What Are Meta Tags?
Meta tags are HTML elements that provide information about webpages to search engines and users. These tags appear in a page’s <head> section:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="description" content="It's time to get backlinks that make a difference. Backlinko is the place for next-level SEO training and link building strategies.">
</html>
</head>In this example, a meta description summarizes the page. Search engines like Google often display meta descriptions in search results:

By adding this meta tag, you can influence how your page appears in search results and attract more users to click through to your site.
Which Meta Tags Does Google Support?
Google supports many meta tags. This table describes them:
| Meta tag name | Description | Example |
| description | Provides a short description of the page. This text may appear as a snippet in search results | <meta name="description" content="Make your business visible online with 55+ tools for SEO, PPC, content, social media, competitive research, and more."> |
| robots | Controls how search engines crawl and index your pages. Use “noindex” and “nofollow” to prevent indexing or link following. “index” and “follow” are default if unspecified | <meta name="robots" content="noindex,nofollow"> |
| googlebot | Works like the robots meta tag but applies specifically to Google | <meta name="googlebot" content="noindex,nofollow"> |
| notranslate | Stops Google from automatically translating your page in search results | <meta name="googlebot" content="notranslate"> |
| nopagereadaloud | Instructs Google not to use text-to-speech (TTS) services to read the page aloud | <meta name="google" content="nopagereadaloud"> |
| nositelinkssearchbox | Prevents Google from showing a sitelinks search box in your site’s search results. | <metaname="google" content="nositelinkssearchbox"> |
| google-site-verification | Verifies website ownership for Google Search Console. This tag is case-sensitive | <meta name="google-site-verification" content="+nxGUDJ4QpAZ5l9Bsjdi102tLVC21AIh5d1Nl23908vVuFHs34="> |
| Content-Type and charset | Specifies the content type and character set. Helps with rendering non-ASCII characters, such as accented letters | <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> |
| refresh | Redirects users to a new URL after a set time. Not recommended for SEO. A server-side 301 redirect is better | <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="5; url=https://website.com"> |
| rating | Indicates that the page has explicit content | <meta name="rating" content="adult"> |
| viewport | Adjusts how the page displays on mobile | <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> |
Two important notes regarding meta tags:
Meta Keywords Tag: This meta tag used to help search engines understand a webpage’s content by including a list of keywords. Google and other major search engines no longer support the meta keywords tag due to misuse.
Hreflang: The hreflang attribute is not a meta tag but is often mistaken for one. It goes in the <link> element in the <head> and tells search engines about the language and geographical targeting of a webpage.
Why Are Meta Tags Important?
Meta tags are important because they can help you:
Boost Click-Through Rates
Meta tags for SEO (like meta descriptions) help control how your webpages appear on search engine results pages (SERPs).
A relevant, compelling meta description can encourage users to click your link and improve your organic click-through rate (CTR). Optimizing these tags with relevant keywords, unique selling points, and calls to action (CTAs) can attract more qualified traffic to your site and lead to more conversions.
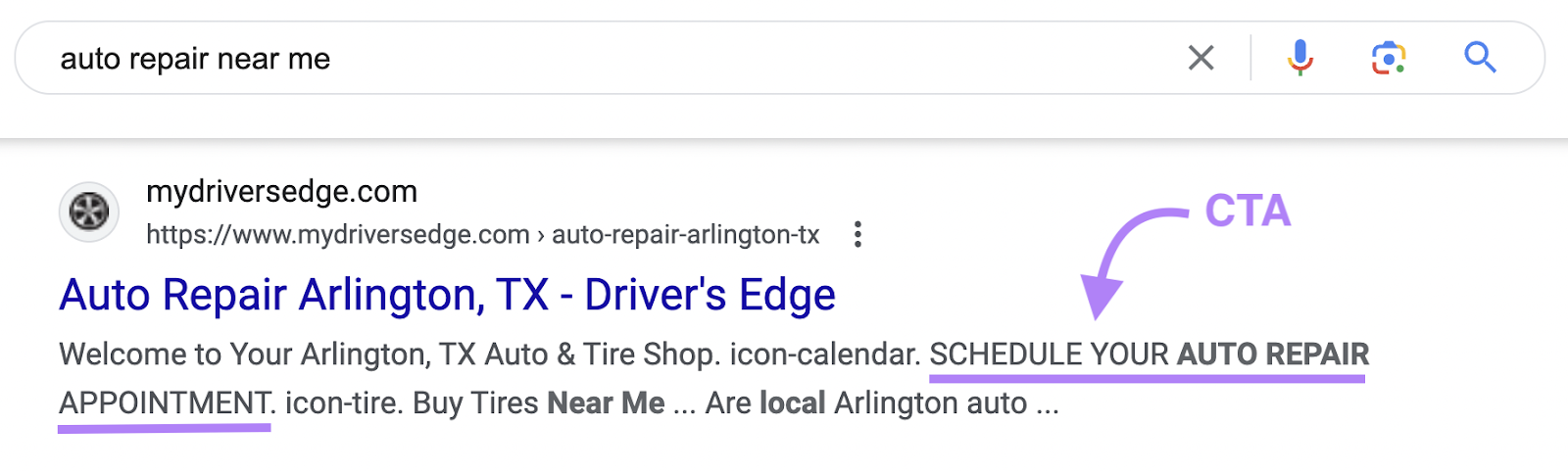
Provide Instructions to Search Engines
The meta robots tag defines how search engines crawl and index your webpages, so you can use it to avoid indexing duplicate or thin content.
