What Is Local SEO Keyword Research?
Local SEO keyword research is the process of finding keywords that people use when searching for products, services, or amenities in their areas—and they reveal what potential customers are searching for.
If you rely on local business, that information is valuable.
Optimizing your pages for local keywords can:
- Increase your visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs)
- Attract more organic (unpaid) traffic to your site
- Increase foot traffic and inquiries
- Boost sales
Consider a keyword like "[service] in [your location]." The top of the organic search results for this type of local keyword look like the image below:

Using Semrush’s Keyword Overview tool, we see the top-ranking page gets an estimated 7.6K visits per month from organic search. This page also likely attracts traffic from social media, backlinks, and other sources.

This business also appears in the local pack (the section with business listings and a map). The local pack listing attracts even more attention.

Effective keyword research for local SEO can help your business earn top placements in organic results and the local pack.
Implicit vs. Explicit Local Keywords
Local queries have local intent, meaning users want products or services in a specific area.
This local intent can be explicit or implicit.
Explicit local keywords specify a location or use a spatial term like “near me,” making the user’s need for a local result clear.
For example, a resident who lost keys might search “locksmith near me” or “locksmith [city].”

Implicit local keywords don’t specify a location or a spatial term, but the user still wants something nearby.
For example, a user searching “locksmith” expects local results. Google understands this local intent.

Google has algorithms to detect local intent and various ways to determine a user’s location. The search engine delivers local results whether the intent is explicit or implicit.
How to Do Local Keyword Research
Follow the five steps below to perform local keyword research for SEO.
After the main steps, we’ll explain how to optimize your Google Business Profile with local keywords.
1. List Your Solutions and Locations
Begin by listing words and phrases relevant to your business that will become your seed keywords.
List the following types of terms to use for local keyword research:
- General terms associated with your business type
- Products and services relevant to you that people might search for
- Problems or pain points customers may have that you can address
Next, list location terms that serve as keyword modifiers and make local intent explicit (city name, neighborhood name, etc.)
Use these seed keywords and location modifiers in the next steps.
2. Find Relevant Local Keywords
Use local keyword research tools to find queries people use and related data for those queries (e.g., search volume).
Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool has the largest keyword database on the market and can be used to find relevant local terms.
Open the tool and enter one of your seed keywords. Add your site’s URL for domain-specific insights, choose your target country, and click “Search.”
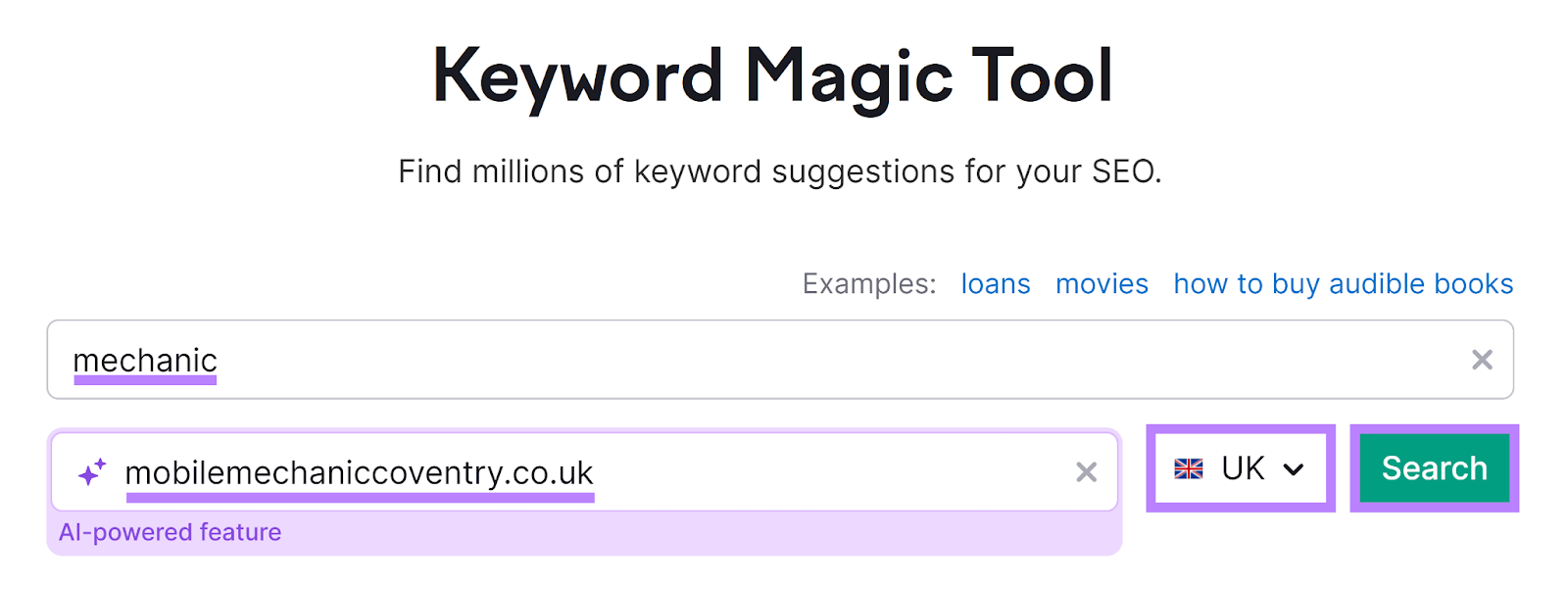
You’ll see a list of keywords containing your seed keyword or a variation of it.

Use filters to find keywords with local intent.
Select “Include keywords,” choose the “Any keywords,” option, enter your location modifiers, and click “Apply.”

