What Is a Target Audience?
A target audience is a group of people that products, services, or marketing efforts are aimed toward, typically defined by traits like age, gender, income, interests, challenges, and goals. Targeting the right audiences can help you reduce costs and increase conversions.
For example, a target audience for a high-end fashion brand might be affluent women between the ages 30 and 45 who are interested in luxury goods.
We’ll talk more about how to find your target audience later. But if you want to jump straight in, use Semrush’s One2Target tool.
Enter up to five rival domains. (Or click “Create List” and enter up to 100.) And the tool will gather information about their audiences’ demographics, socioeconomics, and behavior.
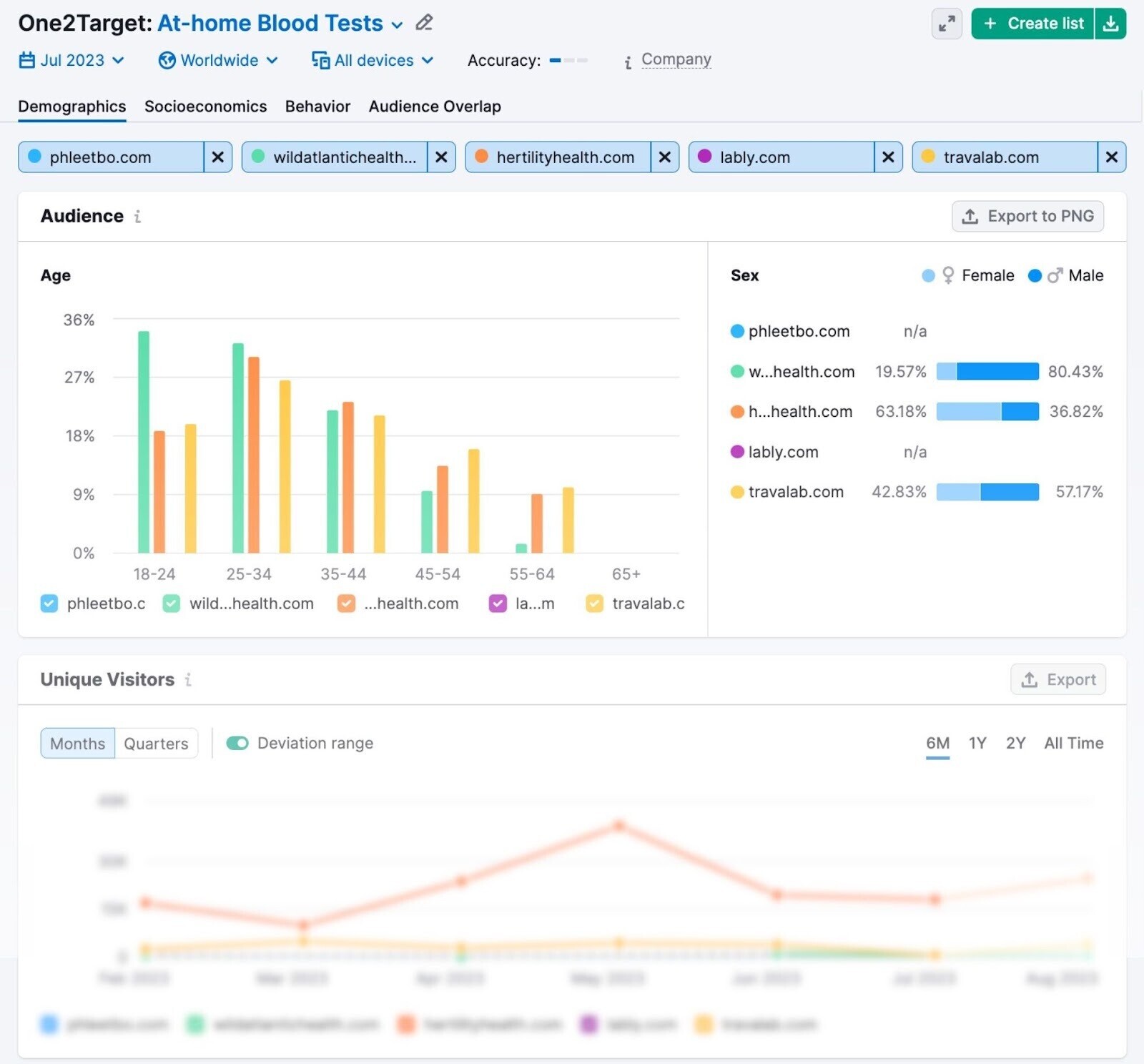
You can use this data to create more effective marketing materials and campaigns.
Next, let’s see how the target audience definition differs from target market and buyer persona definitions.
Target Audience vs. Target Market
A target market is the entire group of people who might be interested in your products or services. This means the target audience is a subset of the target market.
For example, the target market for a high-end fashion brand might include not only the affluent women in the target audience, but also the friends and family members who may purchase gifts for them.
Tip: If you want to know how to find your target market, check out our market research guide. Or jump straight in with Semrush’s Market Explorer tool.
Target Audience vs. Buyer Persona
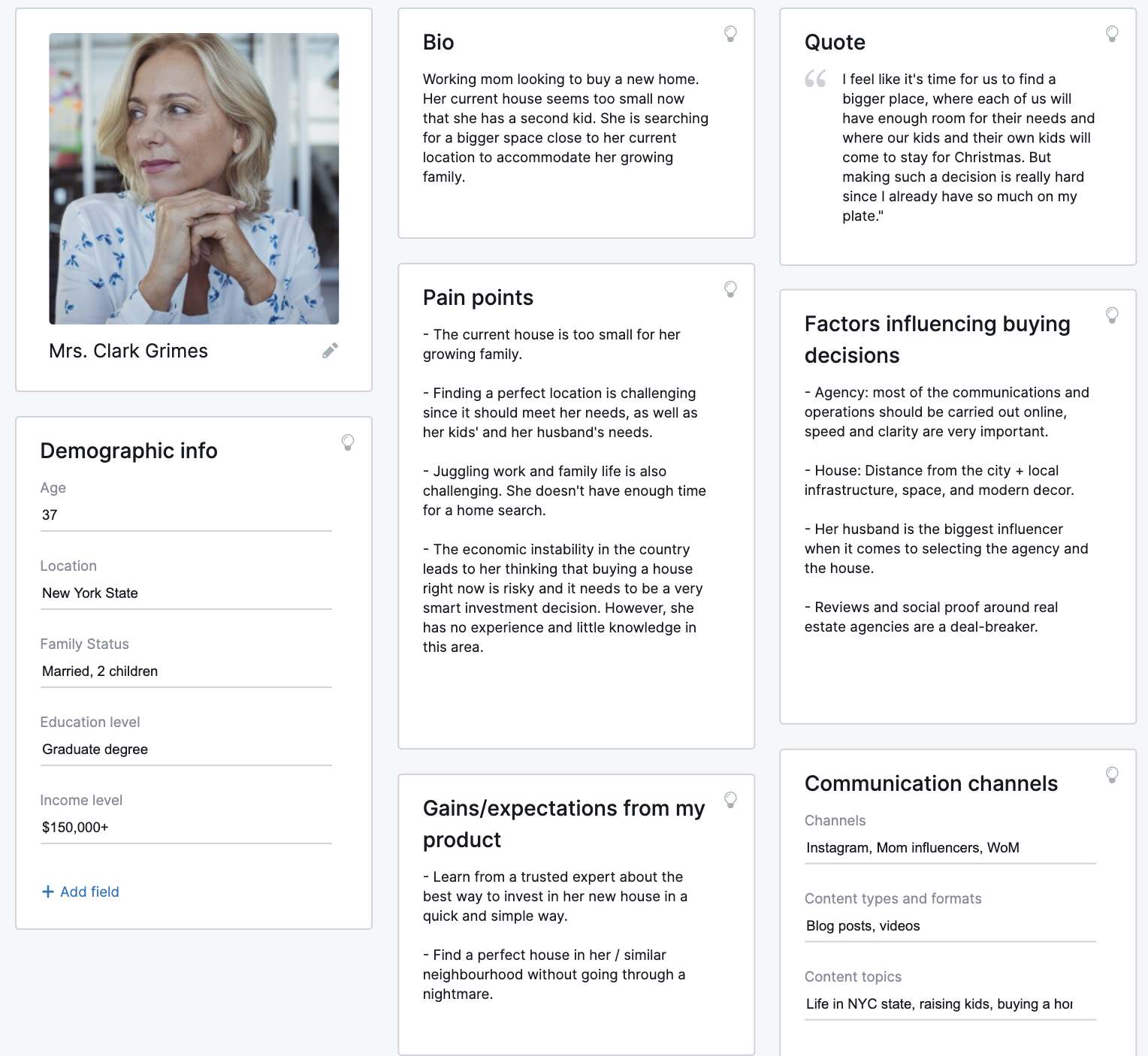
A buyer persona is a profile that represents an archetypal member of a target audience. It should provide a detailed idea of who you’re addressing. To help you engage them effectively.