This process is more precise than relying on the robots.txt file.

Improve UX and Accessibility
Meta tags like viewport and Content-Type (with charset) improve user experience (UX) and accessibility across devices by adapting your site for different screens and ensuring correct character rendering.
Enhance Social Media Sharing
When users share your webpages on social media platforms, the title, description, and image are typically auto-populated in the social post:
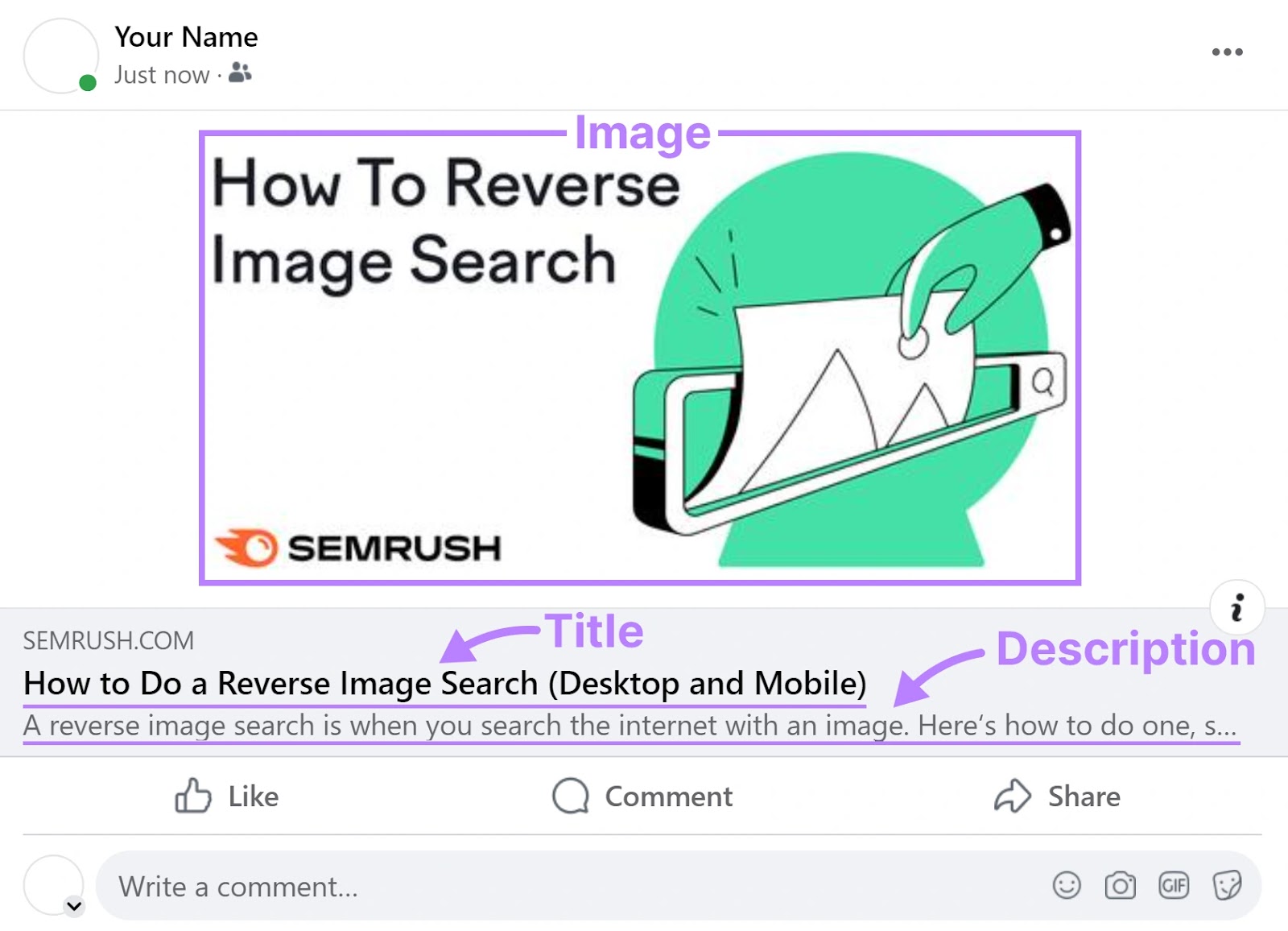
You can control these elements using Open Graph tags like "og:title," "og:description," and “og:image.”

Using engaging, descriptive Open Graph meta tags can make your content more appealing and clickable when shared on sites like Facebook, LinkedIn, and X (formerly Twitter).
Although these tags do not affect Google’s search results, they can improve visibility and referral traffic from social media.
How to Optimize Your HTML Meta Tags for SEO
Let’s look at some of the most important SEO meta tags in more detail and how you can optimize them.
