What Is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, is the process of optimizing webpages and their content for search engines and users. This process helps pages rank higher on Google and drive more organic traffic.
Common on-page SEO tasks include optimizing for search intent, refining title tags, adding internal links, and improving URLs.
Below, we’ll cover various techniques to optimize your site for on-page factors.
First, learn how on-page SEO differs from off-page SEO:
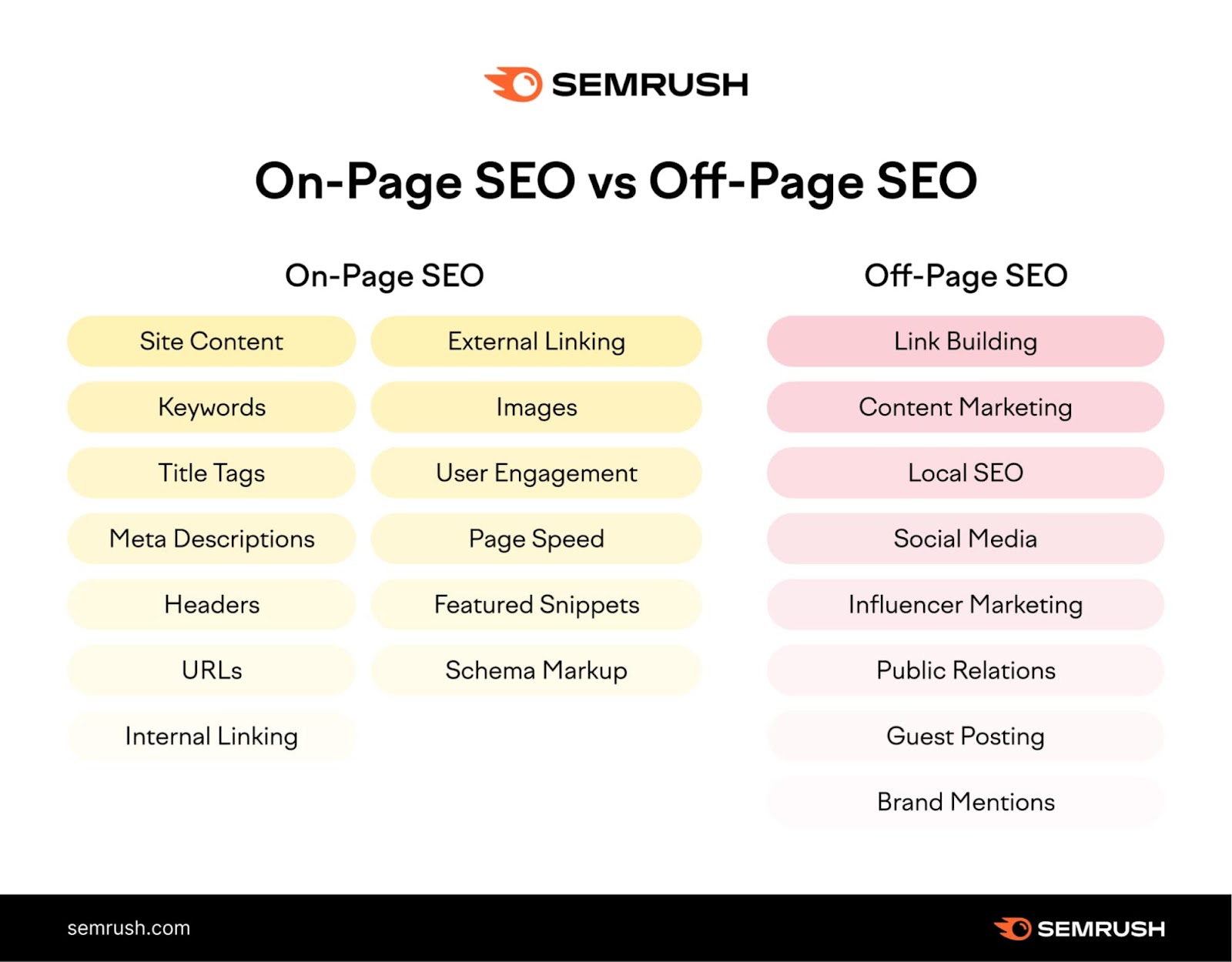
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO
On-page SEO involves any task performed on a webpage (or internally) to improve rankings, while off-page SEO involves any task performed outside your site (or externally) to boost rankings.
Backlinks are a major off-page SEO factor. Other off-page methods include social media and public relations.
Both are crucial for a strong SEO strategy. However, you can directly control on-page SEO factors.
Focusing on these factors is a good place to begin.
Why Is On-Page SEO Important?
On-page SEO is important because search engines rely on keywords and other on-page SEO elements to determine whether a page matches a user’s search intent.
When a page is relevant and useful, Google displays it to the user. Google’s algorithm changes often, but user experience remains a priority. Google recommends focusing on “people-first content,” which means creating valuable content that aligns with user intent is more important than ever.
Next, learn how to update your content to reflect on-page SEO best practices.
9 On-Page SEO Techniques for Your Website
Here are key on-page optimization techniques to consider:
- Write unique, helpful content
- Place target keywords strategically
- Write keyword-rich title tags
- Write click-worthy meta descriptions
- Use headings and subheadings to structure your page
- Optimize URLs
- Add internal links
- Add external links
- Include and optimize images
Below, learn more about each technique.
1. Write Unique, Helpful Content
Creating high-quality content that matches readers’ search intent is a crucial on-site SEO step.
Use a keyword research tool to find relevant topics and target keywords. For example, enter a term like “audio book” into the Keyword Magic Tool.
The tool will generate a list of related keywords, sorted by search volume.
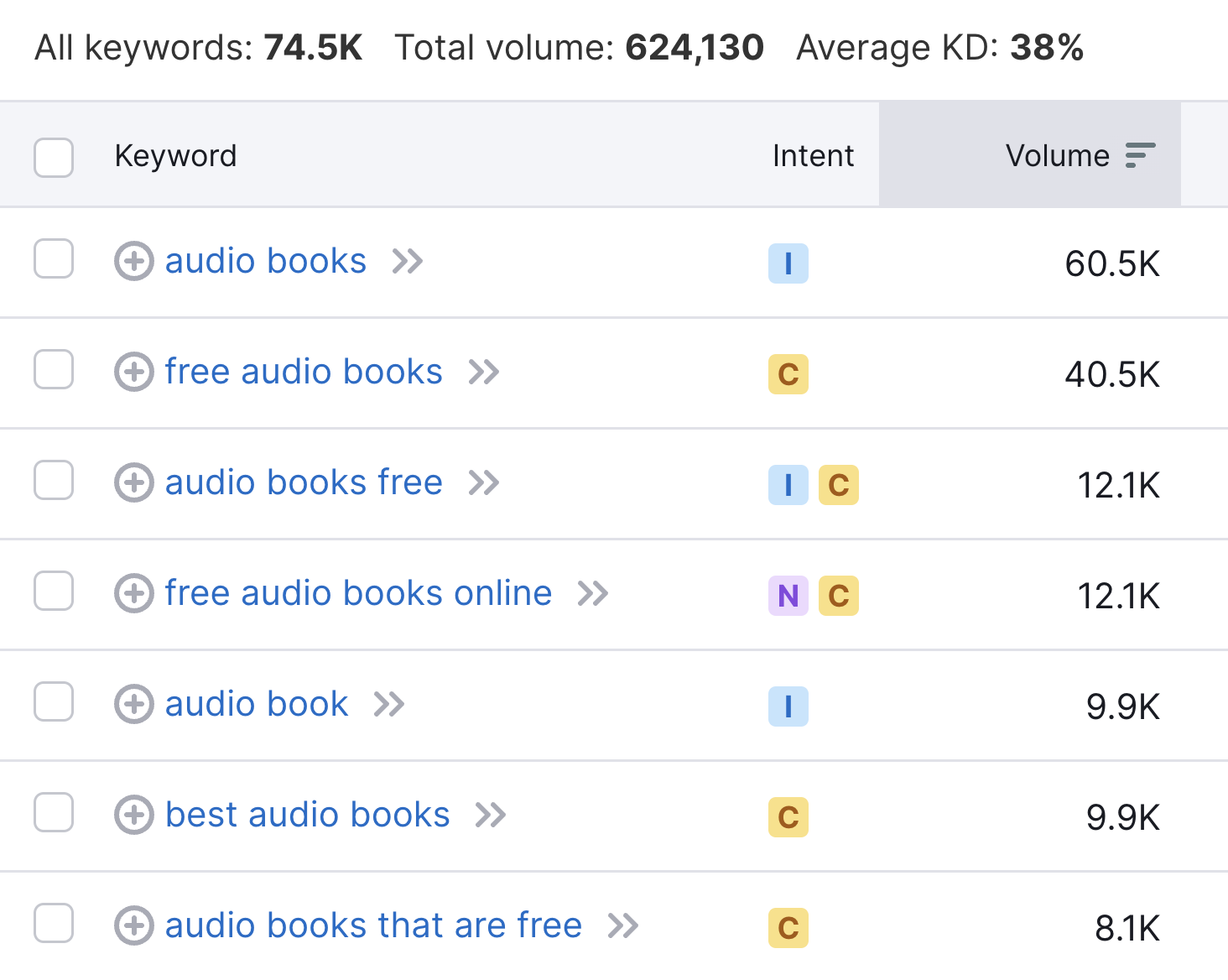
High-volume keywords can be attractive, but also check keyword difficulty (KD %). Higher KD % means tougher competition.