For example, here’s a persona built with the Semrush Persona tool:
Why You Should Find Your Target Audience
Finding your target audience allows you to tailor your marketing strategies to the right people: People who are likely to buy your products or services. And therefore increase conversion rates.
Plus, advertising to a narrower audience tends to be cheaper.
Getting clarity on your target audience can benefit the following areas of your marketing and more:
- Copywriting: How should you describe your offers to attract and convert your target audience?
- Content marketing: What blog posts, videos, and podcasts should you create to attract your target audience?
- Email marketing: What specific messaging should you use in your email campaigns?
- Social media marketing: Which platforms are most important to be present and active on?
- Social media advertising: Which users should you target? What kind of content should you promote?
- Pay-per-click (PPC): Where should you spend your dollars? And what targeting options should you utilize?
- Search engine optimization (SEO): Which keywords do your target audiences use?
Researching and understanding your target audience profile is the first step of any marketing campaign.
Types of Target Audiences
Let’s look at some of the most useful types of target audiences. Marketing to these groups can help you achieve important goals and get better results.
| Target Audience Type | Description | Marketing Tips |
| Localized audience | People located in a particular area. This can be broad (e.g., a country) or narrow (e.g., a town). | |
| Early adopters | People who are willing to try new products or services as soon as they’re available. |
|
| Competitors’ customers | People who currently use a competing product or service. |
|
| Influencers | People who might influence your other target audiences (e.g., industry bloggers and podcasters). |
|
| Previous customers | People who have already purchased a product or service from your brand. |
|
Here are some other useful ways to define and segment your target market:
| Segmentation Type | Description |
| Demographics | Age group, gender, income level, household size, etc. These can all influence the audience’s needs, habits, and preferences. |
| Behavior | Find out where your audience spends time online so you can reach them there. And consider how lifestyle habits affect their buying decisions. |
| Interests | Understanding your target audiences’ interests can help you create marketing campaigns that resonate with their passions and motivations. |
| Purchase readiness | Where is the target audience in the marketing funnel? The earlier in the funnel they are, the less salesy your approach should be. |
| Values | Knowing how much your audience cares about price, quality, eco-friendliness, etc. helps you engage them effectively. |
| Goals | By knowing what your audience wants to achieve, you can tailor your messaging to appeal to their specific needs and aspirations. |
| Challenges | Understanding the pain points of your target audience can help you create messaging they relate to. |
| Knowledge level | How familiar is the target audience with your product or service? This will determine how much you need to educate them. |
Target Audience Examples
We’ve come up with some target audience examples for Spotify. To help you get a better sense of what a target audience is—and how it differs from a target market and buyer persona.
Target market: Listeners
- Target audience example: U.S. college students aged 18-23 who listen to music while studying
- Persona example: Sarah is an undergraduate engineering student with a tight budget. When she’s at the library, she listens to lo-fi beats in noise-canceling earphones to aid concentration. She sometimes listens through her Macbook instead of her iPhone.
- Marketing tactic ideas: Student discount promotions, landing pages for study playlists, App Store SEO
Target market: Content creators (musical artists and podcasters)
- Target audience example: Emerging artists with over 3,000 followers on Instagram and at least five tracks on Bandcamp
- Persona example: Luna Louise plays the guitar and uses digital audio workstations to produce electro-folk music. She plays at venues in her home state of Texas and wants to expand her audience, but she’s concerned about the streaming income model.
- Marketing examples: Spotify for Artists events, videos, blog posts
Target market: Advertisers
- Target audience example: Medium-sized businesses with a primarily Gen Z audience and an advertising budget of over $2,000 per month
- Persona example: Carla is the owner of the Eatwell Box, a subscription service containing organic snacks and superfoods. It’s aimed at health-conscious young professionals. She is struggling to achieve sales through Instagram advertising.
- Marketing examples: Spotify Advertising webinars, research reports, case studies
How to Find Your Target Audience
Let’s look at the research methods you can use to gather all the details about your target audience.
1. Research Competitor Audiences
You and your direct competitors often share the same target audience. Or at least a really similar one.
So getting insights about your competitors’ target audiences could help you define your own.
Semrush’s One2Target tool can help you uncover demographic, socioeconomic, and psychographic data.
Let’s use Ikea as an example to see what we can learn about their audience.
Open the tool, enter the domain, and hit “Analyze.”
You’ll get a complete overview of your competitor’s target audience.
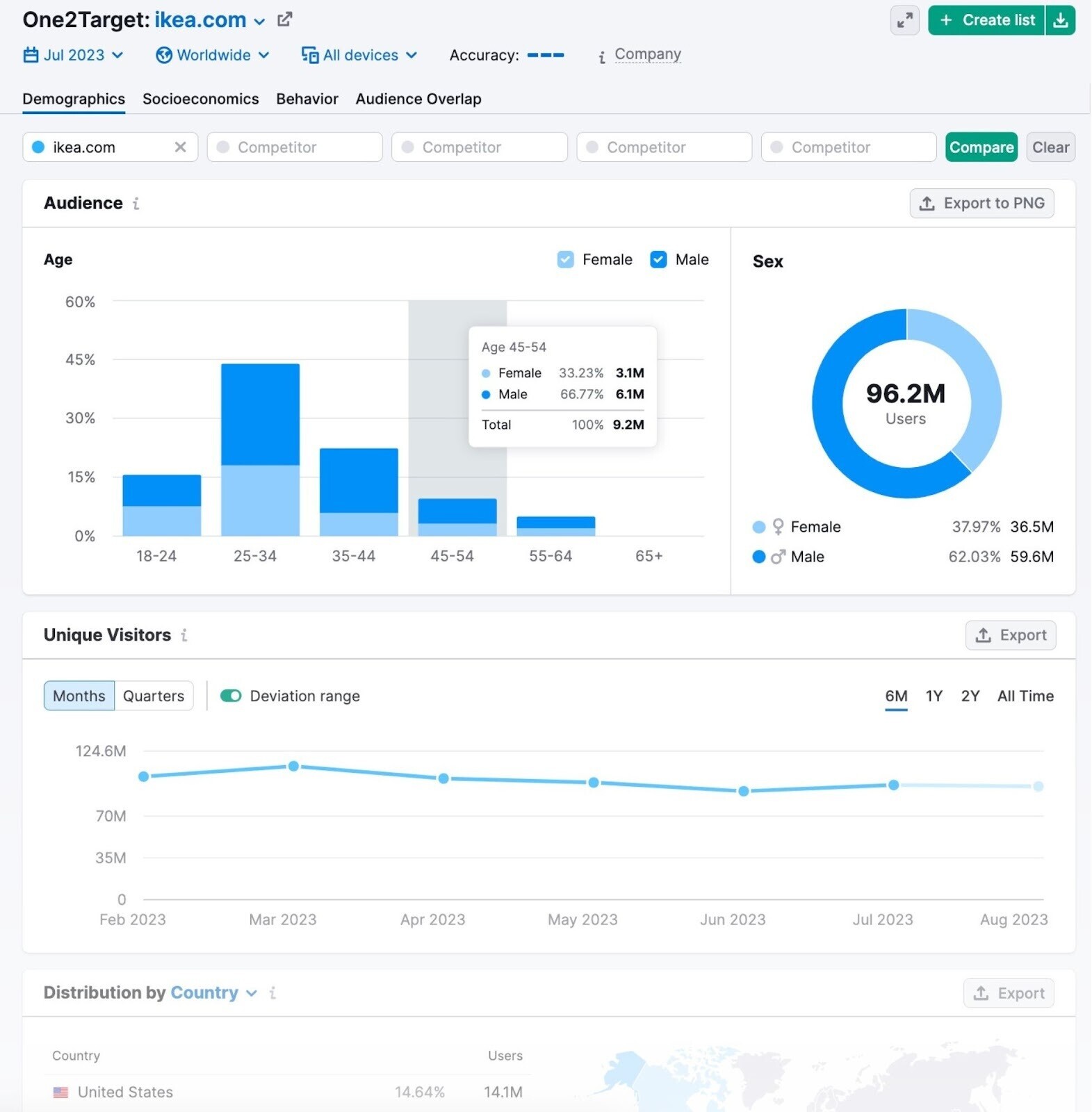
In the “Demographics” tab, you’ll find a breakdown of their audience by age, sex, and country.