Review these keywords and select those that match your business and local audience needs.
If you entered your domain name, check the Personal Keyword Difficulty (“PKD %”) column—that metric indicates the difficulty of ranking your specific website based on your site's authority and content relevance compared to top-ranking competitors.
Narrow your list by selecting the “Personal KD %” drop-down and setting a range of 0-49, which represents terms you have a good chance of ranking for.
Then click “Apply.”
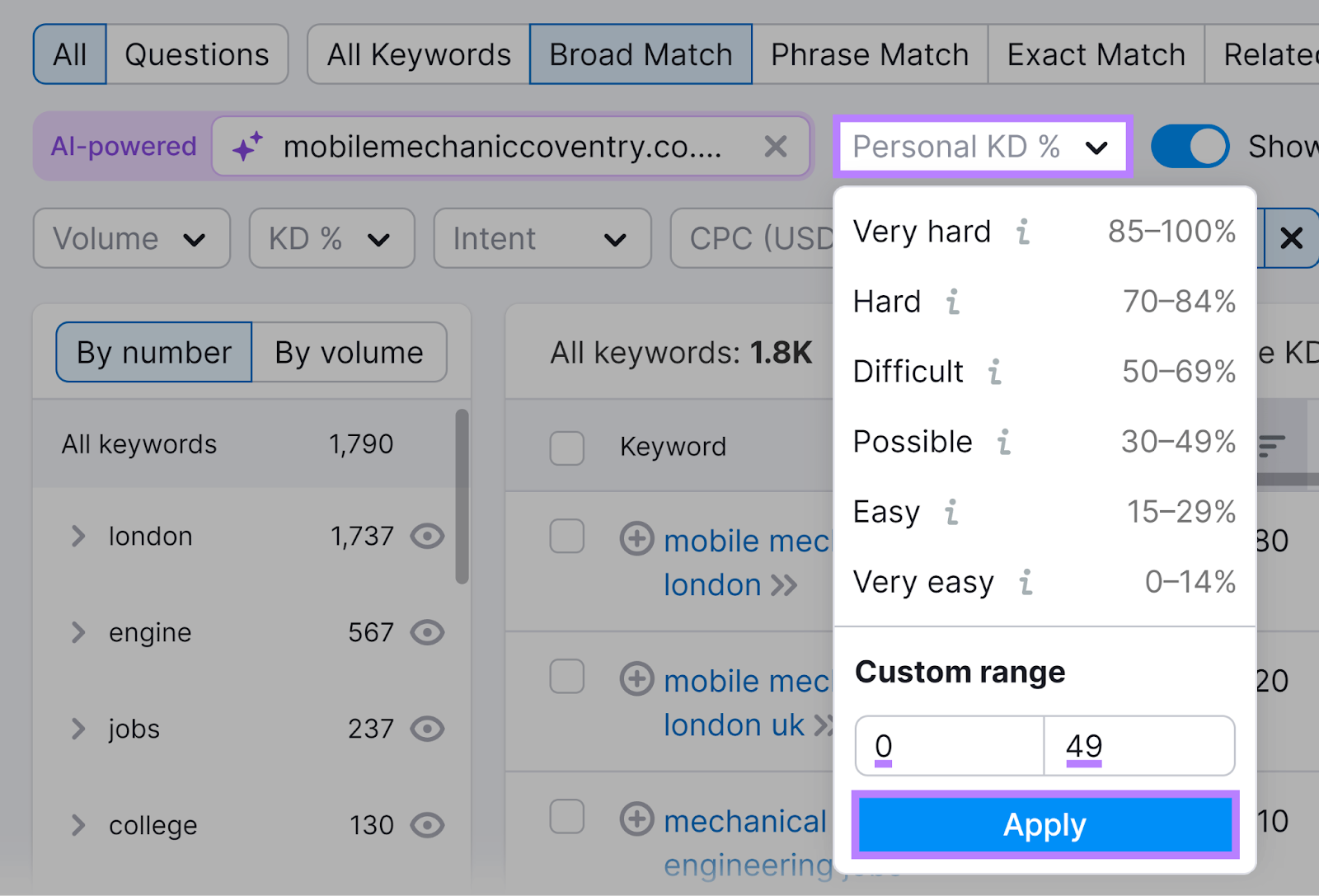
Aim for keywords with a good balance of search volume and feasible Personal Keyword Difficulty.
Save relevant keywords by selecting the checkboxes next to them and clicking “+ Add to keyword list.”
The keywords you save can be used in Keyword Strategy Builder later on.

Or use the “Export” icon to download your keywords.
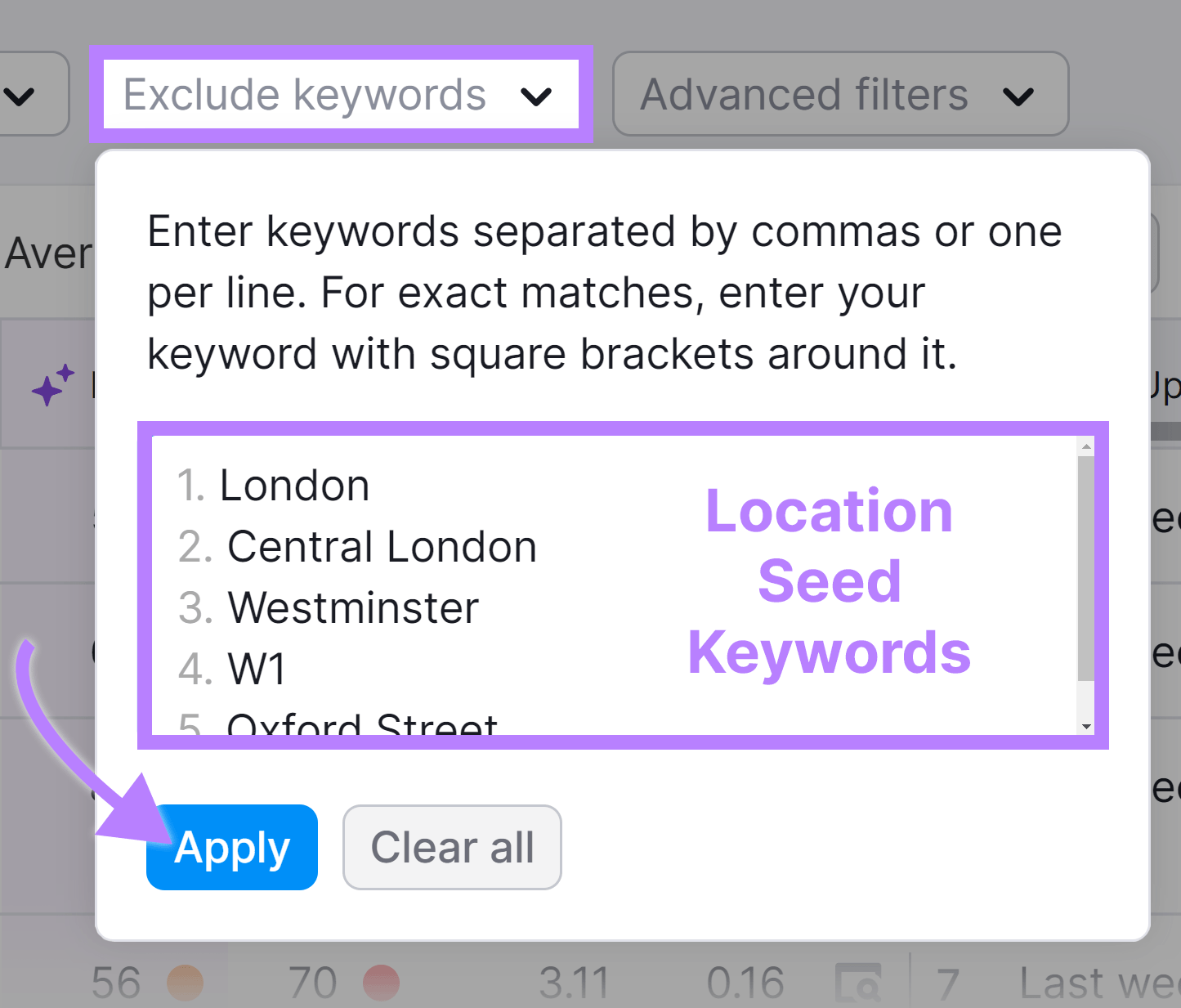
Next, find implicit keywords.
Move your location modifiers to the “Exclude keywords” filter to hide explicit keywords.
Then, apply a filter to show only queries that trigger the local pack.
Click “Advanced filters,” select the box next to “Local pack” from the drop-down below “SERP Features,” and click “Apply.”

Review these implicit local keywords for search volume and Personal Keyword Difficulty. Add relevant ones to your list.
3. Evaluate Local Metrics
Check each saved keyword’s metrics to prioritize terms you have a good chance of securing good rankings for in your specific location.
Use the Keyword Overview tool to study keyword metrics.
Enter a keyword, select your location, and click “Search.”