Meta Description
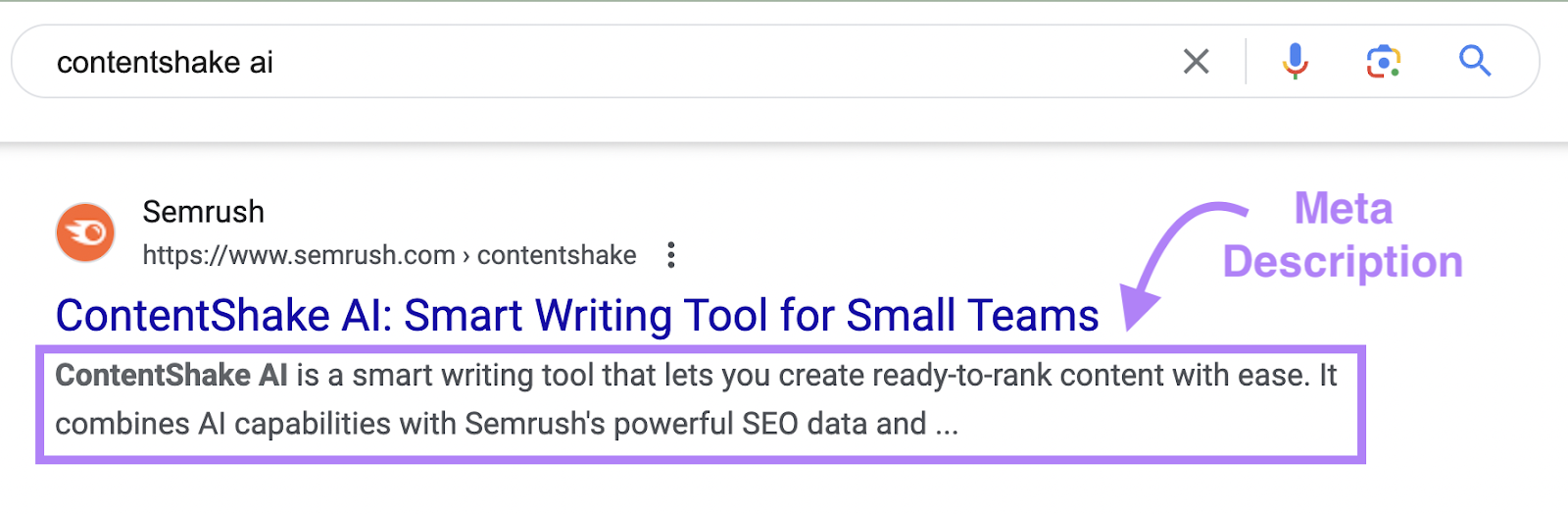
A meta description summarizes a webpage’s content for both search engines and users.
It can appear under the page title on the SERP, but Google might rewrite the one you created in order to suit specific search queries:
The code for a meta description tag looks like this:
<meta name="description" content="This is your meta description">Meta descriptions don’t directly affect your rankings in Google, but a well-written meta description can encourage users to click on your link instead of scrolling past.
Here are some tips to help you create effective meta descriptions:
- Keep it concise: Aim for around 105 characters to avoid truncation
- Include your target keyword: Google often bolds the keyword when it matches the user's query. Add your primary keyword naturally and avoid keyword stuffing.
- Add a CTA: Use action-oriented language, such as “Learn more,” “Get started,” or “Shop now” to provide clear direction and motivate clicks.
- Write unique descriptions for each page: Writing unique descriptions helps search engines and users understand how your pages differ.
Use Semrush’s Site Audit tool to find missing or duplicate meta descriptions.
Enter your domain in the tool and click “Start Audit.”
Then, configure the tool.
When you’re ready, click “Start Site Audit.”

When the audit is complete, go to the “Issues” tab and search for “meta description.”
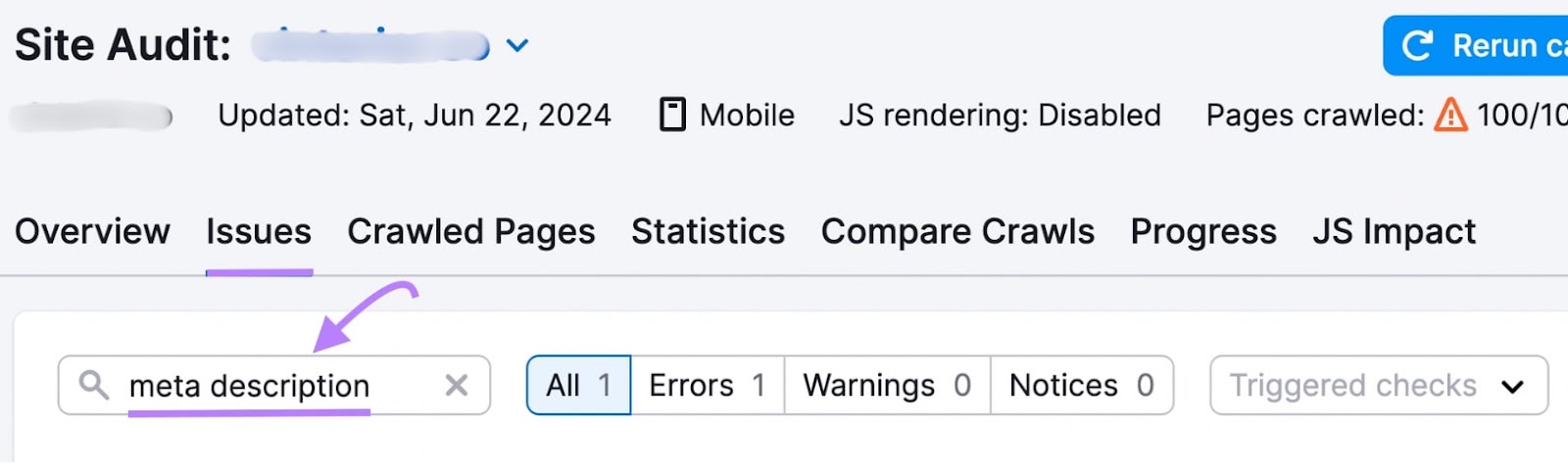
If you see the "# pages have duplicate meta descriptions" error, click on the linked number for more details.