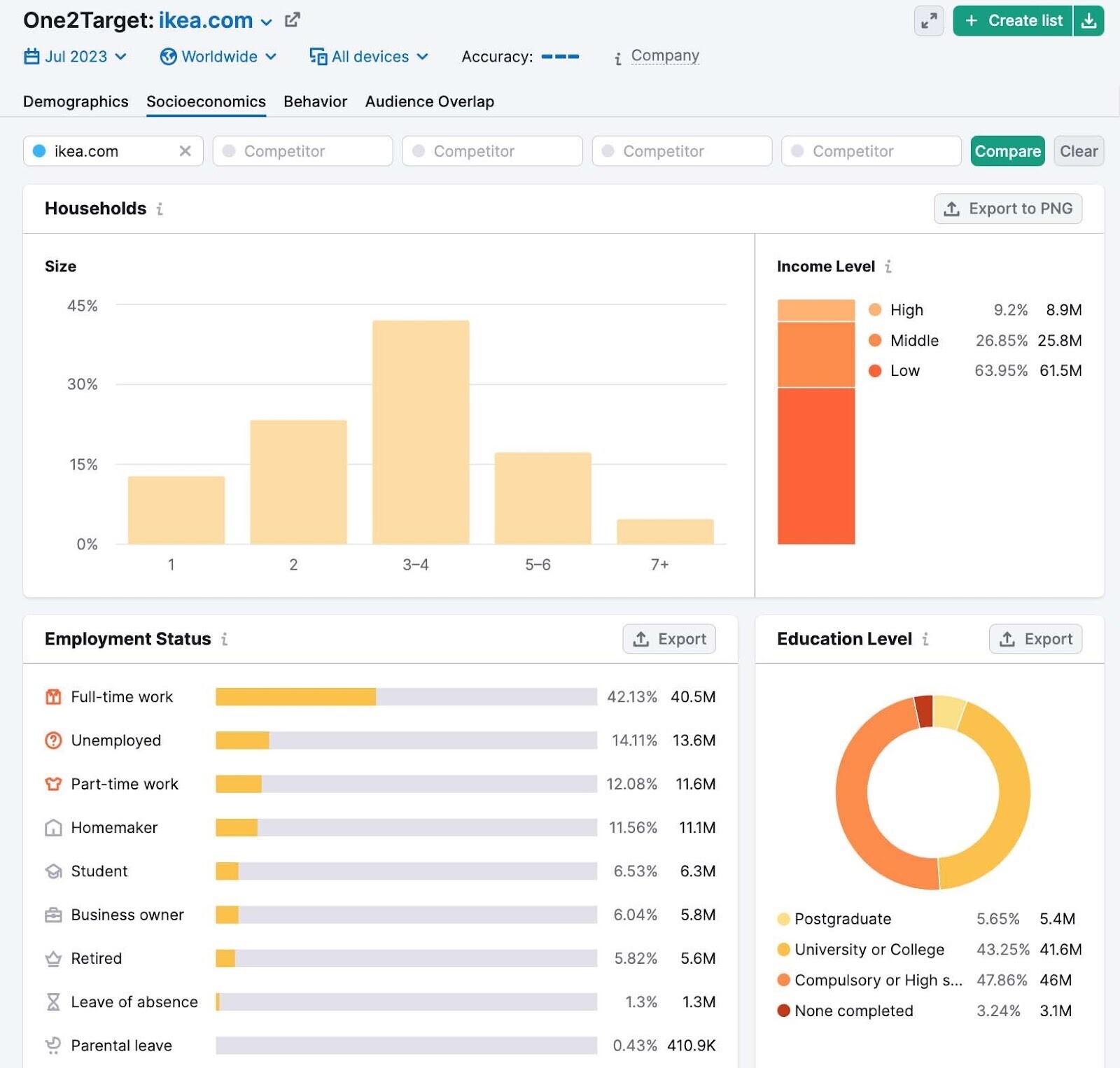
In the “Socioeconomics” tab, you’ll find their audience’s household size, household income, employment status, and education level.
In the “Behavior” tab, learn about their audience’s interests, device types, and most-used social media platforms:

Looking at the data, here are some key insights we can derive from Ikea’s target audience example:
- The majority of Ikea’s audience is male
- Most of the audience falls into the 25-34 age bracket
- The majority of Ikea’s audience works full-time and has low household income
- 43.25% of the audience has a university or college education
- Ikea’s audience is mostly on mobile and is interested in online services and mass media
- Ikea’s audience uses YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram as their primary social media platforms
This audience information can help you compete with Ikea.
Want to learn more? Read our audience research 101 guide.
2. Analyze Internal Data
Use your internal analytics data to get a detailed understanding of your target audience.
The best thing about using internal data is that it's real user data. So you’re not making any assumptions.
Consider the following internal data sources for analysis:
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Past campaign performance
As an example, let’s use GA4 to understand audience demographics.
Navigate to “Reports” > “User” > “User Attributes” > “Overview.”
You’ll see a breakdown of your website’s audience by country, city, gender, interests, age, and language.