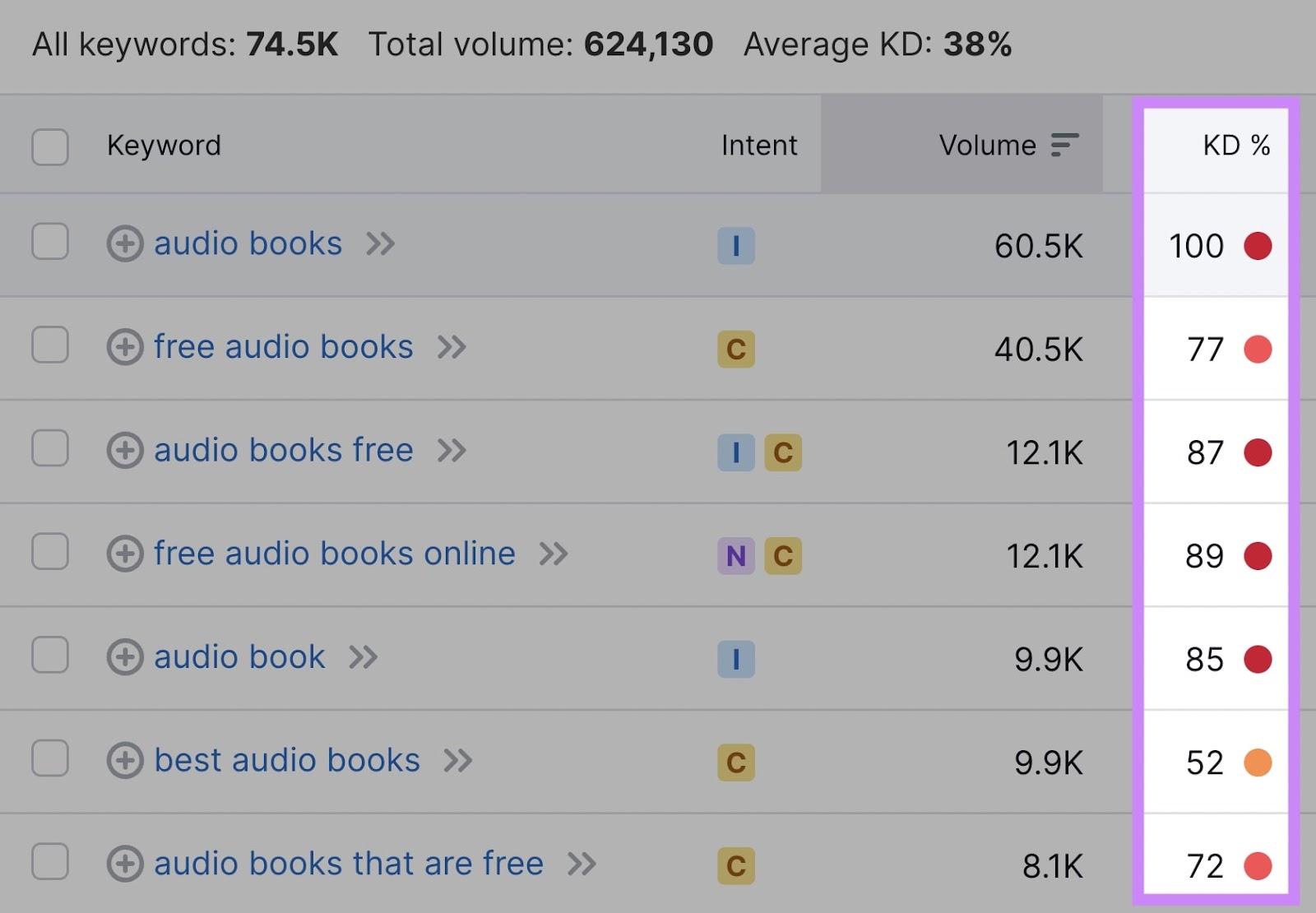
Also target less competitive long-tail keywords. They often have lower volume but are easier to rank for.
After selecting your keywords, create content that is detailed, helpful, and aligned with user intent. Offer unique insights to stand out from competitors.
- Include relevant keywords naturally (avoid keyword stuffing)
- Fully answer the query and offer real value
- Use visuals to enhance comprehension
Further reading: What Is Quality Content & How to Create It
2. Place Target Keywords Strategically
After choosing target keywords, place them in key areas:
- H1
- First paragraph
- Subheaders (H2, H3, etc.)
Google scans these sections to understand the page’s topic. Readers will also quickly see if your page meets their needs.
Analyze your content using the On Page SEO Checker.
Configure the tool for your site. It will show you whether your target keywords appear in important areas.