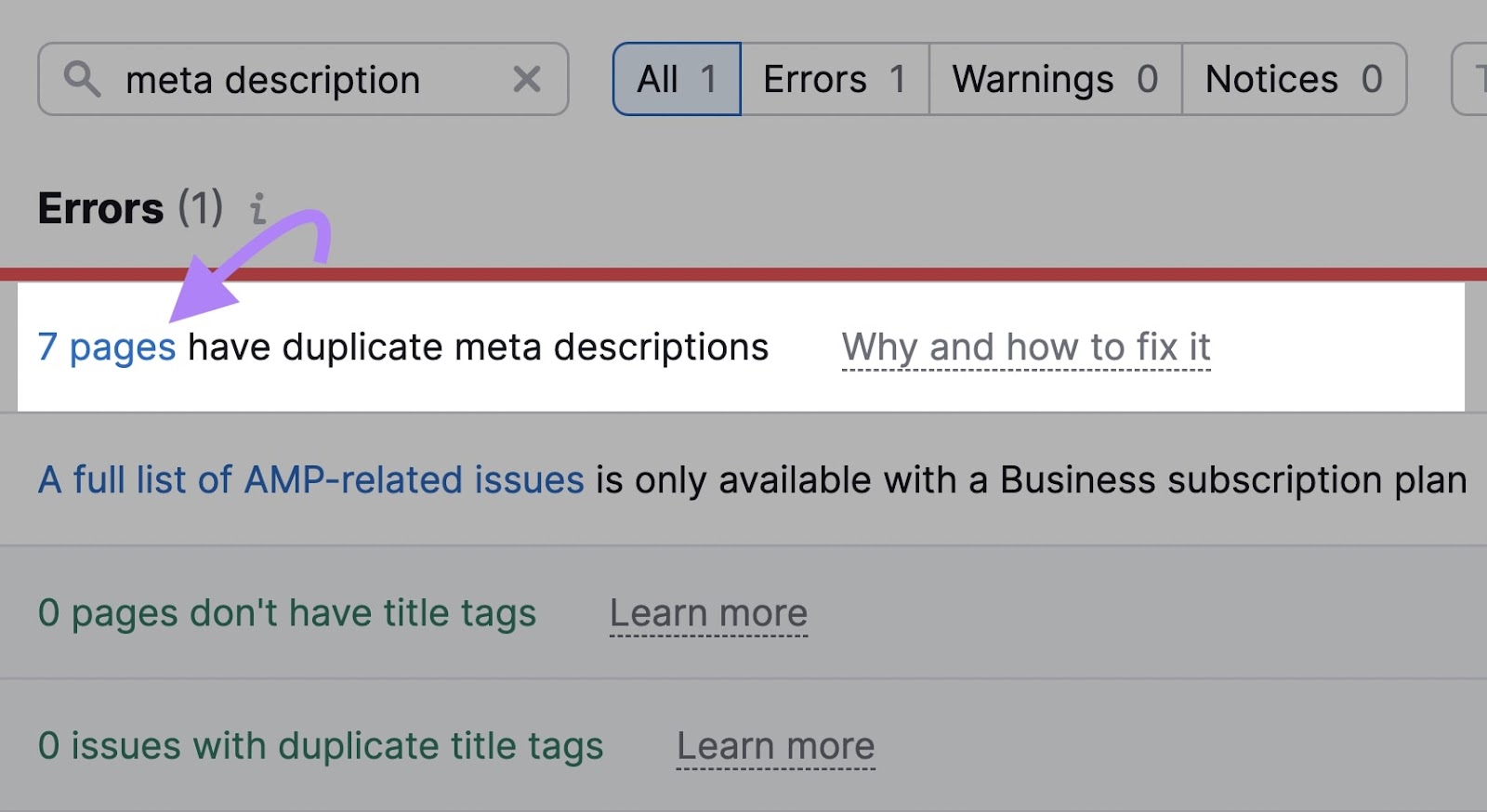
Next, click the arrow in the "Duplicates" column to see the list of URLs that have duplicate meta descriptions.