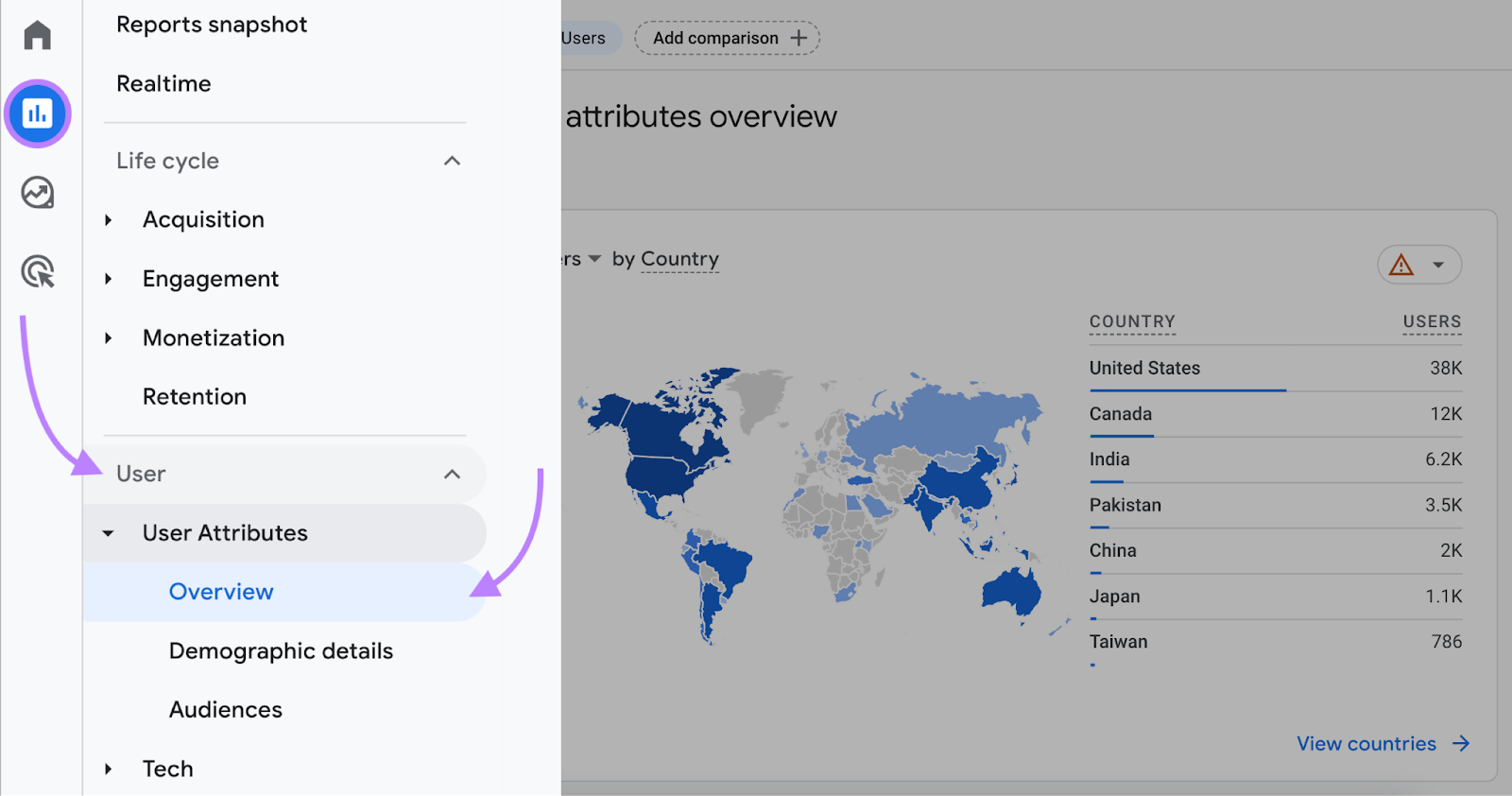
Review the data and feed it into your audience profile.
3. Collect Social Media Analytics
Many social media platforms have analytics built in. Allowing you to learn about your followers’ demographics.
Since these people are interested in your social media content, it’s likely that they’re also interested in your products and services. So it pays to learn about them.
With Semrush’s Social Analytics tool (part of the Social Media Toolkit), you can view Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn data in one place.
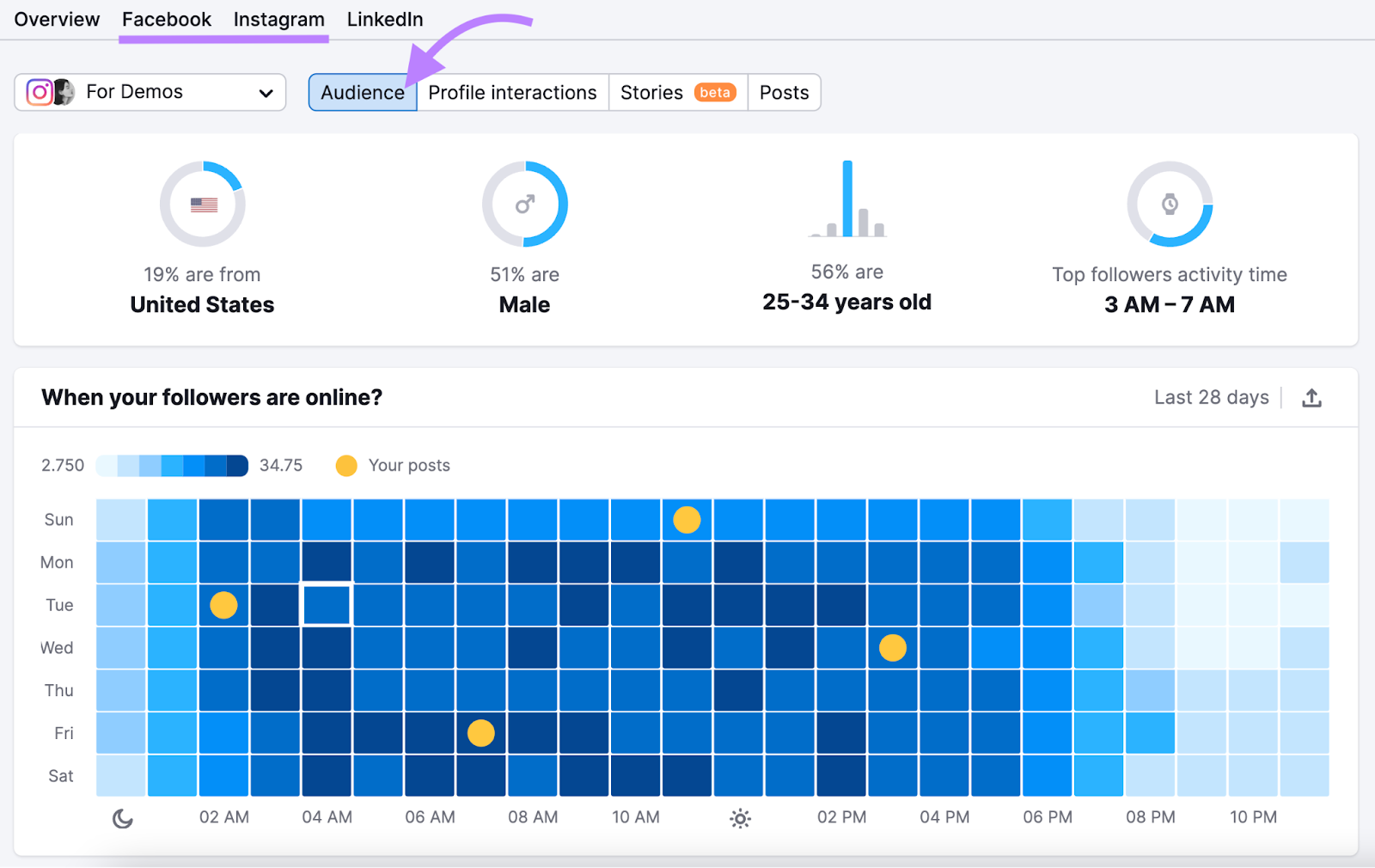
In the Facebook and Instagram reports, use the “Audience” tab to see:
- When your followers are online (which can help you understand their lifestyle)