The overview report shows local data such as search volume and keyword difficulty.
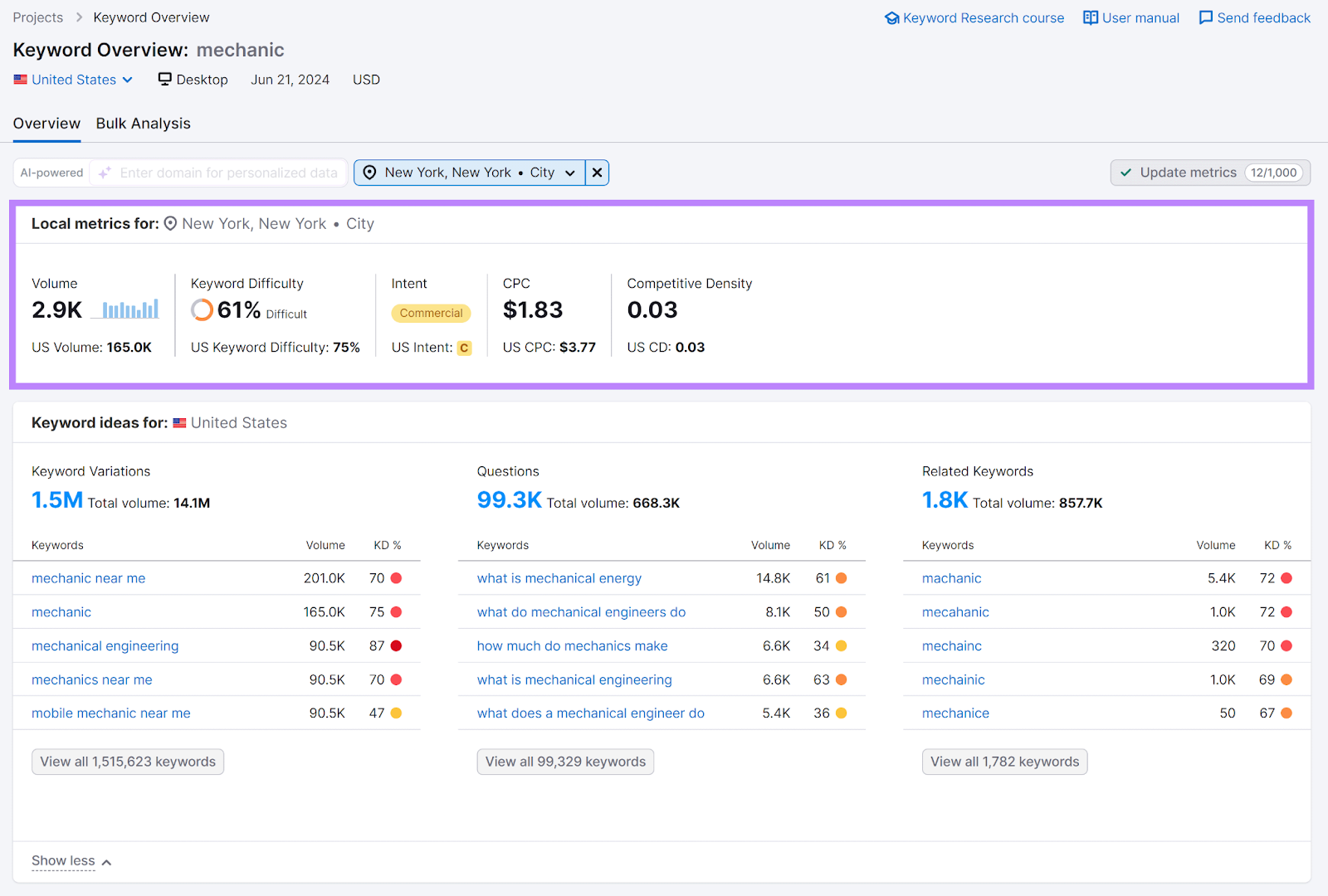
Check all your keywords’ local metrics. Remove terms from your list if they have no local search volume or extremely high difficulty.
Focus on terms that have the highest potential to improve local visibility and drive relevant traffic.
4. Find Competitors’ Keywords
Find additional local keywords by analyzing competitors’ rankings.
Search a local keyword in Google to identify competitors.
For example, the below search reveals a few competitors.

Or use Semrush’s Domain Overview tool to find competitors.
Enter your domain, select your country, and click “Search.”

If you have location-specific pages, search those exact URLs (e.g., “site.com/locations/city”).
Change “Subfolder” to “Exact URL” and click “Search” again to find competitors for the location-specific URL you entered.

Scroll down to “Main Organic Competitors” and note your top competitors’ domains or click “View details” to see more.
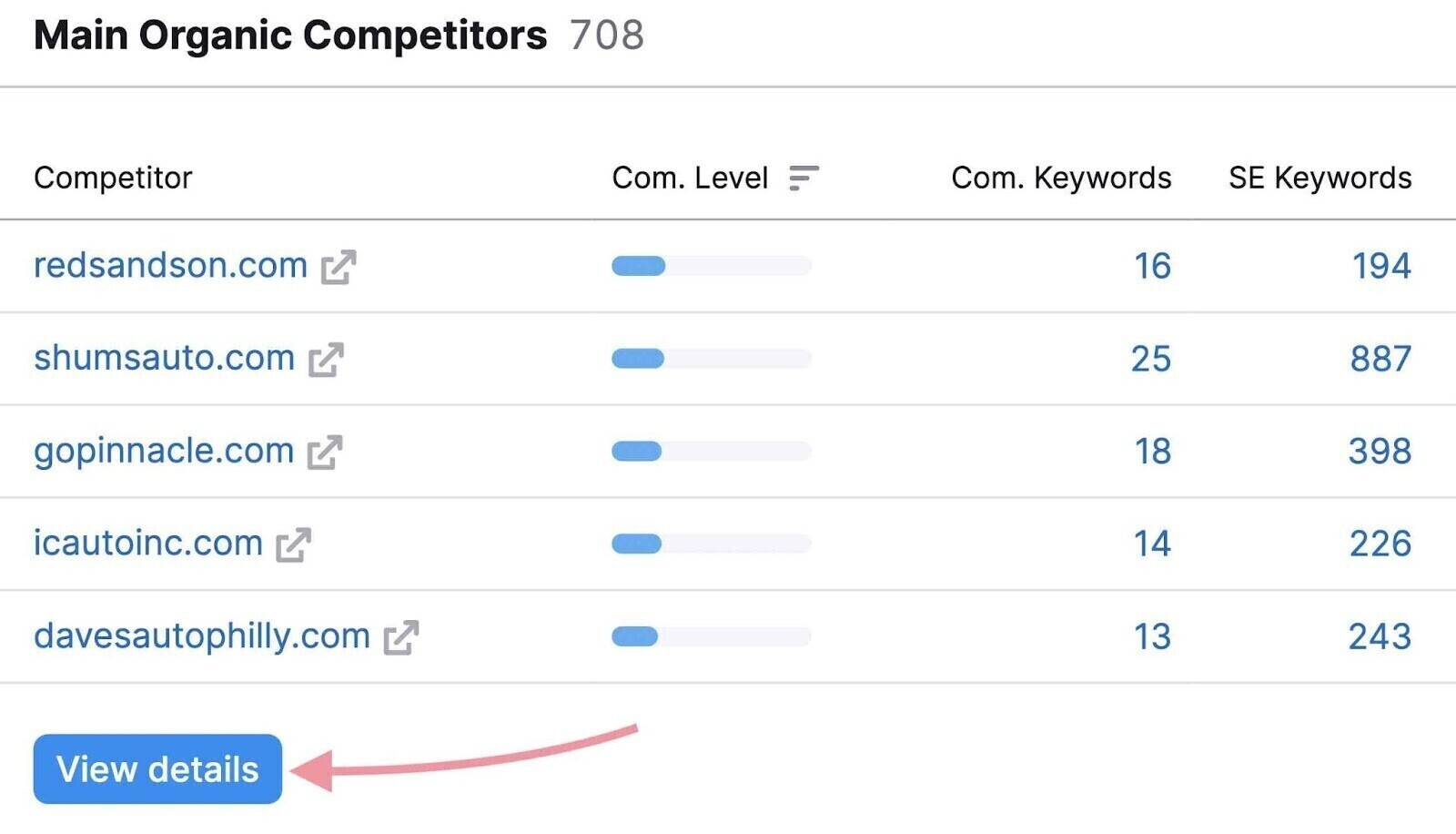
After finding your main competitors, use the Keyword Gap tool to find keywords competitors rank for but you don’t.
Enter your domain and up to four competitors’ domains, choose your location, and click “Compare.”