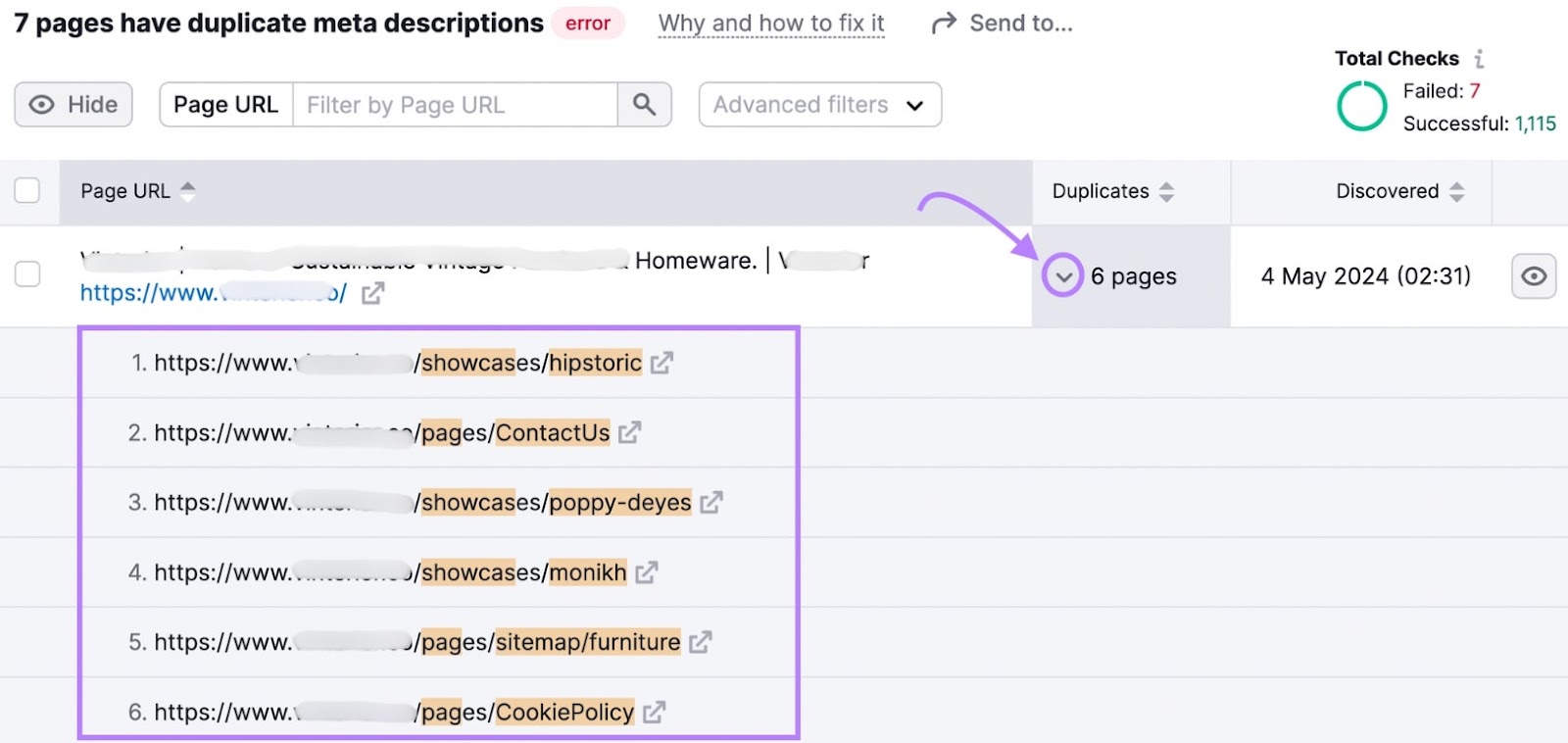
Similarly, in the "Issues" tab, you might also see the "# pages don’t have meta descriptions" warning. Again, click on the linked number for more details.

You’ll see a list of URLs with missing meta descriptions.
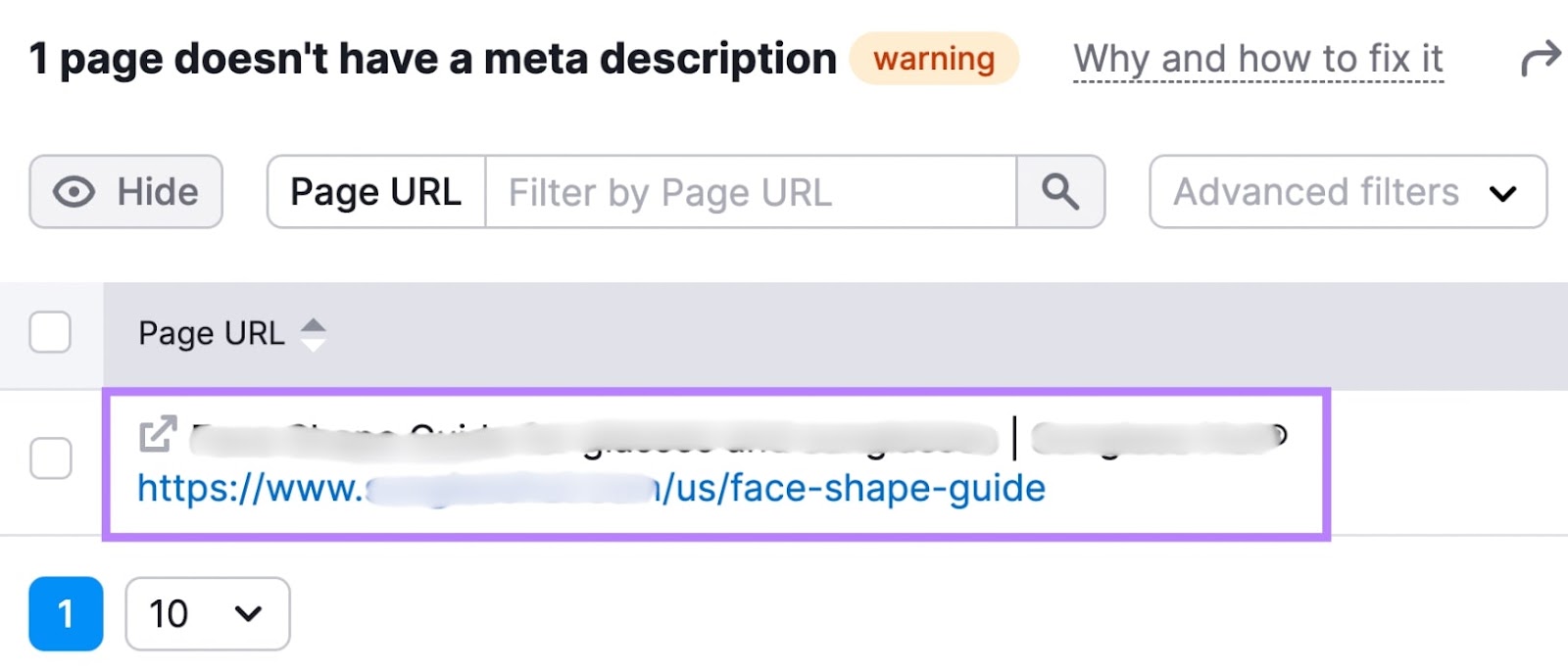
Go through the list of URLs. And write unique meta descriptions for them.