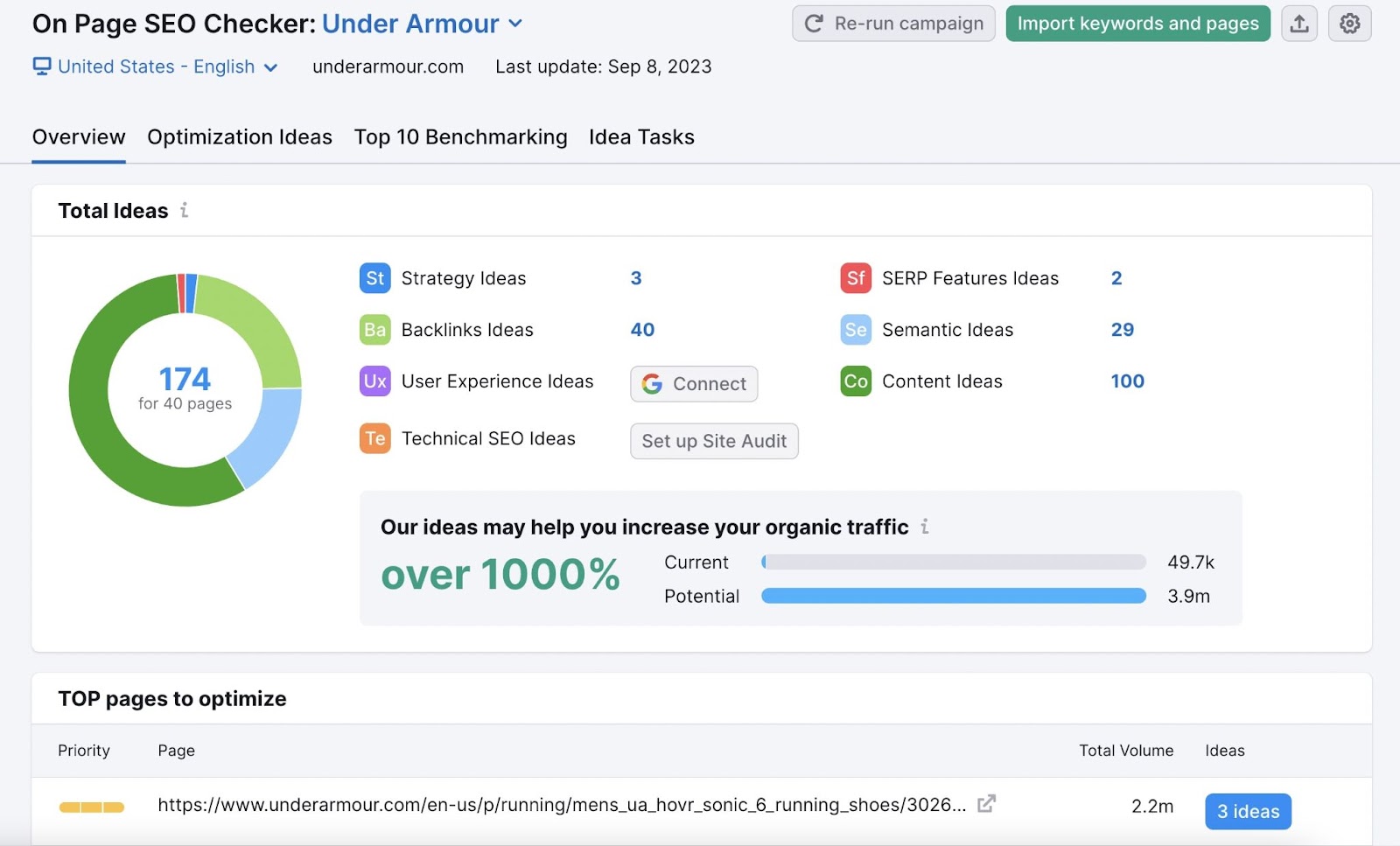
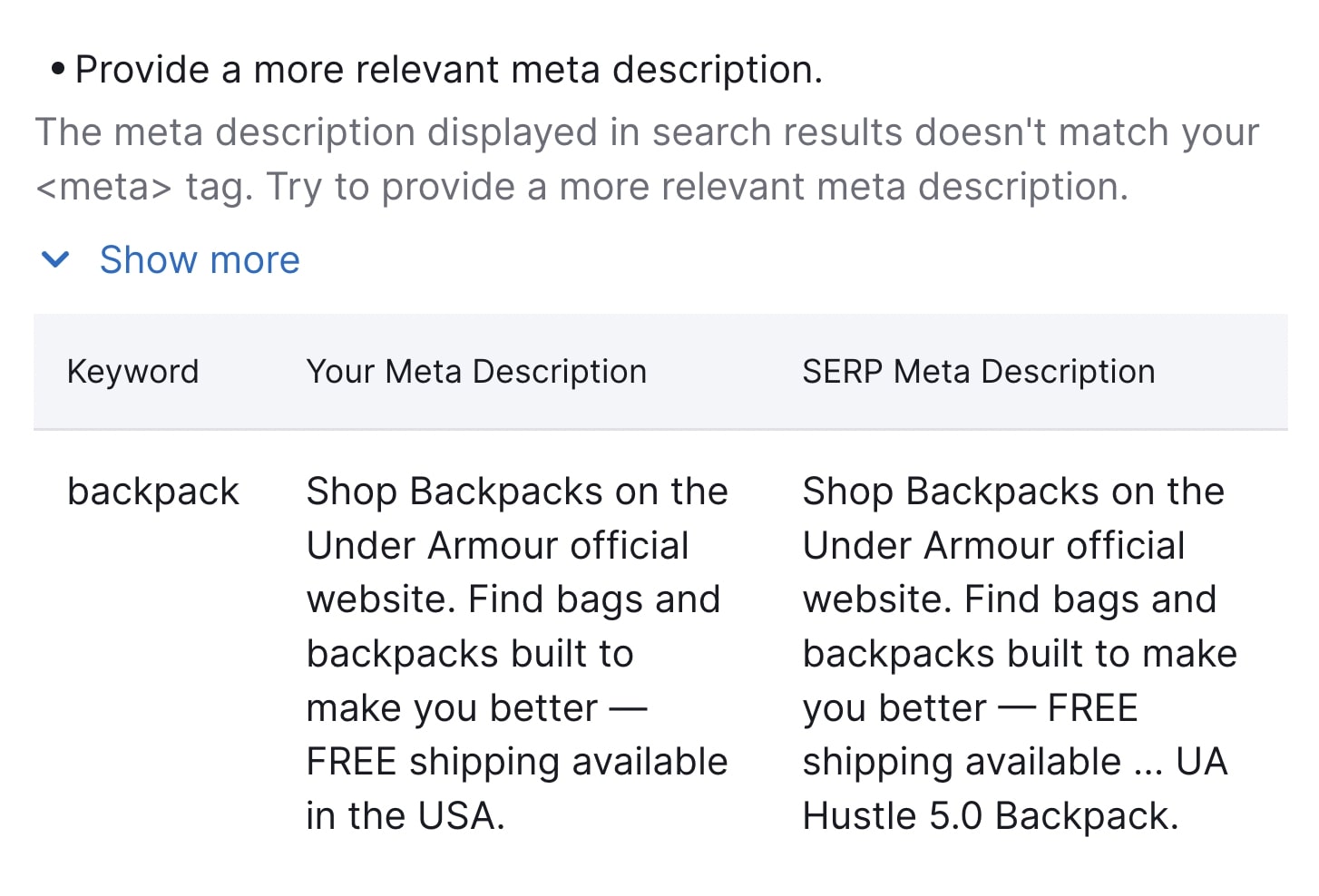
If the tool detects issues, it provides recommendations, like adding a more relevant meta description or refining your title.
It also suggests related keywords you can include.
3. Write Keyword-Rich Title Tags
Title tags are HTML elements that specify a page’s title. They appear in search results, browser tabs, and social media posts. Title tags can impact whether users click on your page.
They can look like this on the SERP (search engine results page):
Below are some best practices for title tags:
- Keep them between 50 and 60 characters so they don’t get cut off
- Include your target keyword for clarity
- Avoid duplicates so each page has a clear, unique purpose
On Page SEO Checker can also offer tips and explain why certain changes matter.