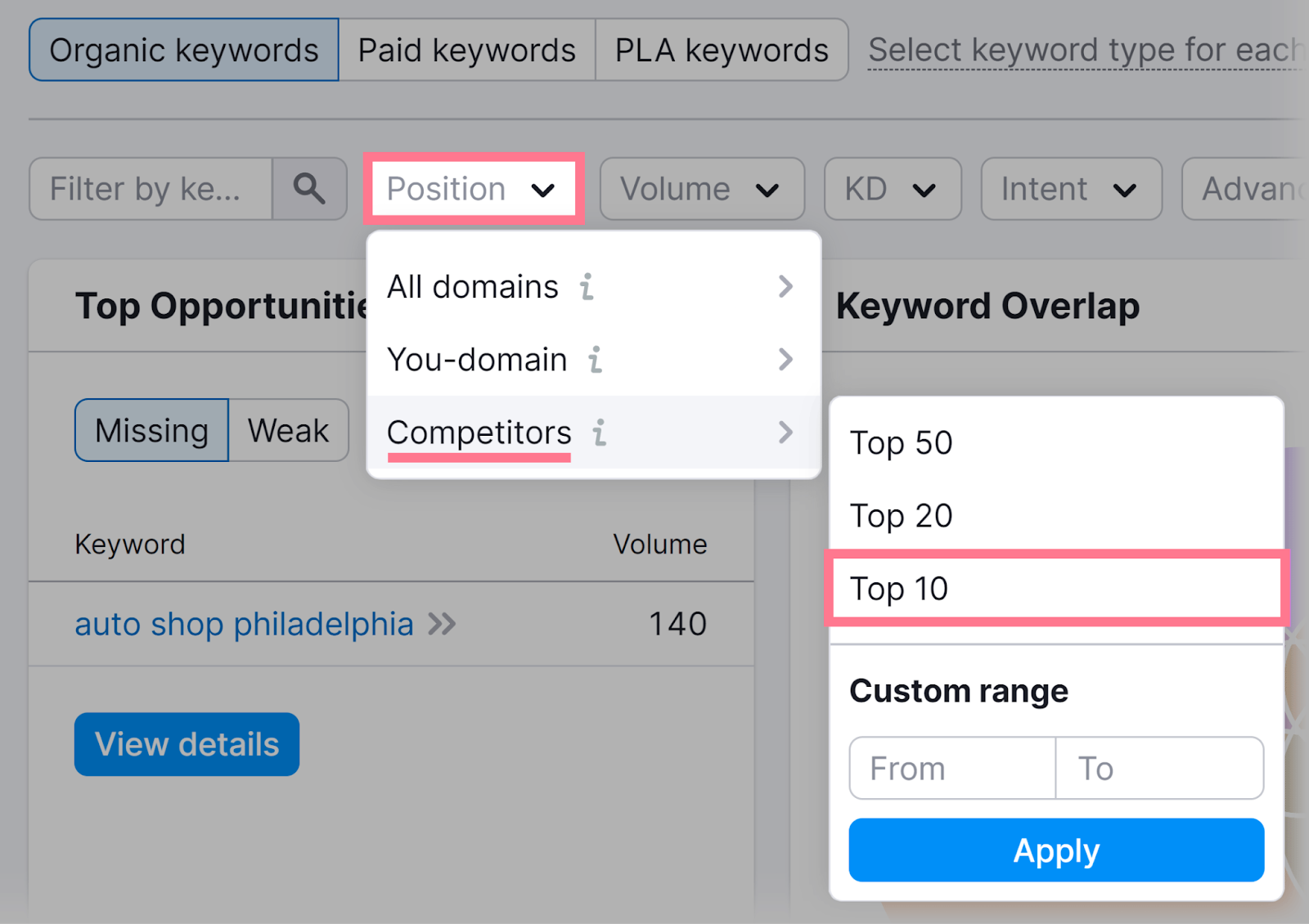
Switch to “Mobile” results, as many local queries occur on mobile devices.