- Where your followers are located
- A gender breakdown
- An age breakdown
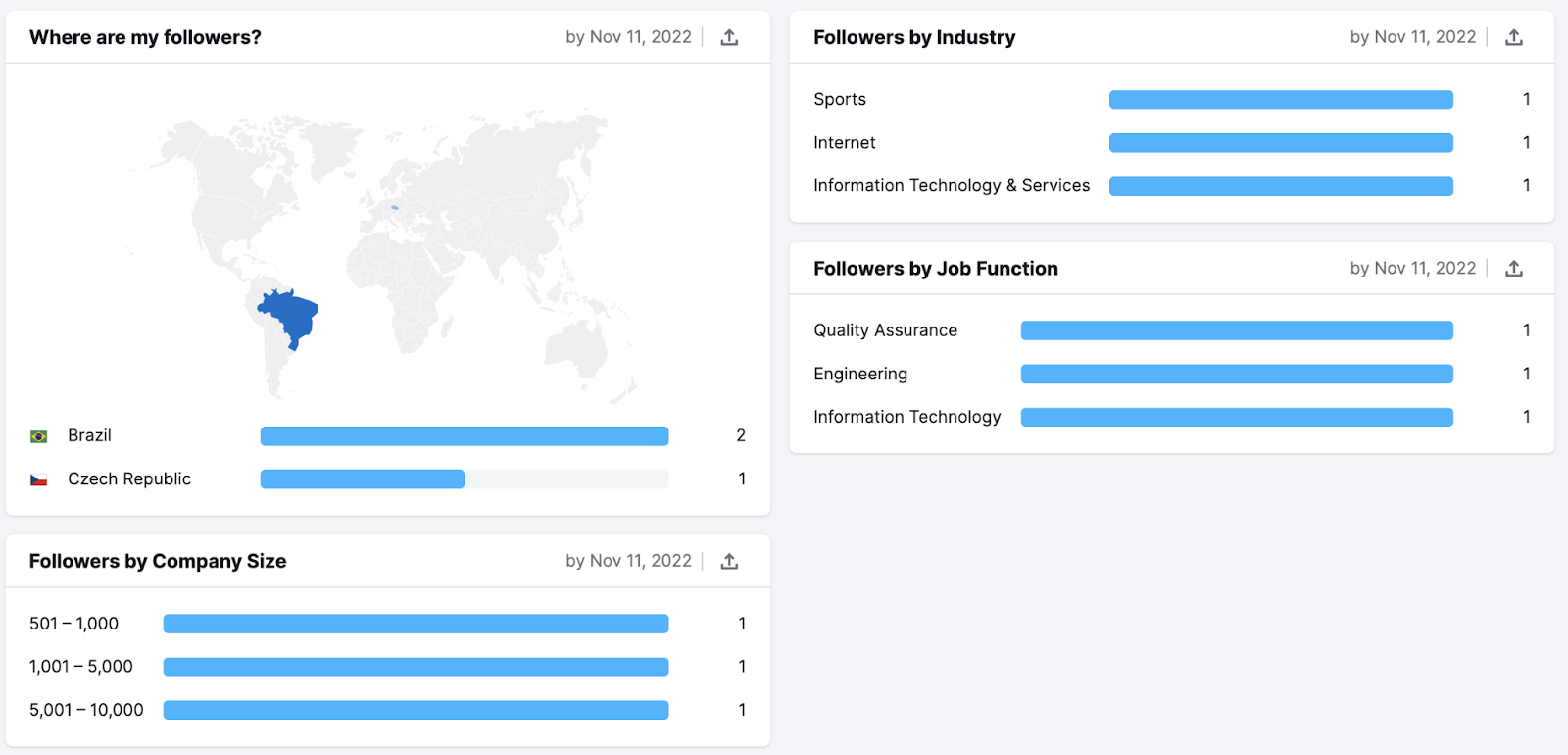
The LinkedIn audience report provides valuable data for B2B marketing:
- Where your followers are located
- Followers by industry
- Followers by job function
- Followers by company size
To get valuable insights into your X (formerly Twitter) followers, use the Audience Intelligence app.
After entering your handle, you’ll see an overview of demographics data, top brands, top influencers, top content sources, and audience segments.
First, head to the “Segments” report.
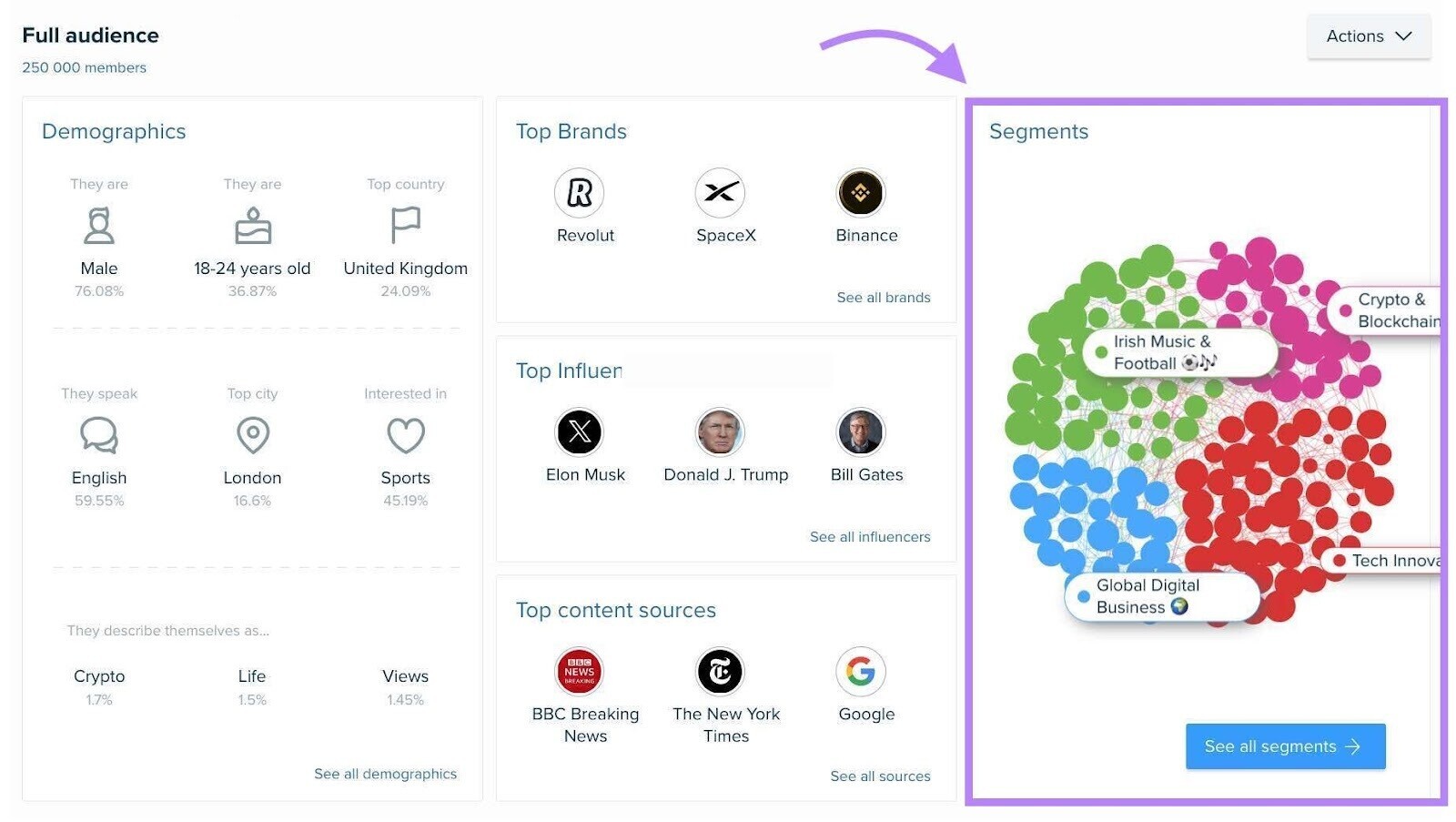
Here, you’ll discover the most prominent communities in your audience.