Title Tag
A title tag (often called a meta title) tells search engines the title of a webpage. Search engines typically display it as a clickable headline in SERPs:
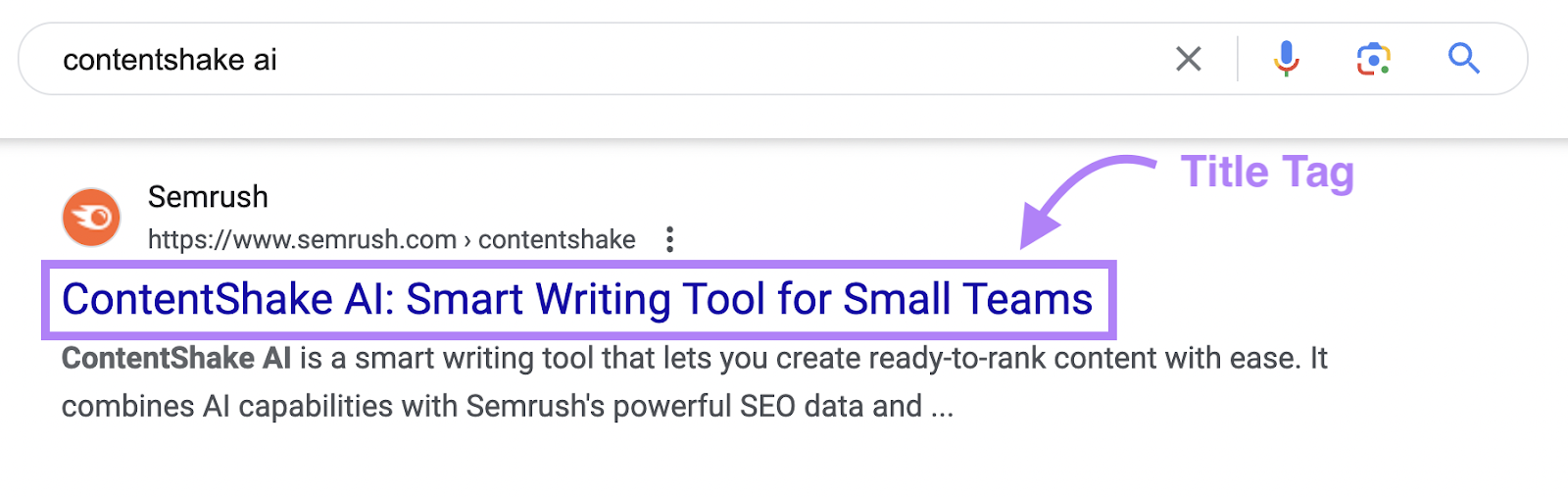
Here’s an example of what a title tag looks like in HTML:
<title>ContentShake AI: Smart Writing Tool for Small Teams</title>Google uses the title tag to determine the page’s topic so it can evaluate and rank the page appropriately.
Follow these best practices for creating meta titles on your website:
- Use 50–60 characters
- Include target keywords without stuffing
- Match search intent (informational, navigational, or transactional)
- Avoid duplicate titles
- Provide an accurate preview (avoid clickbait)
To scan your website for issues with your title tags, use the Site Audit tool. Go to the “Issues” tab and search for “title.”

If there are errors and warnings for your title tags, click on the number of pages (“# pages”) to see the list of URLs in question.
Meta Robots Tag
A meta robots tag directs search engines on whether to crawl and index your webpage. Place it in the <head> section of your HTML:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex,nofollow">Add your instructions for search engines inside the “content” attribute. Common values include:
- Follow: Allows crawling of links on the page (default if unspecified)
- Nofollow: Prevents crawling of links on the page
- Index: Allows search engines to index the page (default if unspecified)
- Noindex:Prevents the page from appearing in search results
Make sure you use these values appropriately.
For example, if you have thank you pages that should only be viewed by users who’ve completed actions like making a purchase or filling out a form, use “noindex” parameters on those pages to prevent them from showing in search results.
You should also avoid using nofollow on internal links unless there is a specific reason.
In Site Audit, search for “nofollow” issues to identify any unintended uses.