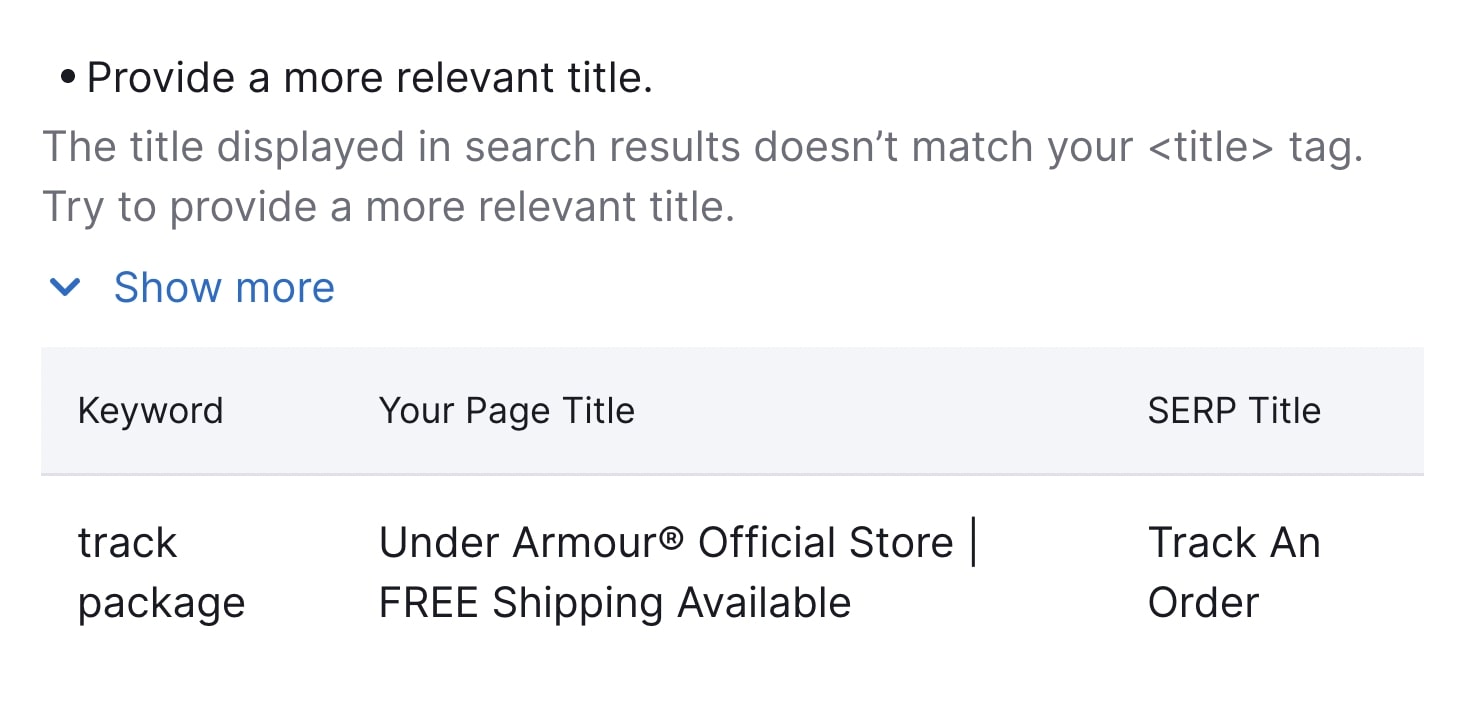
Further reading: What Is a Title Tag & How to Optimize Title Tags for Google
4. Write Click-Worthy Meta Descriptions
A meta description is an HTML element that provides a brief summary of a page. Search engines like Google may display your meta description as the descriptive snippet in search results. This snippet usually appears below your page’s title on the SERP.
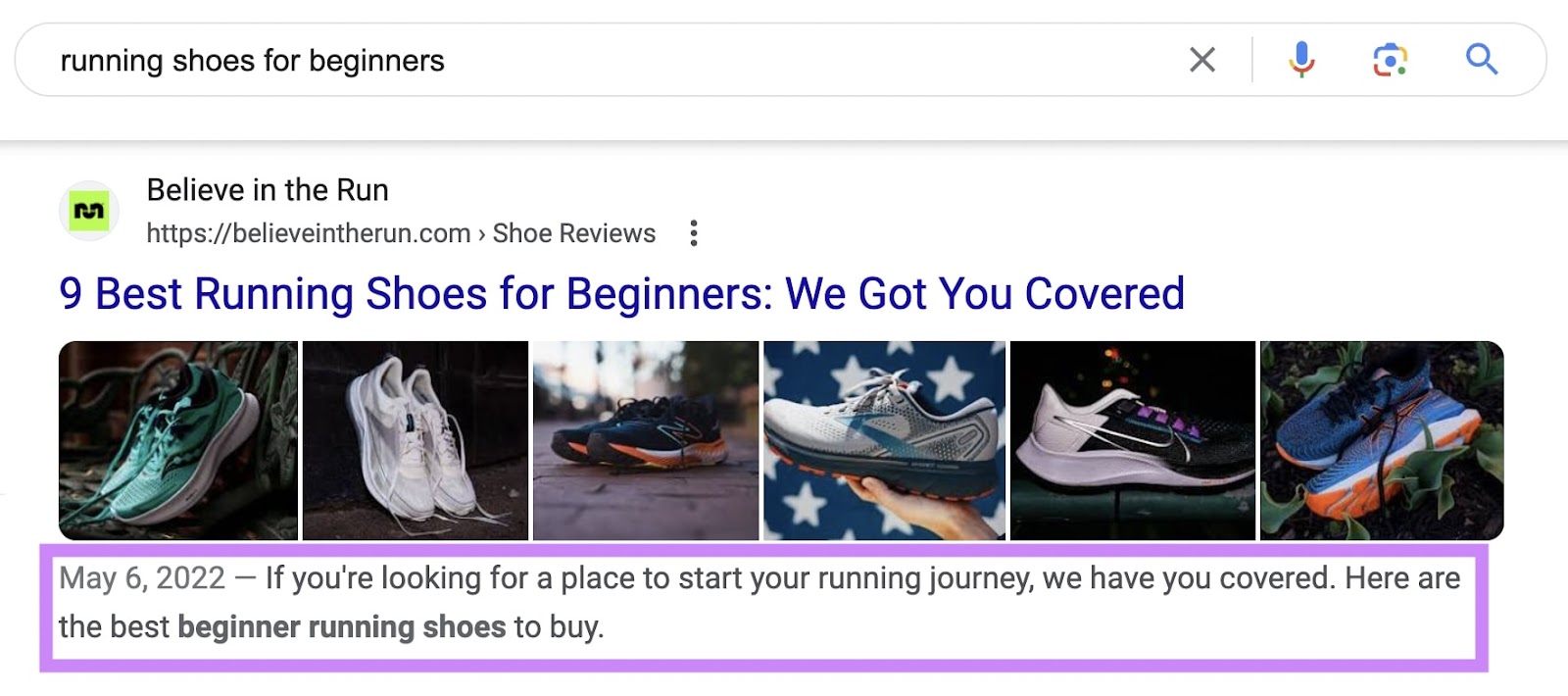
Meta descriptions don’t directly influence Google rankings. But, like title tags, they can influence whether users click on your page. If your meta description doesn’t match user intent or page content, Google may generate its own description.
Follow these best practices to increase the likelihood of Google using your chosen meta description:
- Consider mobile devices: Google truncates meta descriptions after about 120 characters on mobile. Keep them concise.
- Include your target keyword: This can help users see that your page matches their search intent. Google often bolds keywords (and synonyms) that match a user’s query.
- Use active voice: Active voice is more direct and saves space.
- Add a call to action (CTA): Encourage clicks with words like “try for free” or “find out more.”
You can also find meta description tips in On Page SEO Checker if you need more guidance.
Further reading: What Is a Meta Description? (+ SEO & Writing Tips)
5. Use Headings and Subheadings to Structure Your Page
Headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) help users skim your page. They also help Google understand your page’s hierarchy.
Compare a page without organized headings versus one that uses headings effectively. Well-structured headings make your page easier to read.