Find terms your rivals rank highly for by going to “Position” > “Competitors” > “Top 10.” And clicking “Apply.”
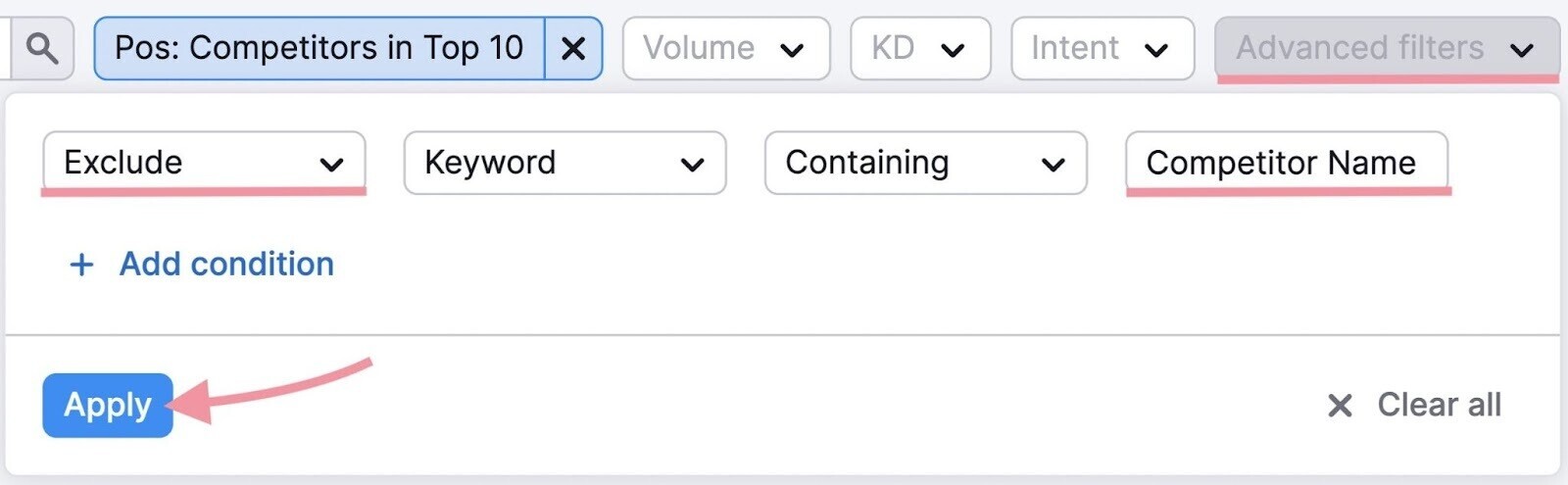
Exclude competitors’ brand names given you typically don’t want to target them.
Go to “Advanced filters” and set the fields to “Exclude,” “Keyword,” and “Containing.” Then, enter “[competitor name]” in the last field.
Next, filter for explicit local intent using your location keywords.
Go to “Advanced filters” and set the fields to “Include,” “Keyword,” and “Containing.” And enter “[location keyword].”
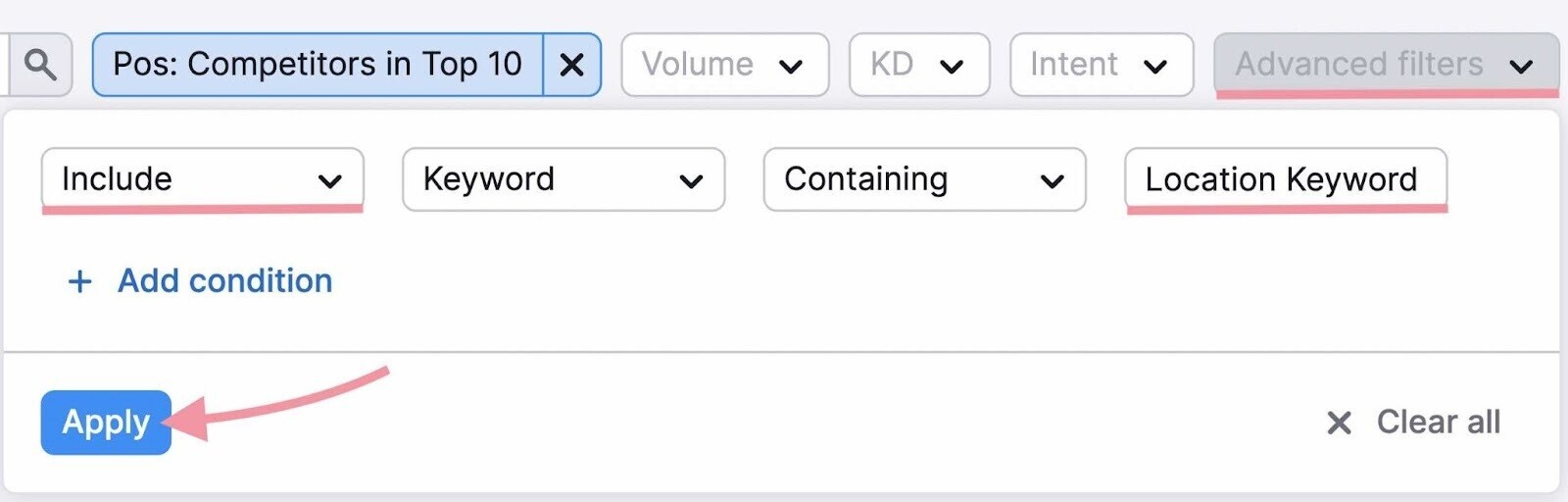
Scroll down and check the “Untapped” tab for keywords competitors rank for but you don’t.

Review the terms in the table and add relevant keywords to your list.
5. Map Your Keywords to URLs
Now that you have a comprehensive list of local SEO keywords to target, the next step is keyword mapping—matching each target keyword to the existing or future page that will target it.
Mapping ensures you have an optimized page for every important search term.
Keyword Strategy Builder can group your keywords into pages automatically—based on relevancy and search intent—to make content planning easier.
Open the tool and scroll down to open the keyword list you created.

If you saved your keywords in a spreadsheet, click “Create a regular list.”

Then click “Add keywords” and paste all your terms in the space provided.
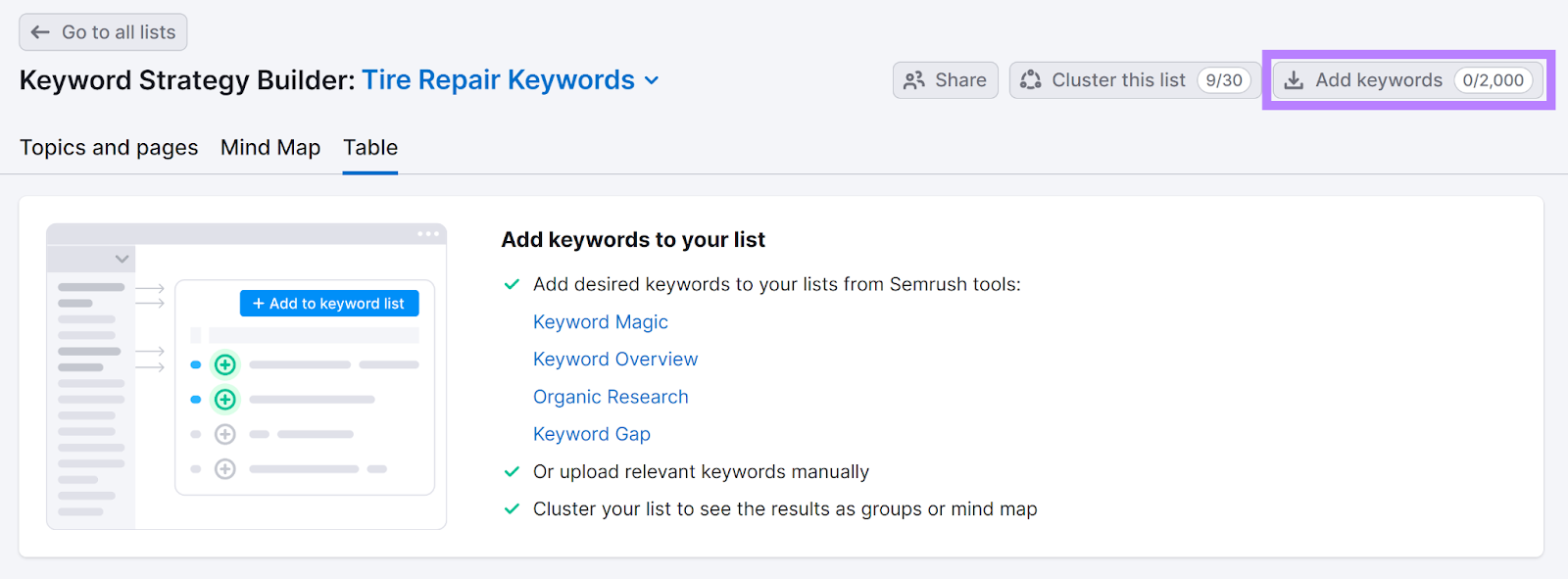
After opening or creating your list, go to the “Topics and pages” tab and click “Cluster this list.”

