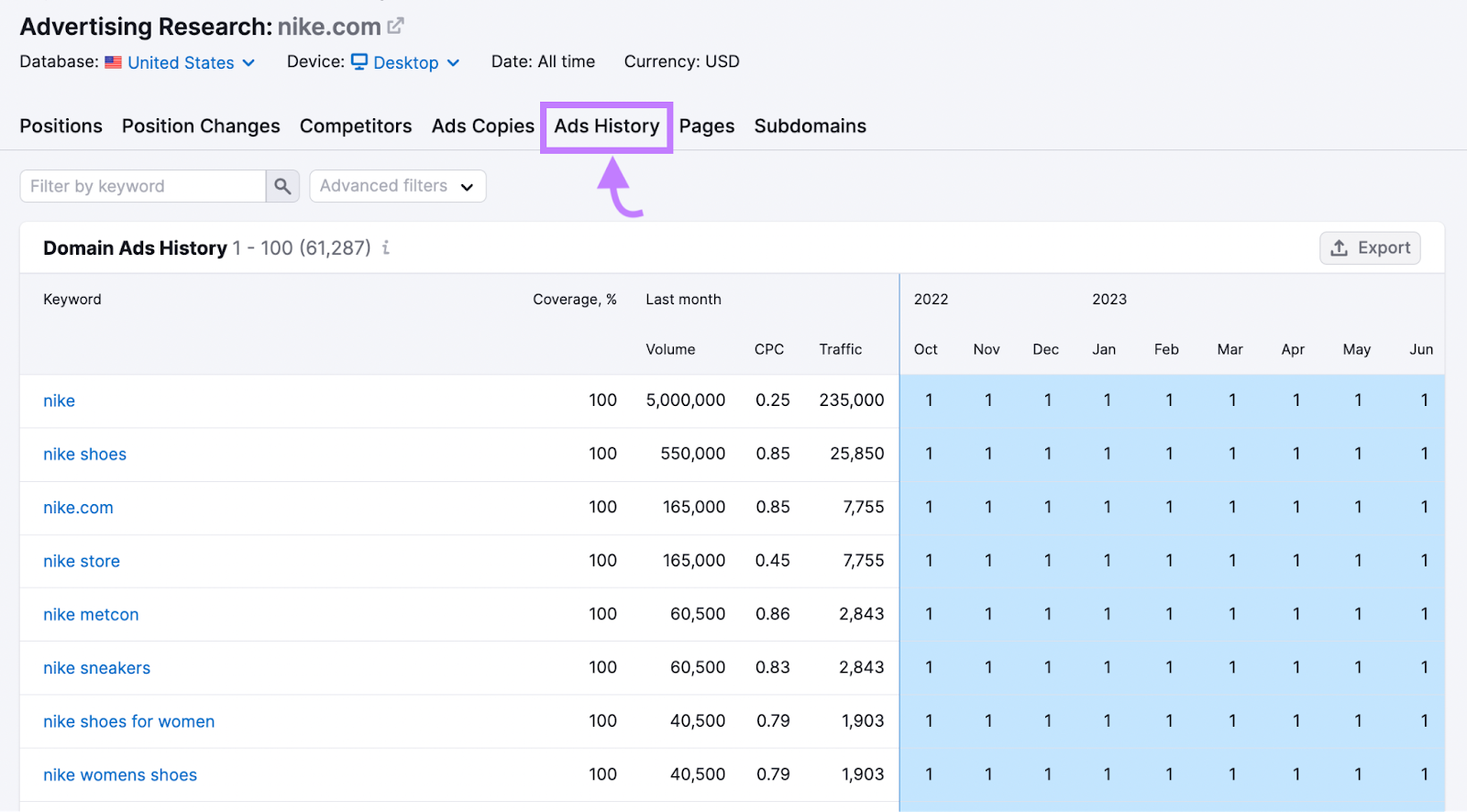
You’ll see how your competitor’s ads and keywords have changed over time, including past ad copy.