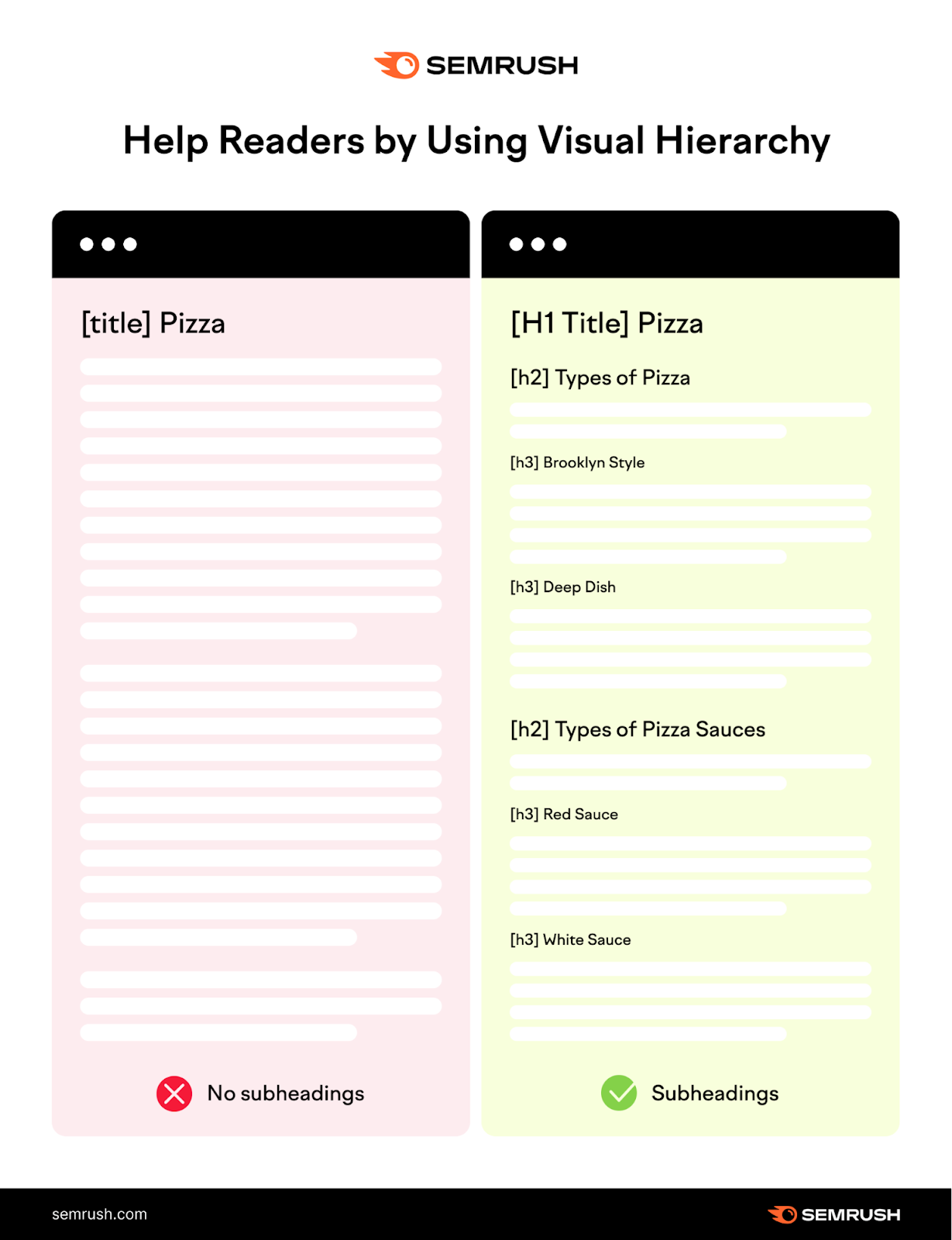
Headings also give Google context about the content on your page. This helps confirm whether your page is relevant for a user’s search.
- Use H1 for your page title or main headline.
- Use H2 for subtopics.
- Use H3 (and deeper headings) for detailed sections within those subtopics.
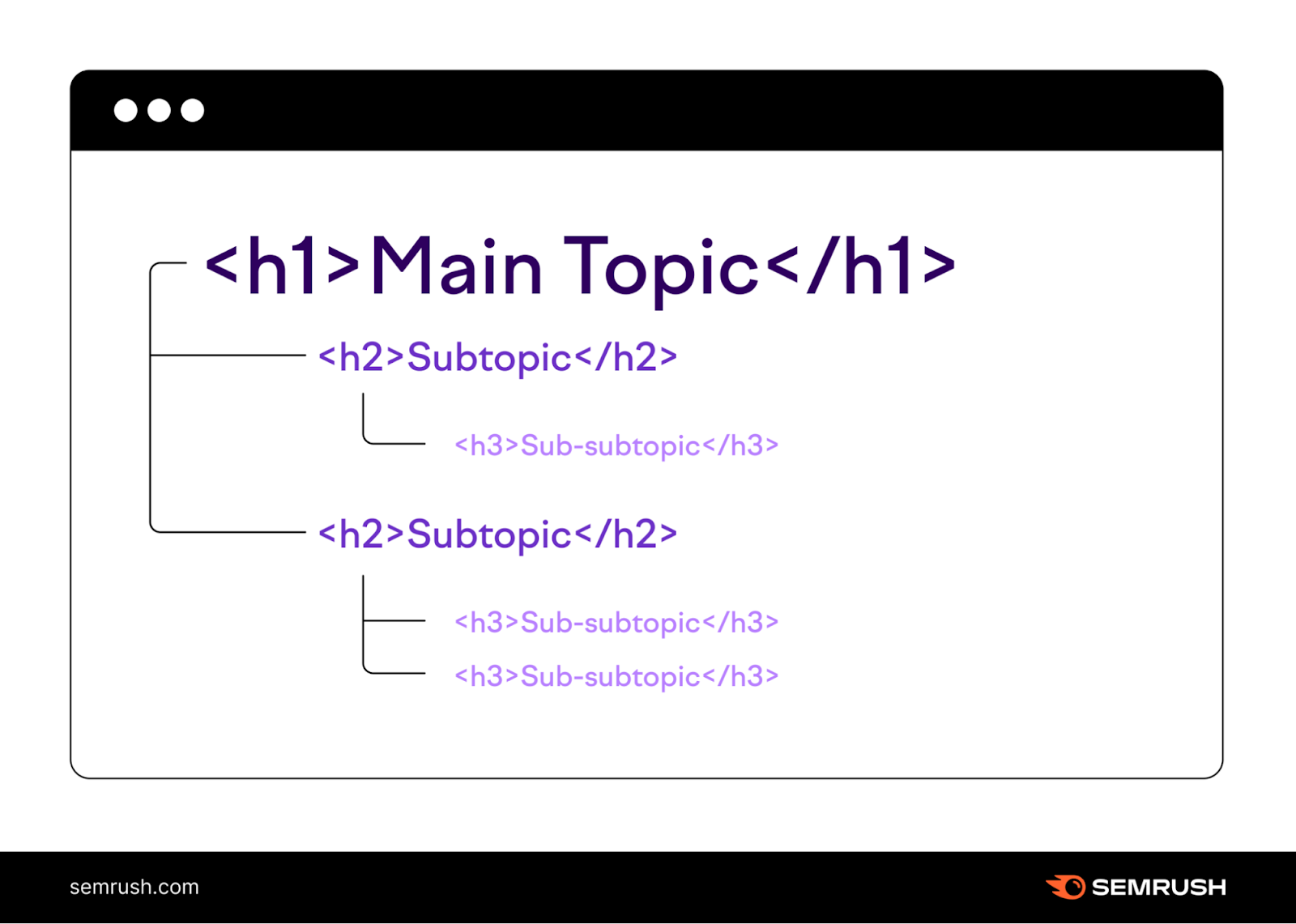
You can include target keywords in these headings to further clarify your content. On Page SEO Checker also provides heading optimization ideas.
6. Optimize URLs
Google advises using simple URLs that do not appear cryptic. This means using words that represent your page’s content. Avoid random numbers, publish dates, or unnecessary text in your URL.
Including your target keyword in your URL can help show Google (and users) what your page is about.
An “unfriendly” URL might look like this:

A more optimized URL could look like this:

Giving Google more context can help it match your page with relevant searches.