Click any segment to explore data in depth.
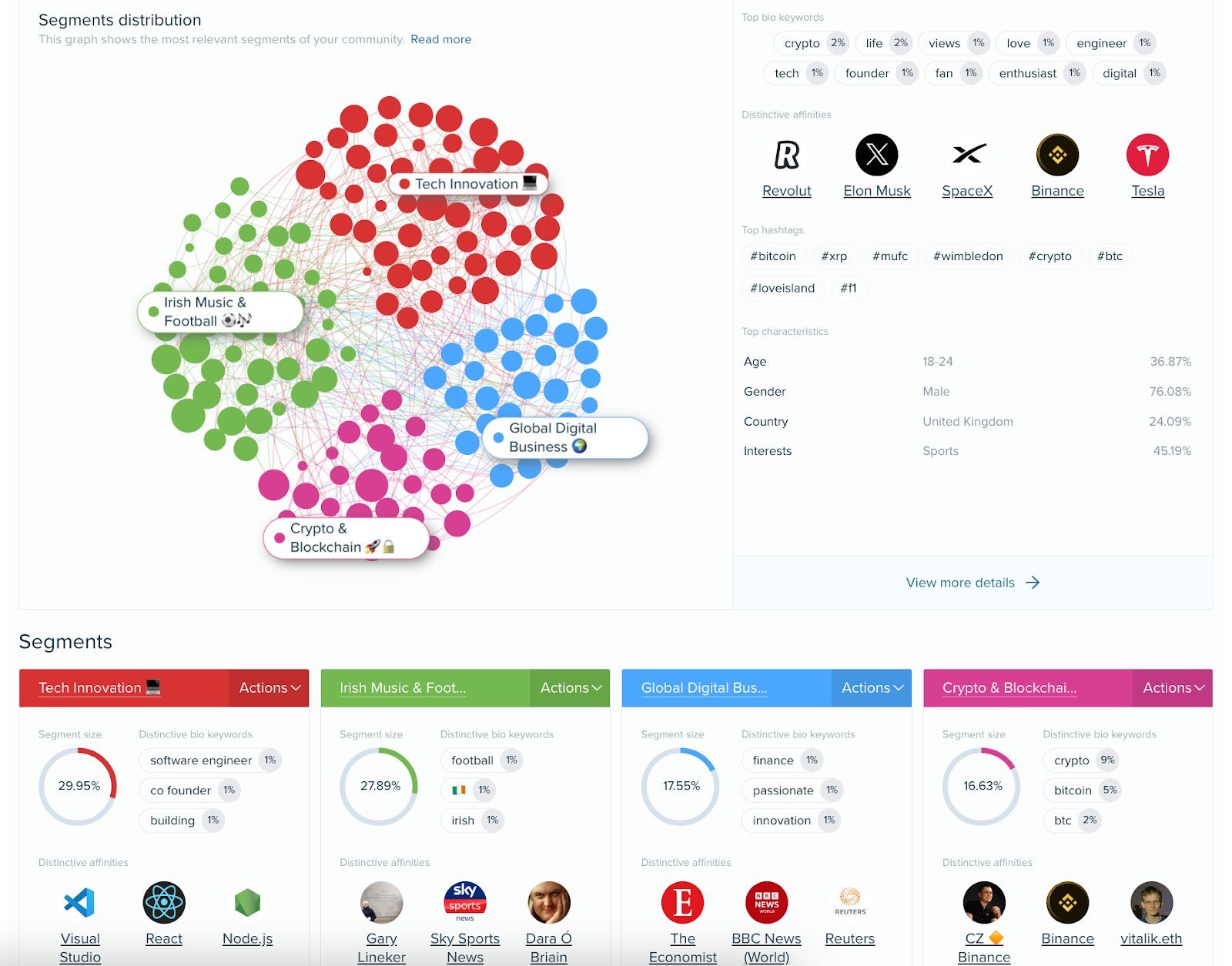
You’ll see the segment name at the top. (You can switch to another segment or view data for your “Full audience” anytime.)
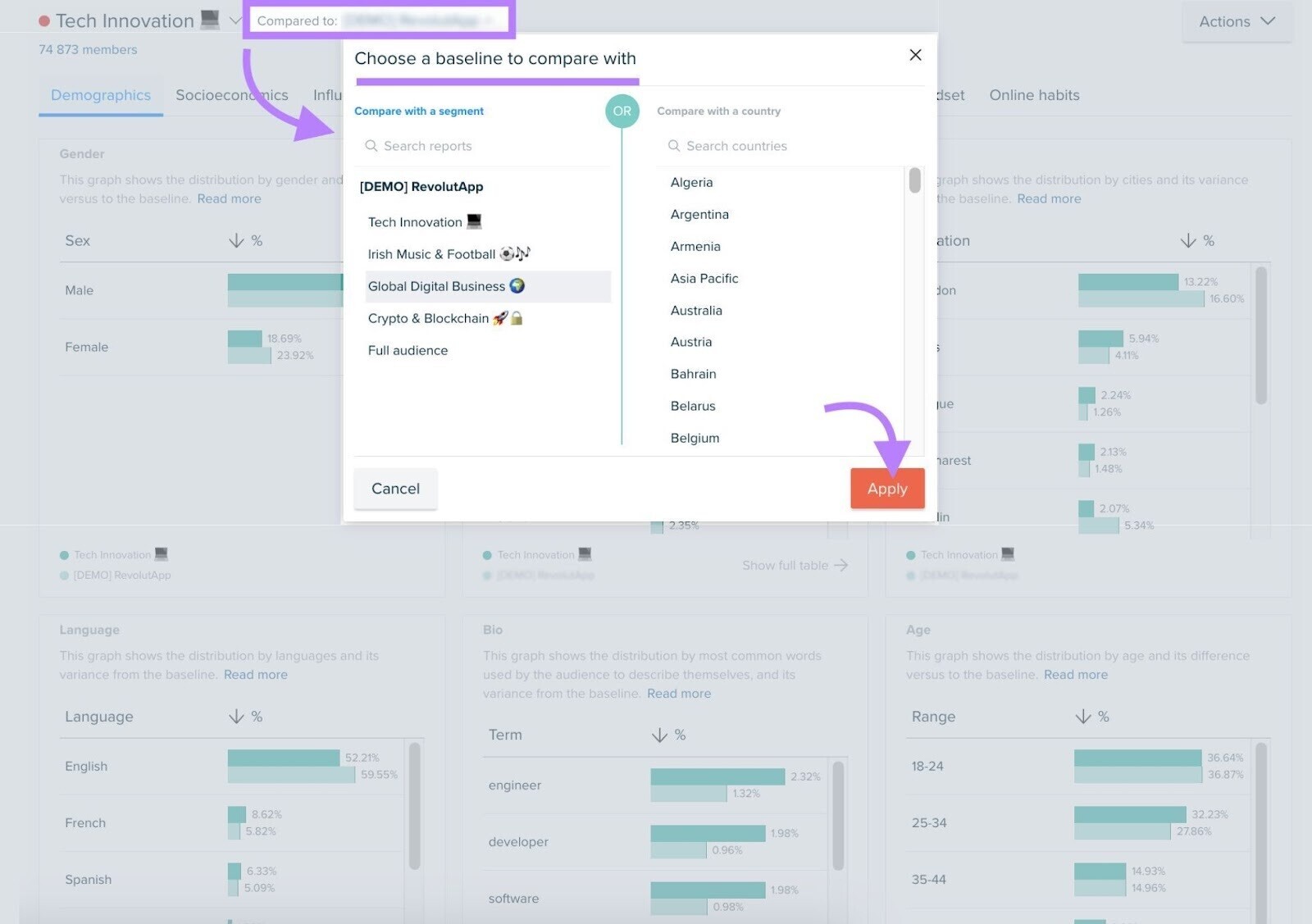
In the “Compared to:” menu, choose baseline data to compare against. This helps you identify trends that are unique to your segment or audience.