You’ll see your keywords grouped into pages. Each page focuses on a primary keyword.
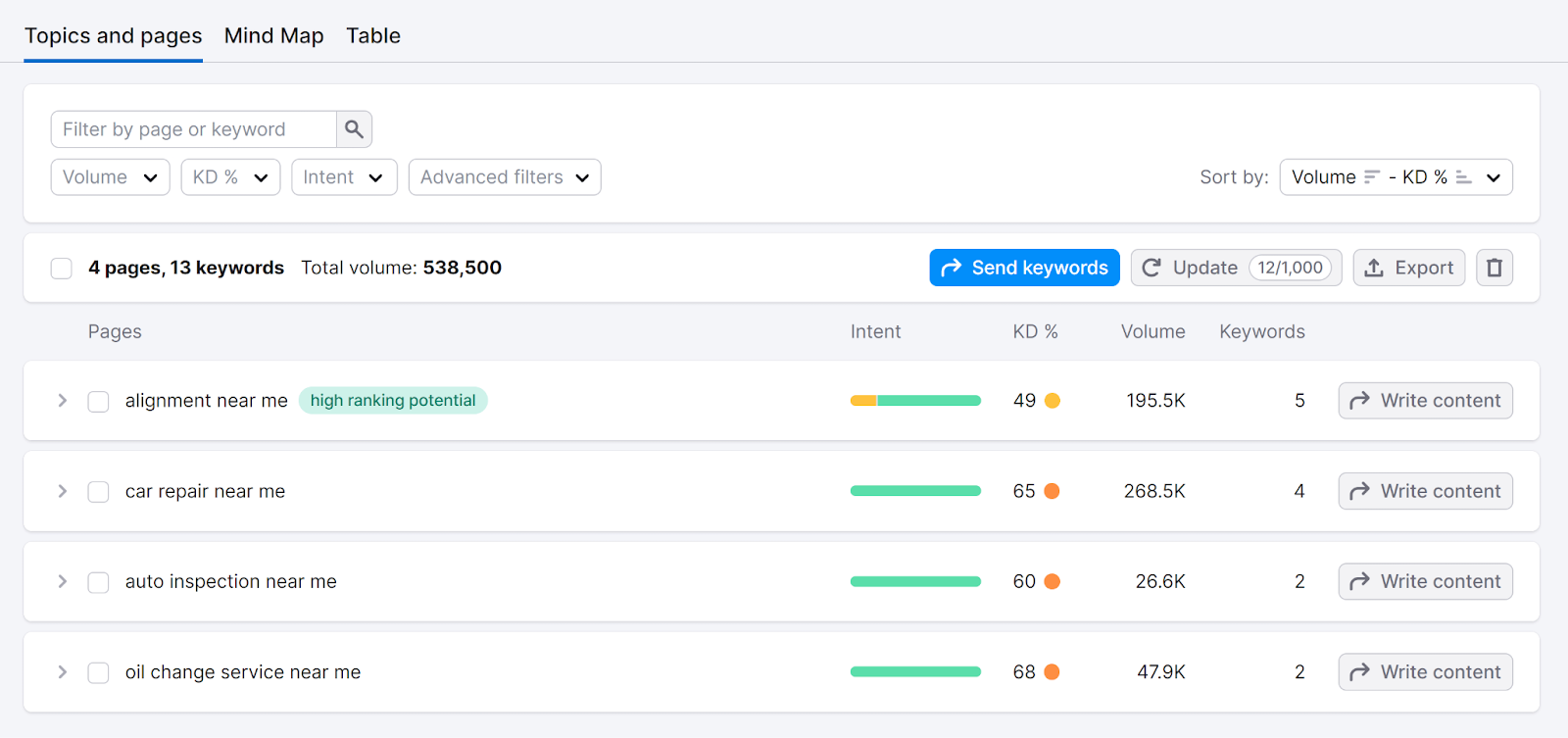
Click the arrow next to a page topic to see:
- Secondary keywords to target for that page
- Top-ranking results for inspiration

Review the top-ranking results to understand what content you need to create. Then, decide which pages you need to create and which pages you need to optimize.
If a page doesn’t exist yet, assign it a target URL and create a page that meets search intent—this means giving searchers (and Google) what they want.
For pages that already exist and need optimization, assign the existing URL.
A simple spreadsheet can help you assign URLs.
Download our free keyword mapping template, and use it to list all your pages, keywords, and target URLs.

Bonus Tip: Optimize Your Google Business Profile
Beyond optimizing your website for local keywords, also optimize your Google Business Profile (GBP) because that information can be used in the local pack.
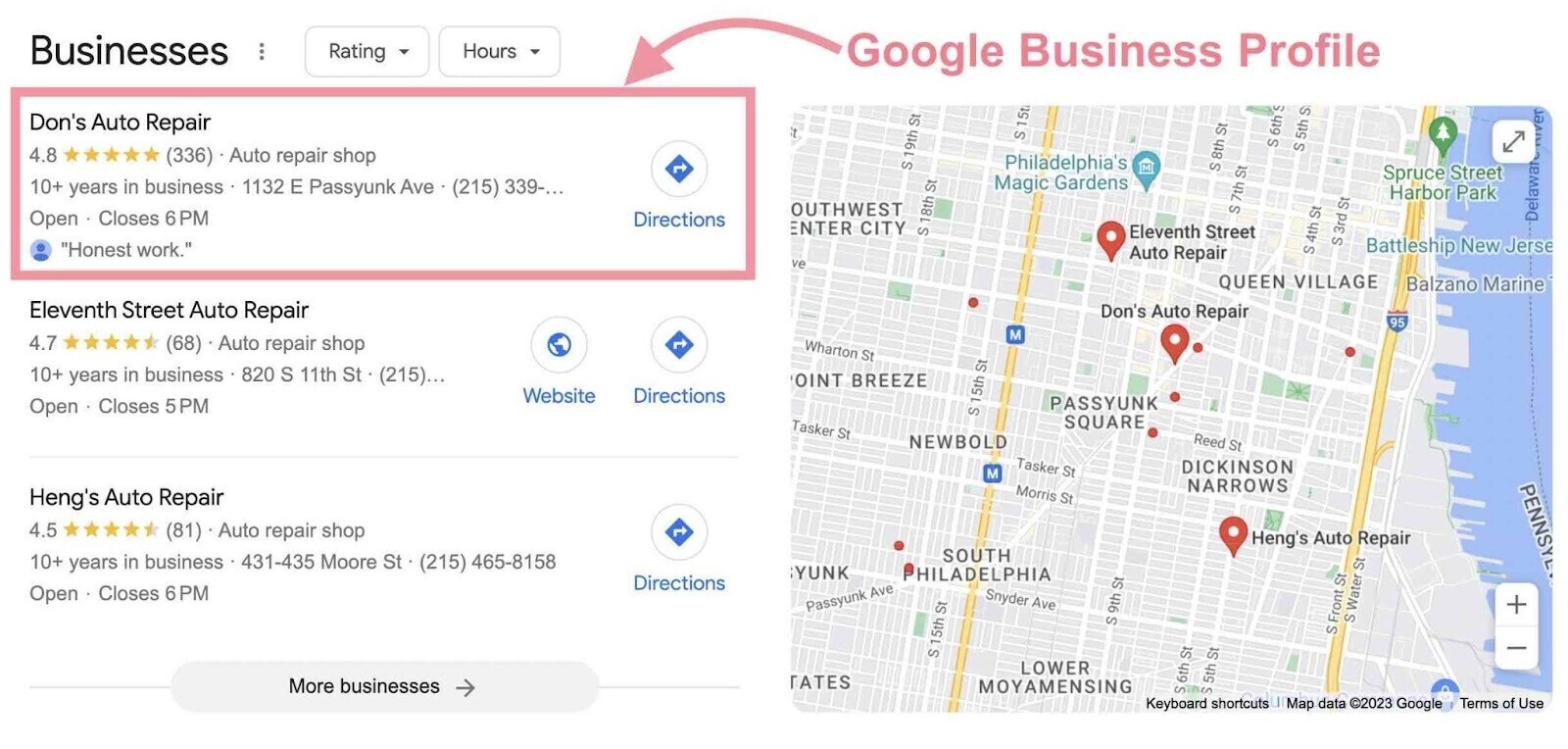
And in other Google Maps results.