Further reading: What Is a URL? Meaning, Structure, and Optimization Tips
7. Strategically Add Internal Links
Internal links are hyperlinks that point to other pages on the same site. For example, a link might say “my favorite area to stay in” and send users to another page on your site.

Internal links are important for on-page SEO because:
- They help search engines understand your site’s structure
- They guide Google crawlers to discover and navigate new pages
- They signal that the linked page is valuable
- They help users move through your site (and stay longer)
Further reading: Internal Links: Ultimate Guide + Strategies
8. Add External Links to Authoritative Sources
External links lead users from your site to other sites. They improve user experience and can build trust with your audience. Google recommends adding links to authoritative external sources to provide value.
Follow these best practices for external linking:
- Only link to high-quality, relevant sources
- Use descriptive, natural anchor text so users know what to expect
- Balance link quantity and placement to avoid looking spammy
You can check for external link issues with Site Audit. Go to the “Issues” tab, type “external” in the search bar, and review any findings.

Further reading: What Is an External Link? + SEO Best Practices
9. Include and Optimize Images
Including images can help you rank in Google Images and drive more traffic. Start by writing descriptive alt text to explain your images to both search engines and users who rely on screen readers.

Here are some tips for writing good alt text:
- Keep it brief (125 characters or fewer)
- Include a target keyword naturally
- Skip alt text for purely decorative images
- Avoid phrases like “image of” or “picture of”
Use the “Issues” report in Site Audit to find missing or inadequate alt attributes.
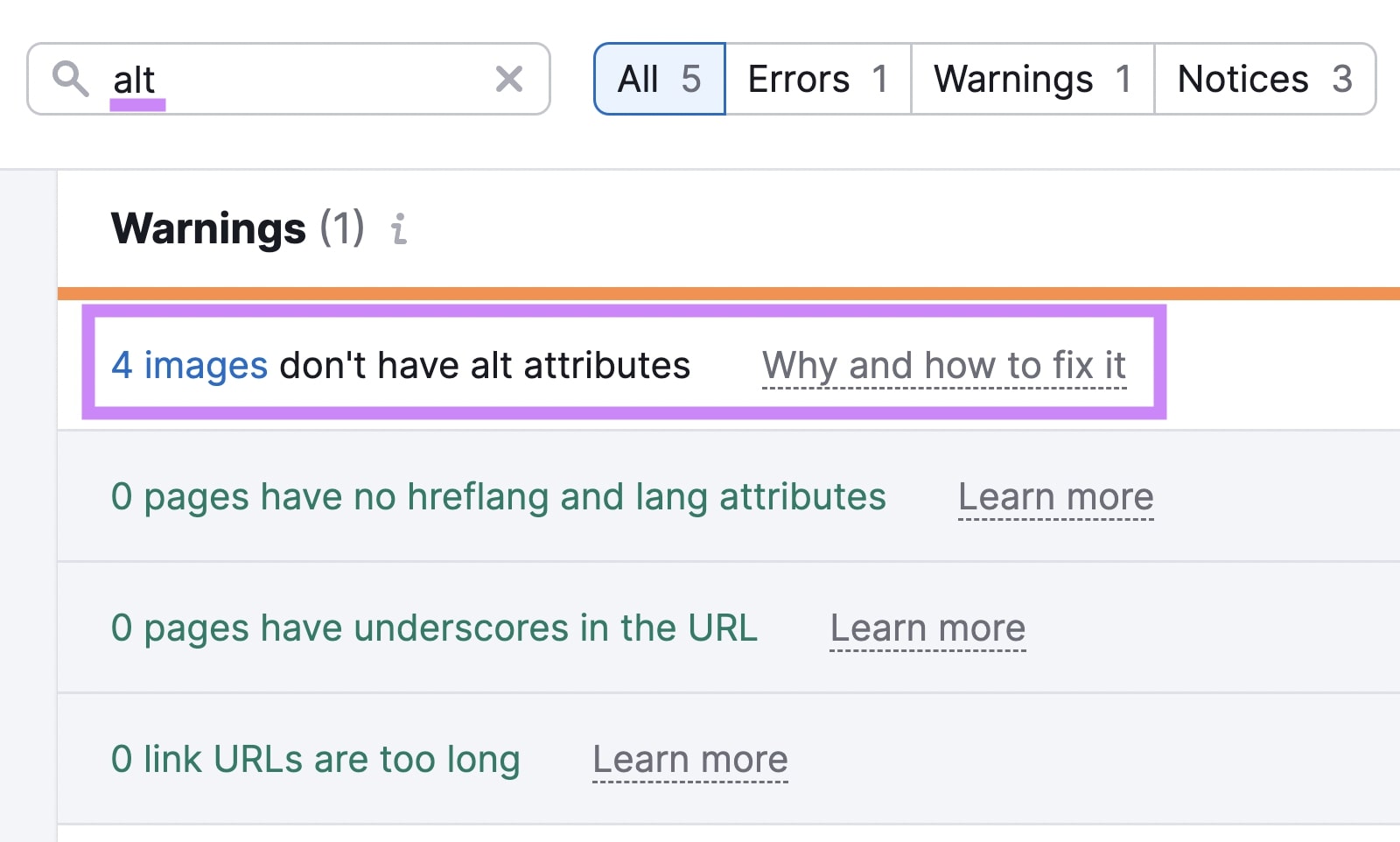
You can also optimize images by using descriptive file names, compressing file sizes for faster page speed, and enabling lazy loading (so images load only when they appear in the user’s viewport).
Further reading: Image SEO and Alt Tags: 10 Image Optimization Tips
Advanced On-Page SEO Tactics
After mastering on-site SEO basics, try these advanced page optimization techniques.
Optimize for Page Speed
Page speed is a confirmed Google ranking factor. You can measure page speed with Google’s free PageSpeed Insights tool, which provides an overall performance score for mobile and desktop. This tool also lists ways to improve page speed.
PageSpeed Insights assesses Core Web Vitals, the signals that affect page experience:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Time for the main content to load
- First Input Delay (FID): Time until the site responds to a user’s first interaction
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Degree to which a webpage shifts while loading
To begin, enter your URL and click “Analyze.”

The results show errors slowing your site and “Opportunities” to fix them.

For deeper technical analysis, open Site Audit. Find Core Web Vitals under Thematic Reports. This report shows metrics like LCP, TBT (Total Blocking Time, a close estimate of FID), and CLS. It also provides recommended improvements and pages affected.