Then, explore the following tabs:
- Demographics: Gender, country, city, language, and age breakdowns. Plus, the most common words from followers’ bios and names.
- Socioeconomics: Education level, job industry, relationship status, family status, and household income (U.S. only) breakdowns.
- Influencers & brands: Other accounts that your audience follows. You can get affinity, uniqueness, and reach data.
- Interests: The main interests of your audience. Click any interest to view a breakdown of sub-interests.
- Media affinity: Your audience’s favorite TV channels and shows, radio stations and shows, newspapers, magazines, events, places, blogs, digital magazines, websites, online shows, and apps.
- Content: Domains, hashtags, users, links, keywords, and formats used in your audience’s posts, most liked posts, and influencers’ posts.
- Personality: Measures of your audience’s neuroticism, openness, agreeableness, extraversion, and conscientiousness. Plus an overview of their personality, needs, and values.
- Buying mindset: Insights into purchase influence factors and consumer behavior.
- Online habits: This includes which devices they use, their most active time periods, content publishing and engagement trends, and how likely they are to use each network.
Audience Intelligence is available through the Semrush App Center.
4. Interview Potential Customers
In interviews, ask customers directly about their specific interests, goals, and challenges. Or speak to other groups to determine whether they’re a good fit for your brand.
There are two main interview styles:
- Structured interview: You prepare your list of questions in advance so your discussion can remain focused
- Unstructured interview: You engage in a free-flowing conversation with your participants
No matter which style you opt for, remember your goal is to get as much information about your audience as possible.
As for how to conduct interviews, you can conduct them in person or over a video call.
Here are some example questions for inspiration:
- What are the main issues you face with X?
- What do you value most about X?
- What do you want to achieve with X?
- What books, blogs, conferences, social media, videos, etc. do you consume?
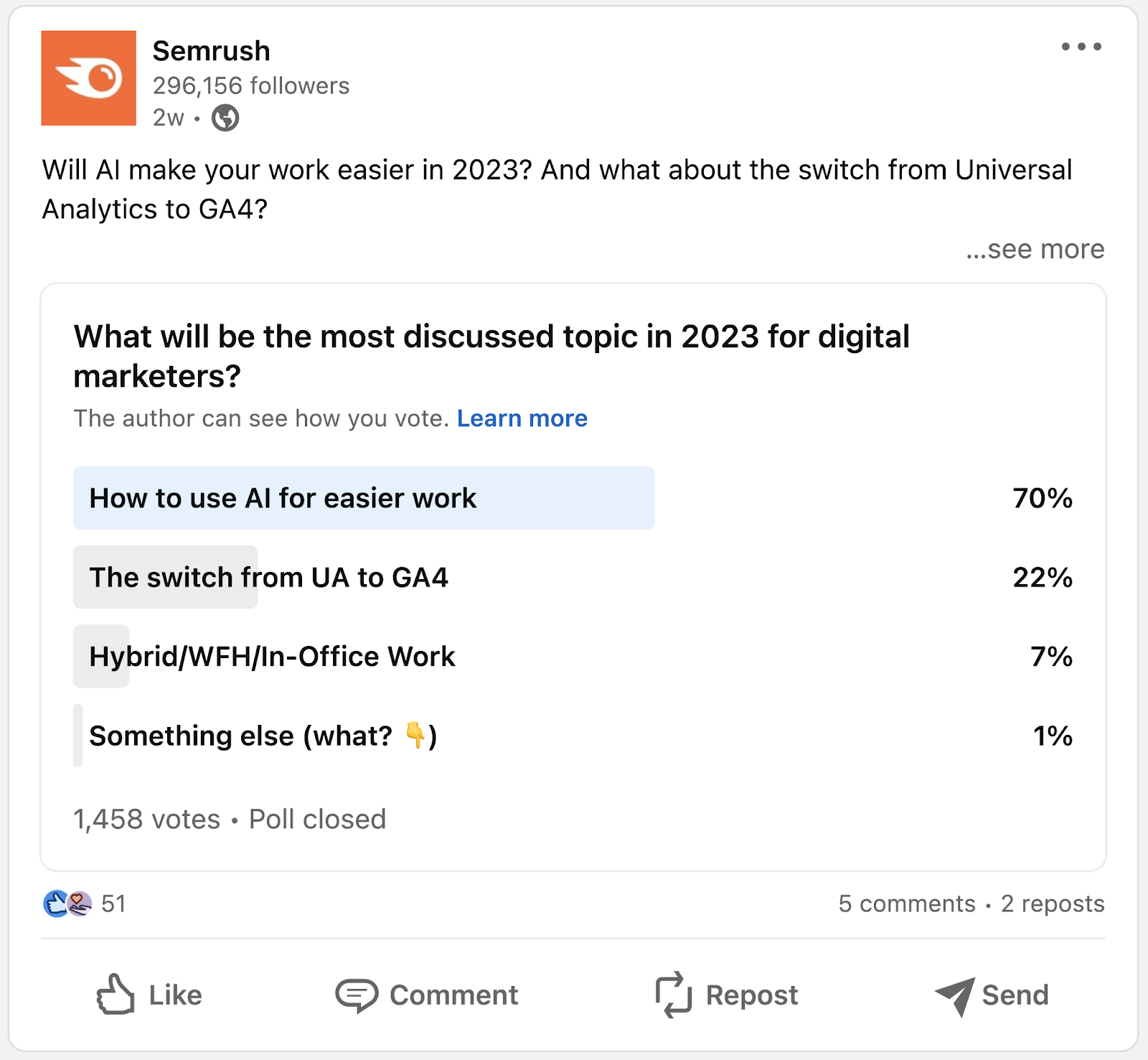
5. Conduct Surveys
Surveys make it easy to gather and analyze audience feedback at scale.
You can also use social media polls to learn customers’ thoughts and preferences.
Here’s an example of a poll Semrush conducted on LinkedIn:
How to Reach Your Target Audience
After you find your target audience, your goal is to reach them and convert them into customers.
Use different marketing channels to accomplish this.
Let’s look at several channels you can use to effectively reach your audience.
1. Rank in Organic Search
Organic search is all about ranking in non-paid, organic listings that appear on search engine results pages (SERPs).