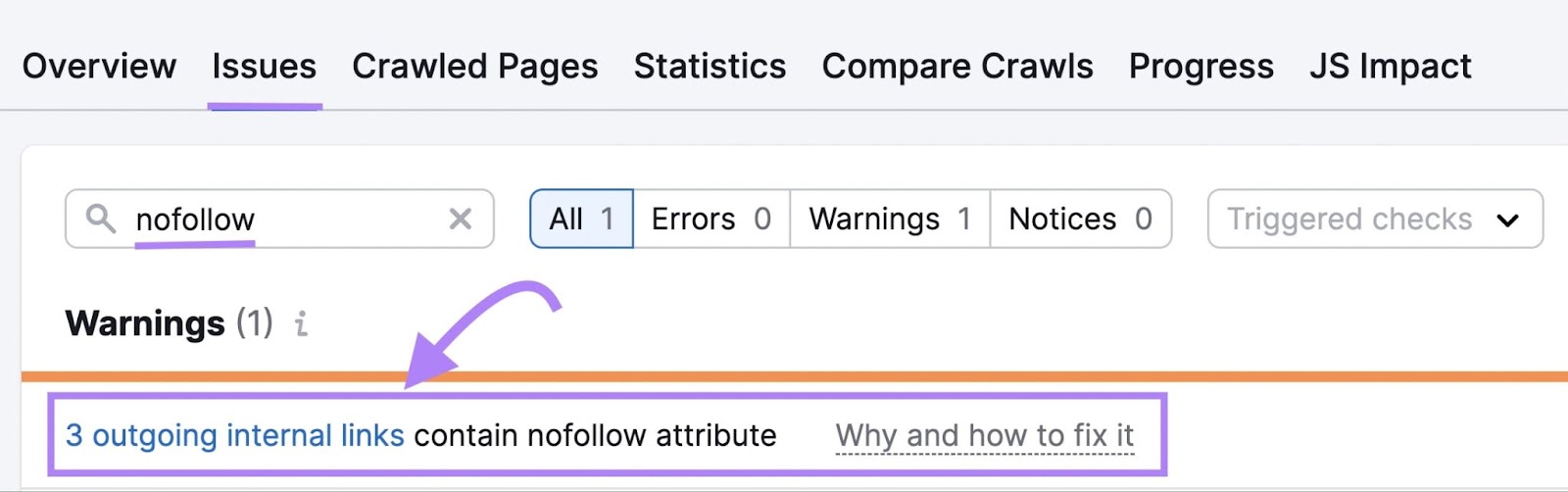
Review those links and remove “nofollow” values if you’ve added them to the page’s meta robots tag by mistake.
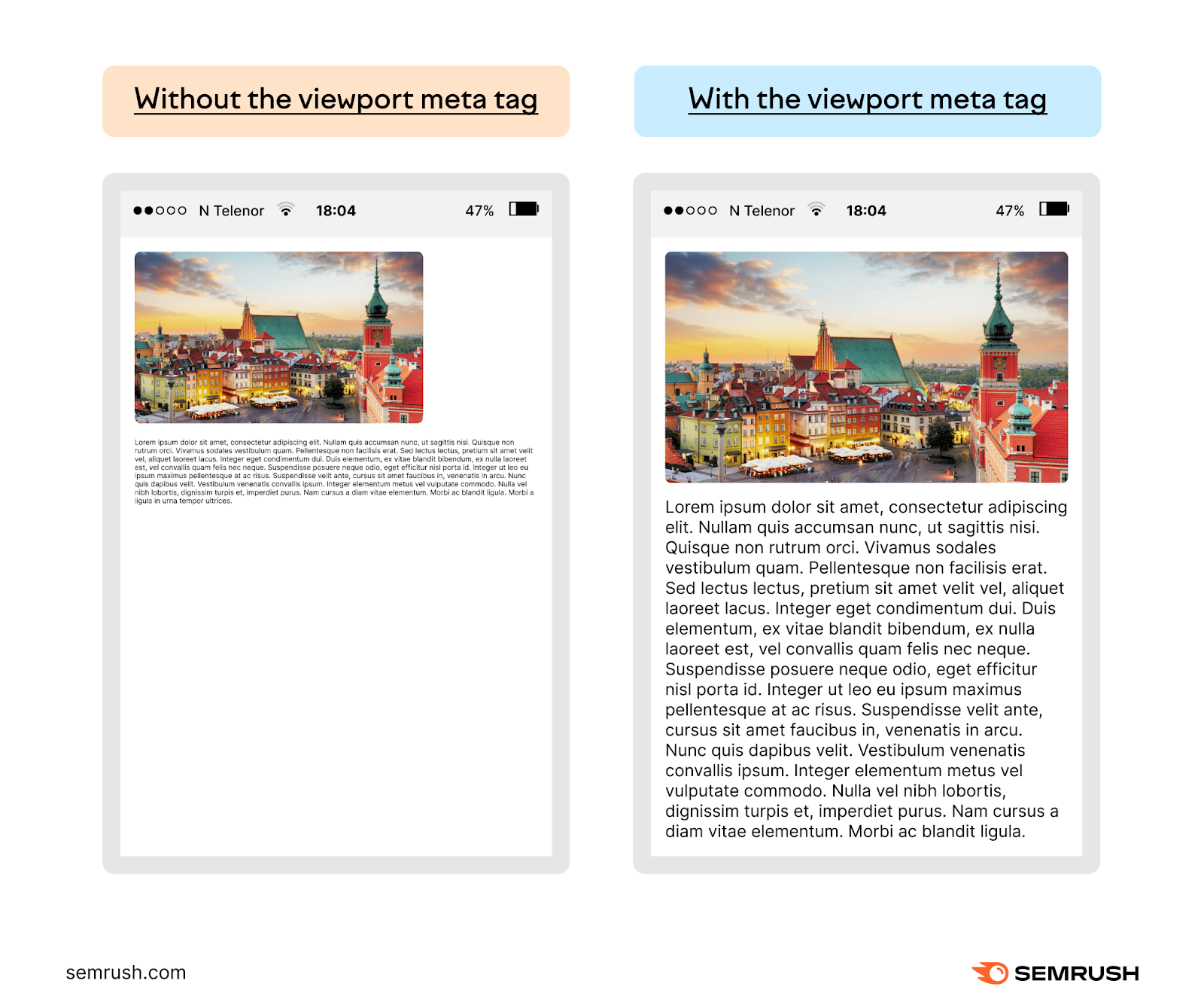
Meta Viewport Tag
A meta viewport tag tells browsers how to scale pages on mobile and other devices.