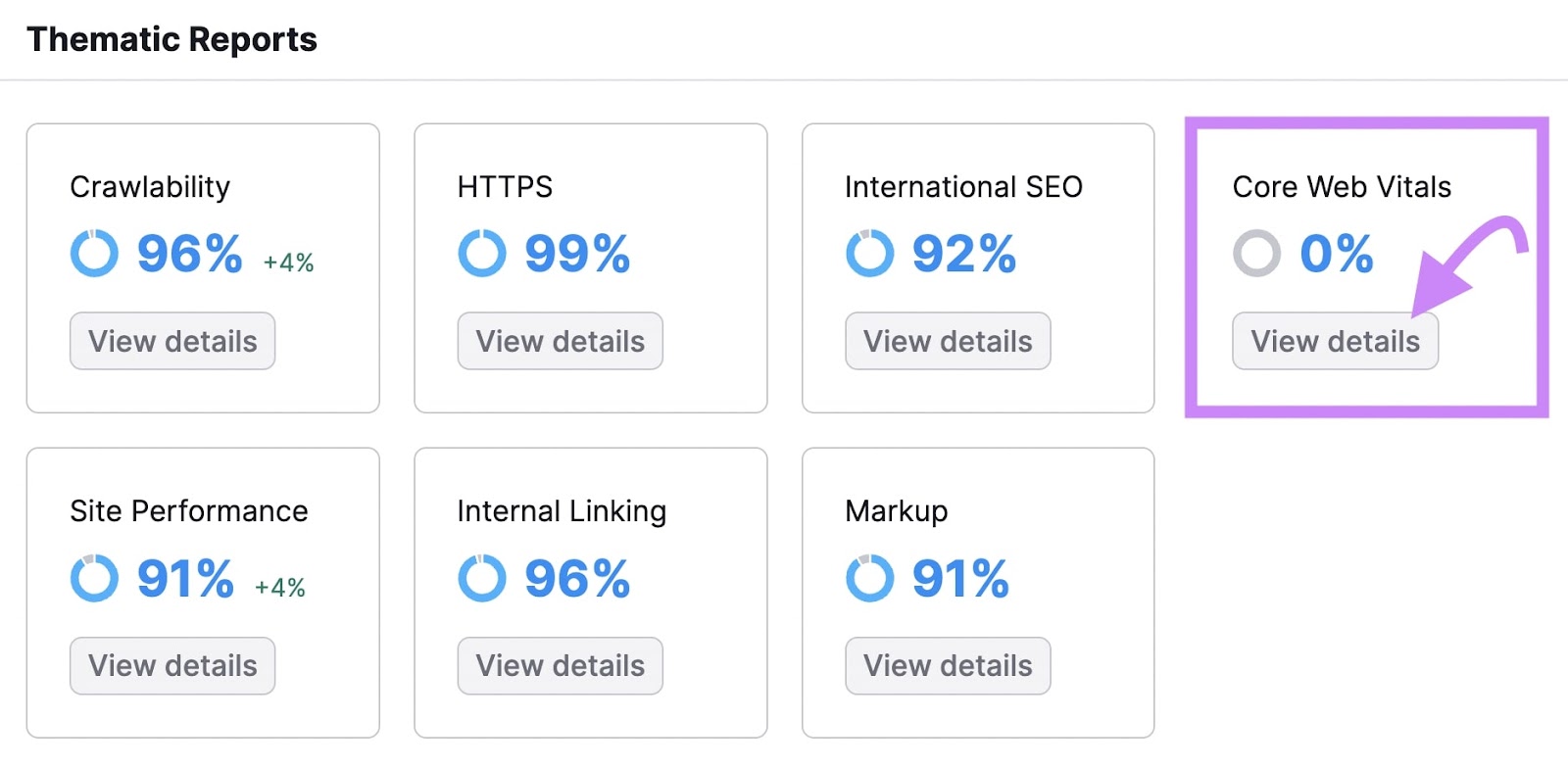
Run this report monthly to stay on top of errors. You can also set up automated reports in My Reports.
Target Featured Snippets
Featured snippets often appear at the top of a SERP (sometimes called “position zero”). Winning a featured snippet can boost click-through rate (CTR).

Common featured snippet formats include:
- Definitions
- Tables
- Lists
- Videos
Check if a keyword has a featured snippet in Keyword Overview. Enter your keyword, click “Search,” then scroll to the SERP Analysis section.
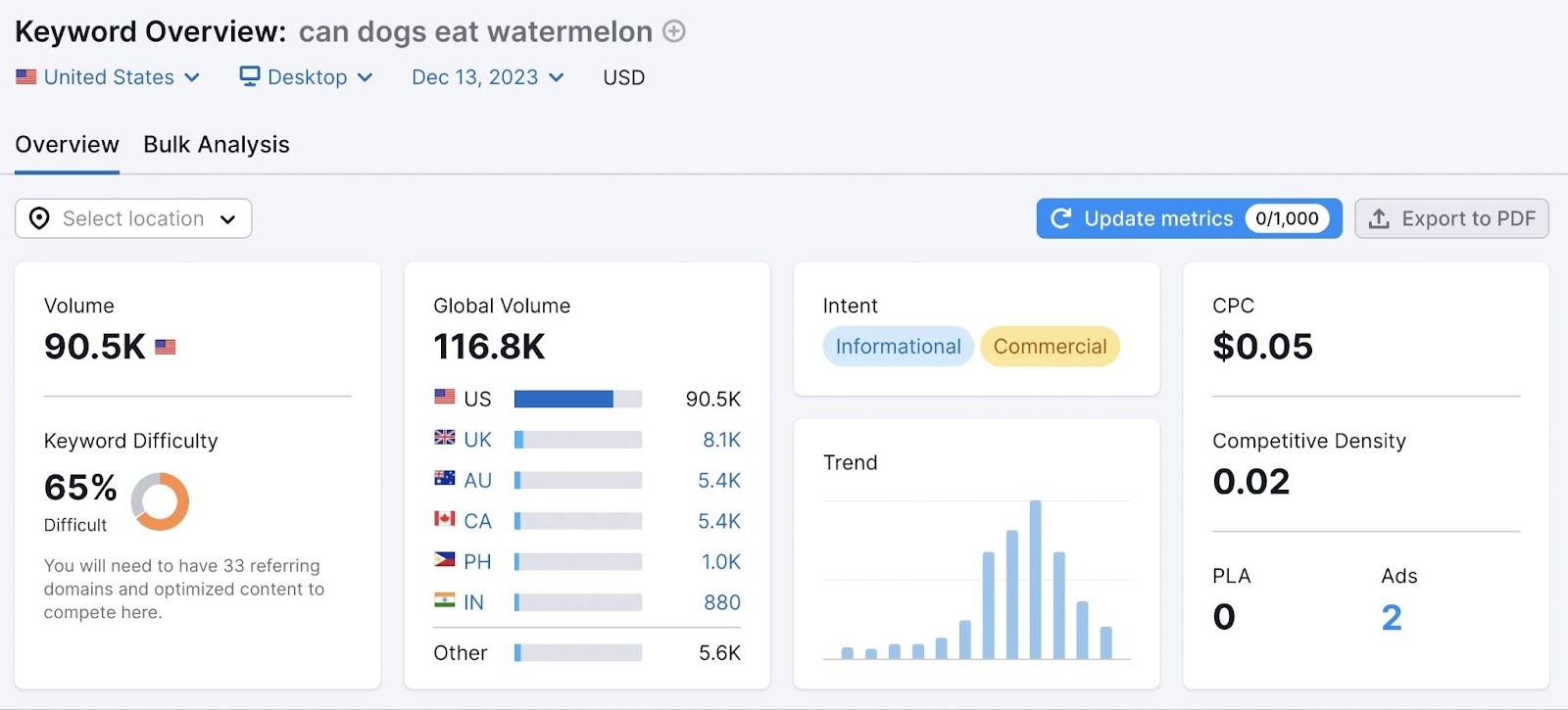
Click “View SERP” to see if a featured snippet exists. If so, optimize your page for that snippet by:
- Providing a concise answer
- Matching user intent
- Formatting the answer effectively (e.g., brief paragraph, list, table)
Add Schema Markup
Schema markup (structured data) helps search engines better understand your page. Schema markup can yield rich snippets in SERPs, which display extra information (e.g., star ratings, event dates).