Adding local keywords to your business description to help Google match your GBP to relevant queries. Appearing for more relevant queries can mean more visibility.

Using local keywords can also reassure potential customers that you have what they want.
Below is an example of a GBP description:

Additionally, local keyword research can help you select your business categories. Categories can influence local rankings.

Only choose categories that reflect your business accurately. Adding non-relevant categories for SEO is against Google’s guidelines.
Simply adding keywords to your GBP content isn’t guaranteed to improve rankings.
However, using the right terms can help potential customers understand what your business offers and whether it’s right for them.
How to Handle Multiple Locations
If you have multiple locations, perform local SEO keyword research for each one to account for the fact that different locations can yield different search behaviors and SERPs.
Replacing location names in keywords alone may not uncover all opportunities.
Once you have location-specific keywords, map them to dedicated location pages. Each page can then target that location’s keywords.
For example, the business below targets the specified keyword with one of its location pages.
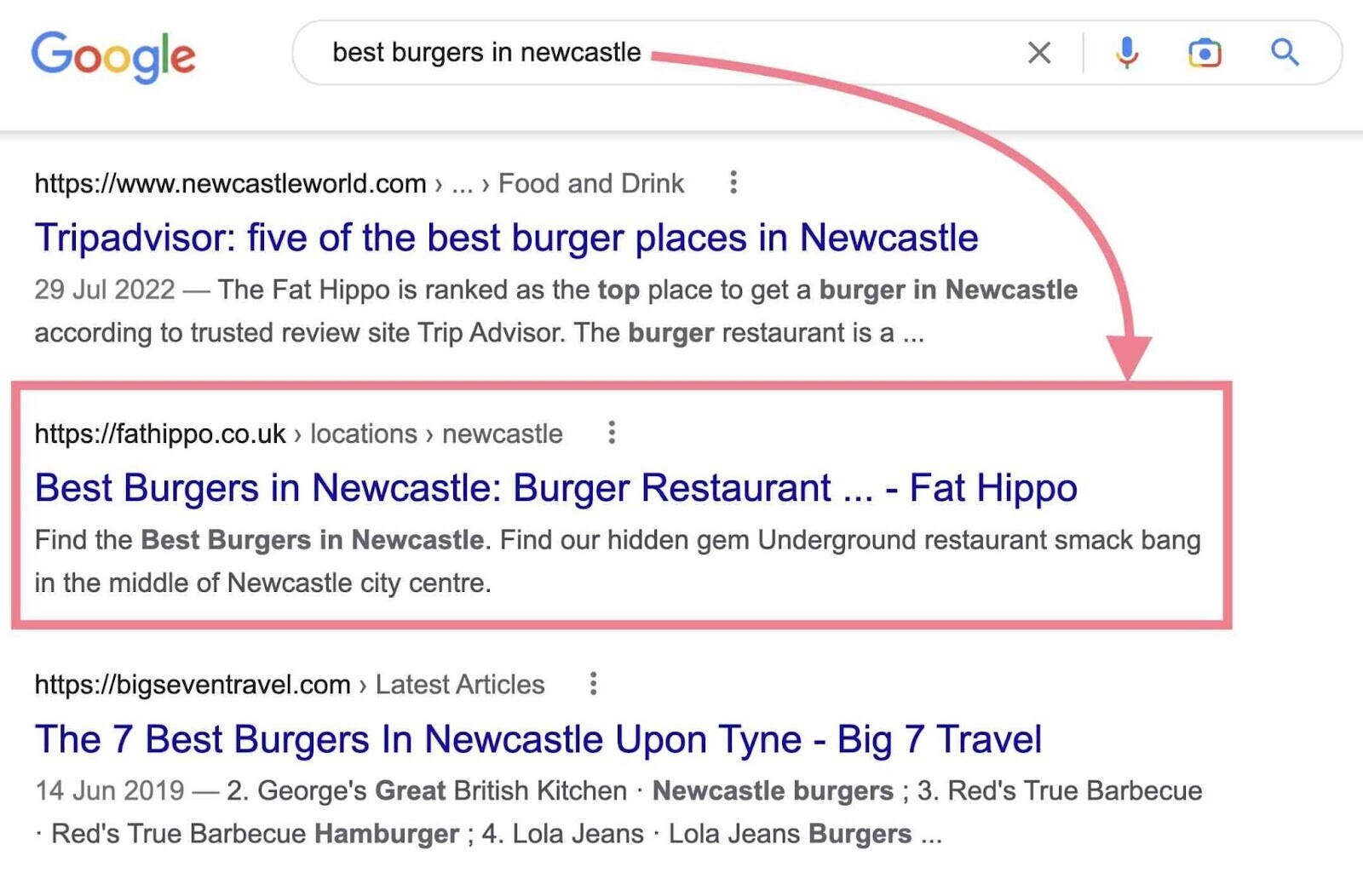
And targets another local keyword on a different location page.

These location pages also provide highly relevant information to searchers in each area. Which can help the business secure more customers.
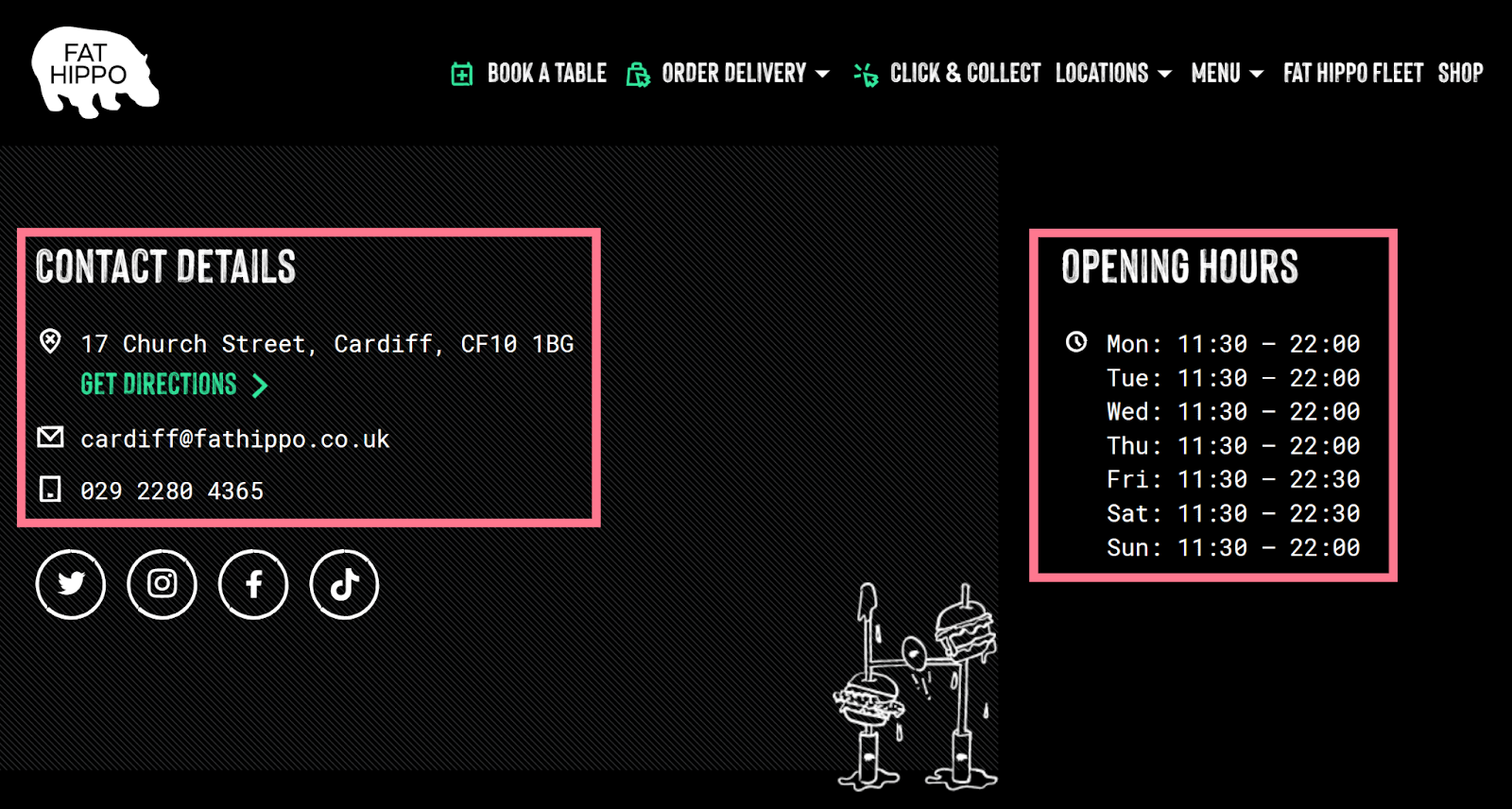
For example, each location page has a location-specific image and a list of amenities.