Here’s what the tag typically looks like:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">Like other meta tags, the meta viewport tag goes into the <head> section of your webpage:
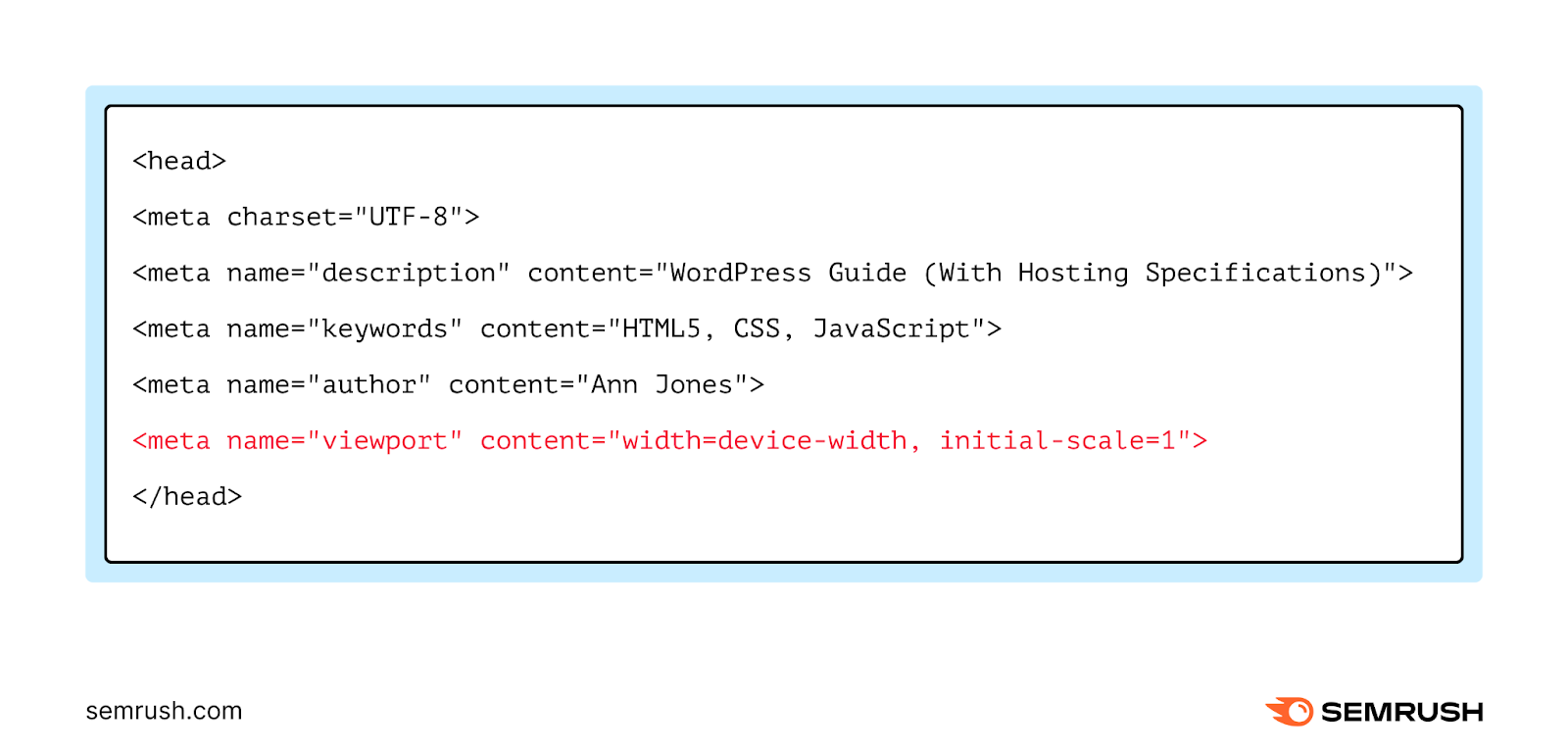
The meta viewport tag shows Google that the page is mobile-friendly. It supports responsive web design, which is important for search rankings.
You can check for viewport tag issues with Site Audit:

Other Meta Tags
Use Site Audit to identify errors in other meta tags.
For example, check for missing charset tags:

Or check for the presence of meta refresh tags:
Optimize Your Meta Tags for SEO and User Experience
Meta tags allow search engines and users to better understand your content. Proper usage can improve click-through rates, user experience, social sharing, and indexing.
Use Site Audit to detect and fix meta tag issues. This process can support your overall SEO efforts.