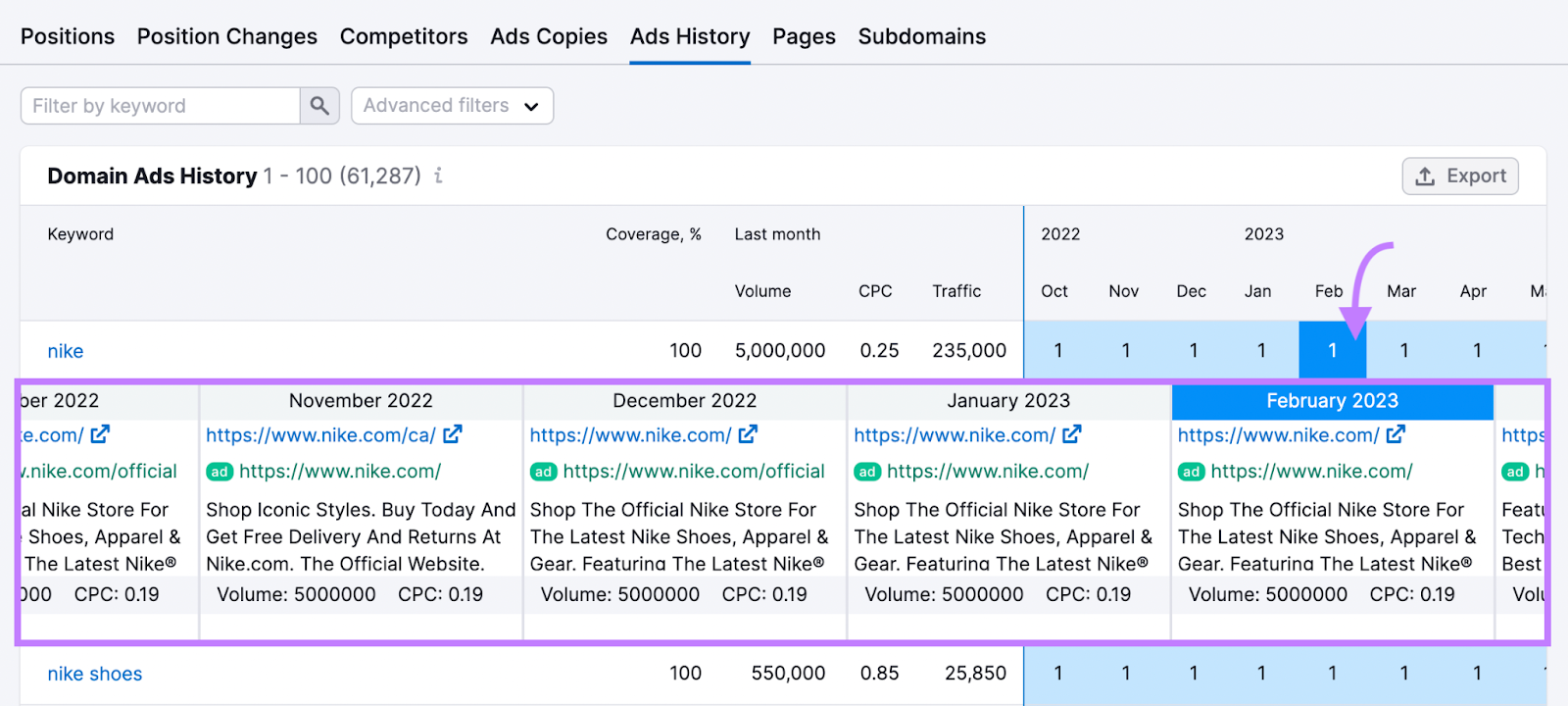
These reports help you create stronger campaigns. You can discover the best keywords, examine your competitors’ messaging, and plan cost-effective ads.
Get started with Advertising Research for free and launch your Google Ads campaign successfully.