The location pages also have contact details and hours.
The brand also creates a Google Business Profile for each location, improving local pack and Maps visibility.
How to Track Your Local Keyword Rankings
Tracking your local keyword rankings shows whether your local SEO efforts are effective by helping you determine whether you’re ranking for new keywords or if your rankings are improving.
Also monitor for ranking drops, so you can take action quickly.
Monitor your local rankings in Google Search and Maps using the methods below:
Track Your Google Search Rankings
Use Semrush’s Position Tracking tool to track your Google Search rankings.
The tool shows where you appear in organic results and whether you appear in the local pack or other SERP features.
Enter your domain and click “Set up tracking.”

If you have multiple locations, set up tracking for each location URL:

Otherwise, complete the setup. Generally, use the following tips:
- Setting “Device” to “Mobile” to track mobile rankings
- Setting a “Location” to track rankings by user location
- Entering your business name exactly as it appears in the local pack to track local pack rankings
Then, click “Continue To Keywords.”

Add keywords from your mapping spreadsheet. Or send keywords directly from the Keyword Strategy Builder using the “Send to” button.
When the tool is done, go to the “Overview” tab and scroll down to the “Rankings Overview” table to see your current and previous ranking for each keyword over your chosen time range.

The “SERP Features” column indicates if a keyword triggers a local pack and if your business appears in it.

Set triggers to receive alerts about changes, like when a keyword enters or leaves the top three results.
Click the gear icon and select “Triggers” to set up a new trigger.

Then click “Add new trigger” to set conditions.
For example, trigger an alert when rankings change by a certain amount or enter a specific position.

Track Your Google Maps Rankings
Use Semrush’s Map Rank Tracker to track your Google Maps rankings.
This tool shows where you rank in different areas of your target location.
Enter your business name and select it from the list.
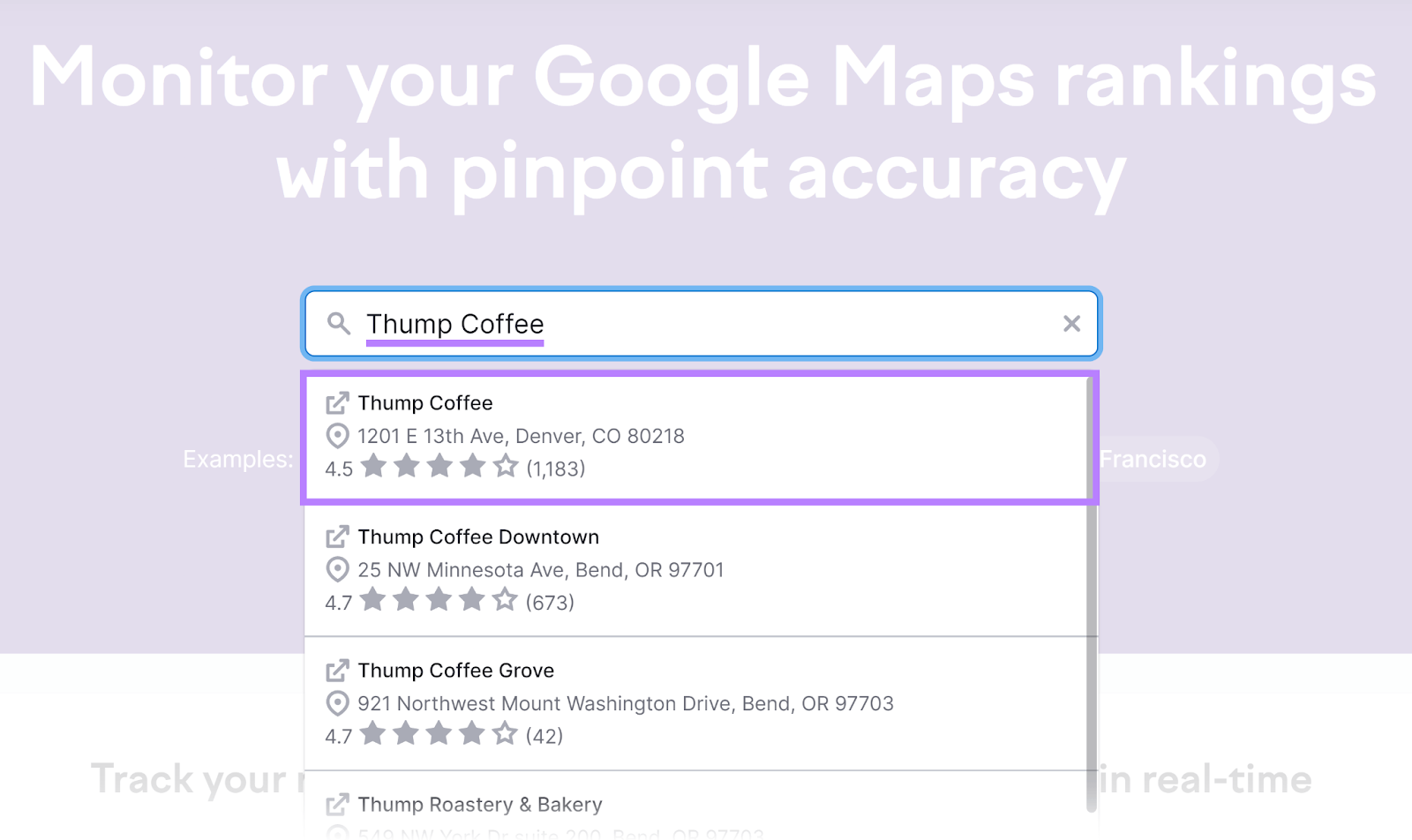
Add the keywords you want to track.

Choose your map grid size (the number of pins correlates to size).

Choose how often to update the data and click “Create campaign.”
You’ll see a heatmap of your local rankings at each pin in your target area.
You’ll also see which competitors appear alongside you.

Improve Your Local Visibility
Local keyword research forms the base of a strong local SEO strategy.
That research helps you find and target keywords that attract nearby audiences, leading to more web traffic, foot traffic, and sales.
Use the Keyword Magic Tool to find valuable terms that fit your local business.