Common schema types include:
- Reviews
- Products
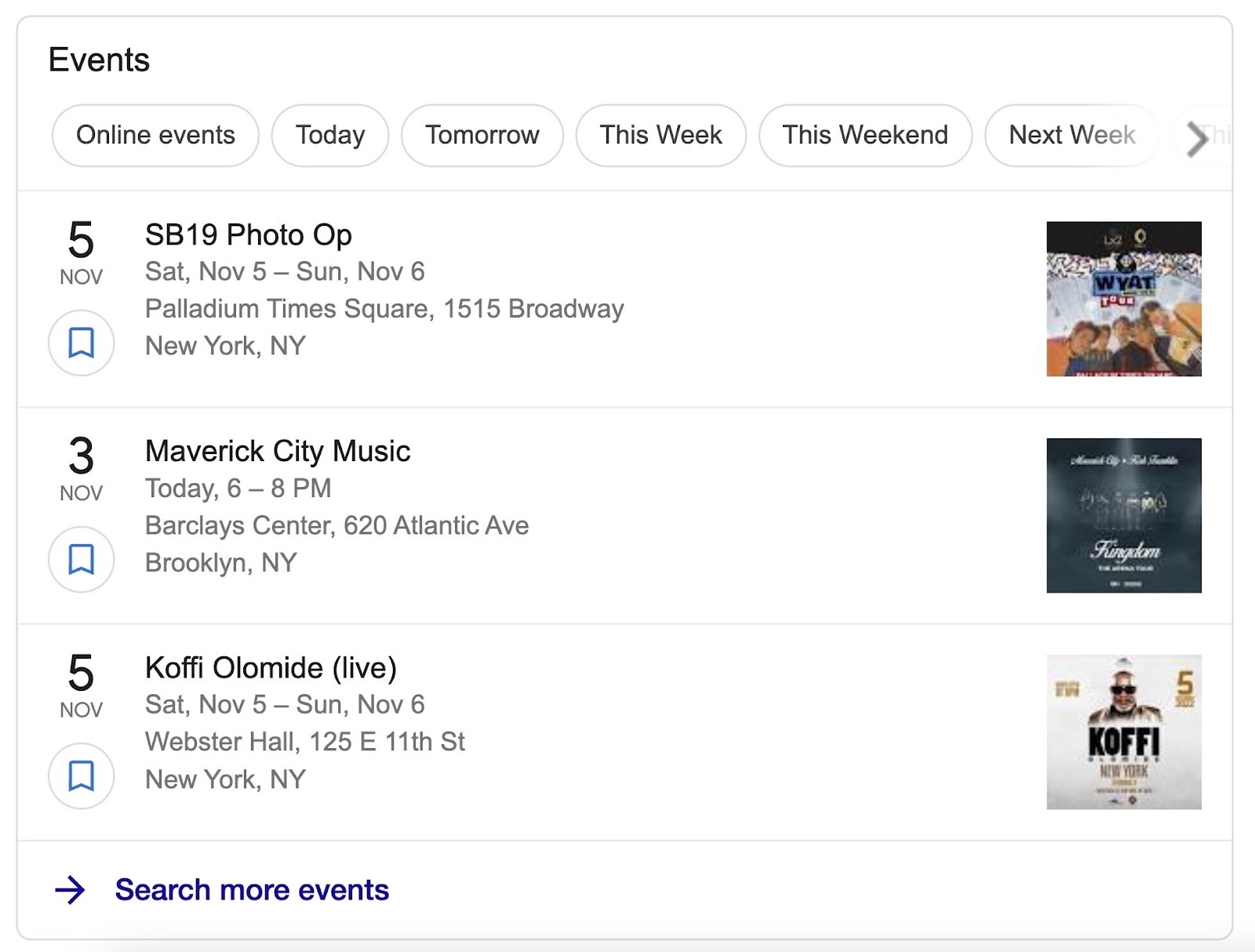
- Events
- Local businesses
For example, “Event” schema can help your listings appear in an “Events” box above regular search results.
Learn about each schema type atSchema.org.
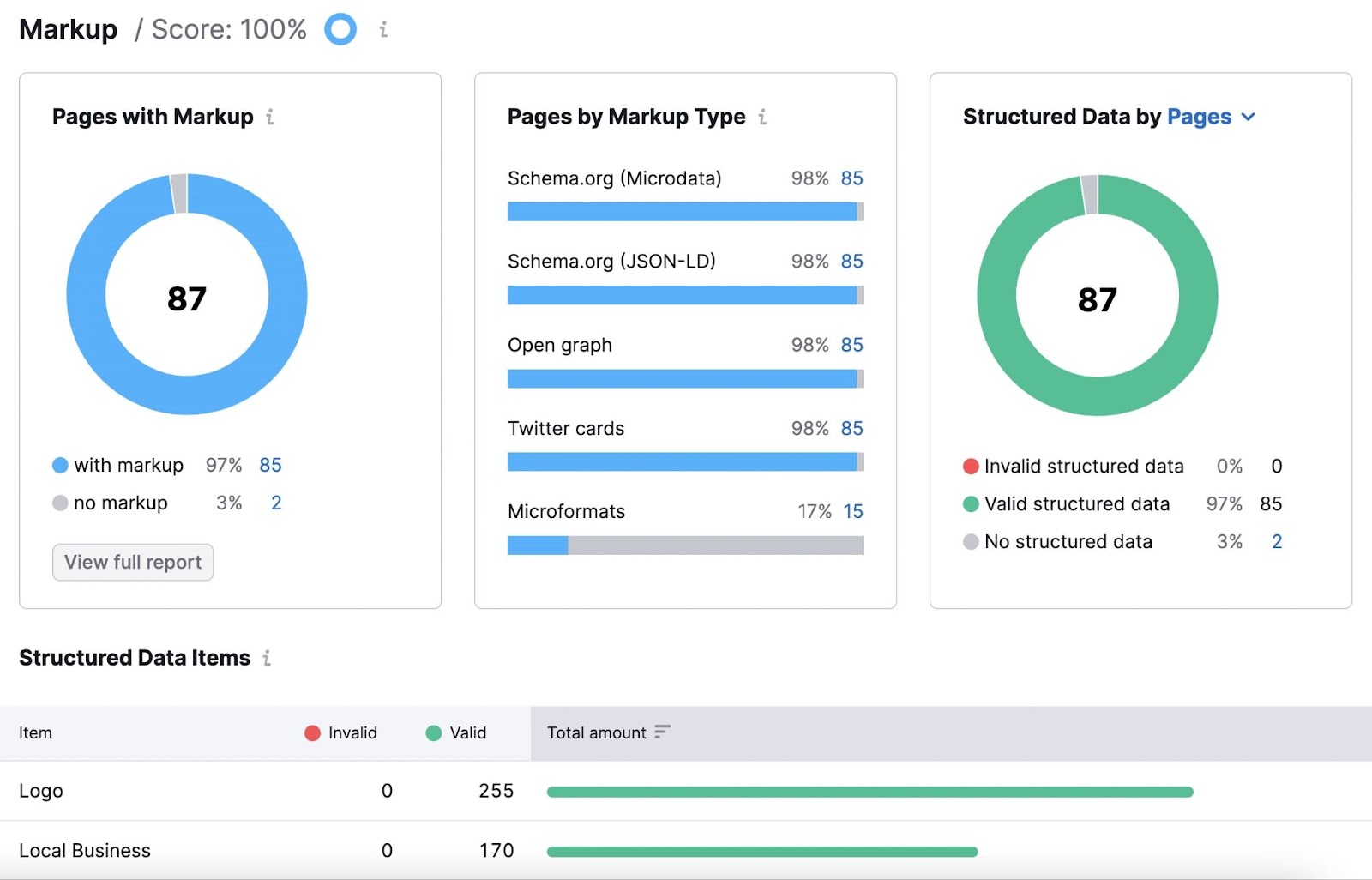
Use Site Audit to check schema implementation. The Markup report highlights pages that contain structured data and flags issues. If problems appear, run the specific URL through Schema.org’s markup validator for further guidance.
Further reading: What Is Schema Markup & How to Implement Structured Data
Implement Proven On-Page SEO Techniques
Now you know advanced on-page SEO tactics. Put them into practice to enhance your rankings and drive more traffic.
Get started with a free Semrush account (no credit card required). You’ll gain access to On Page SEO Checker and other powerful features to:
- Conduct keyword research
- Analyze competitors
- Track keyword rankings
- Audit your site
Following these steps helps your site deliver faster load times, better user experiences, and more compelling SERP displays.