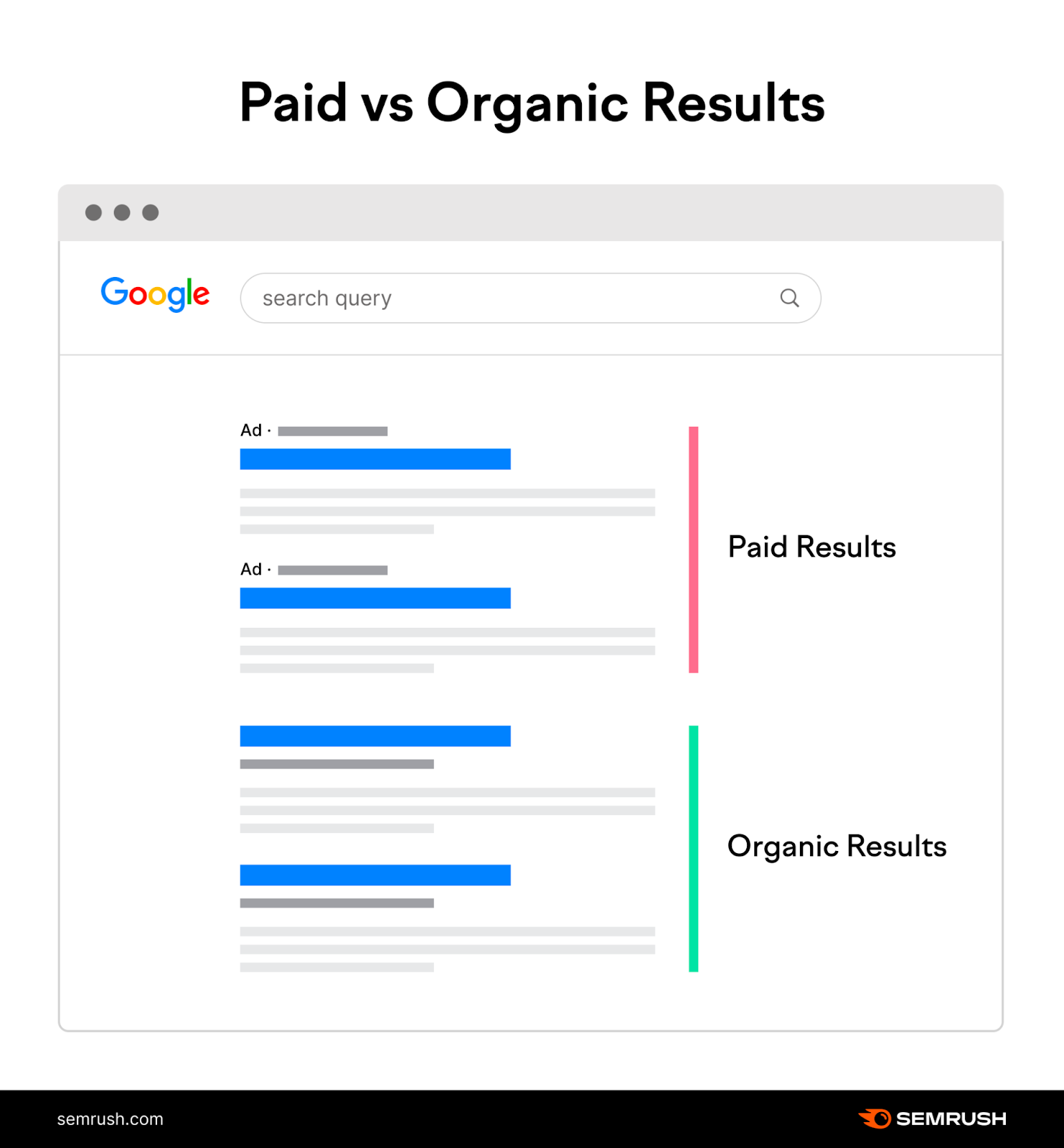
Organic search is arguably the most cost-effective way to get in front of your target audience.
To rank organically, you need to focus on your SEO strategy.
That’s a big part of where we invest our efforts here at Semrush. And the hard work is paying off.
We get an estimated 4.7 million monthly organic visits to our site, according to Semrush’s Domain Overview tool.
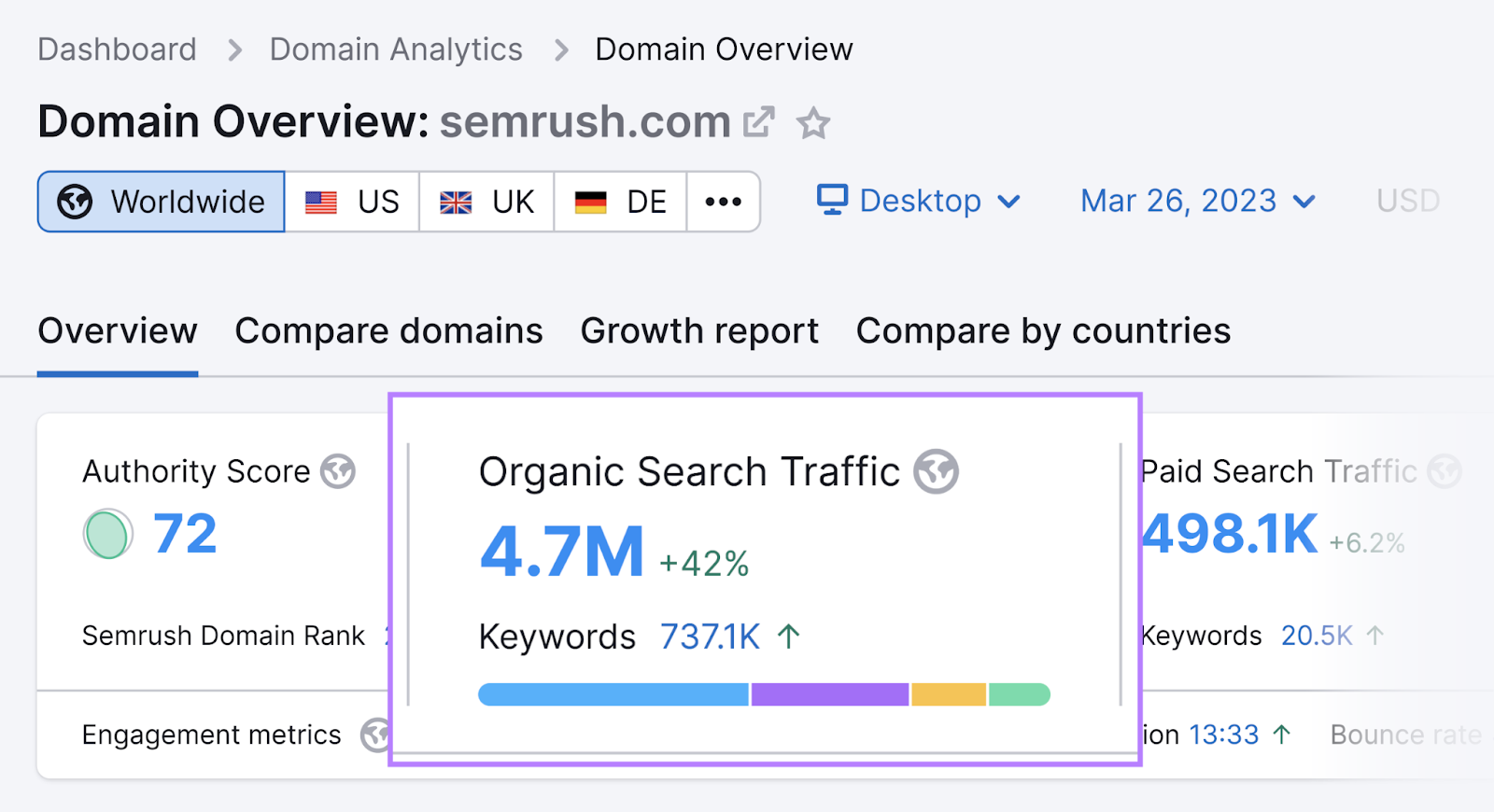
To succeed with this channel, you’ll need to do keyword research, create quality content, optimize content for on-page SEO elements, build backlinks, and follow technical SEO best practices.
Pros:
- SEO traffic has a compounding effect
- Caters to all stages of the marketing funnel
- Increases brand visibility
- Grows sales without ad spend
Cons:
- Ranking high in search engines takes time
- It’s challenging to do well
- Rankings for some keywords can be really competitive
2. Create Social Media Content
Millions of people around the world use social media platforms like Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), Instagram, TikTok, and LinkedIn. That makes them an ideal place for businesses to reach their target audience.
While you can promote your products or services directly on these platforms, your target audience will likely be using these platforms for entertainment and/or education.
So think of these networks as a place to build relationships, share expertise and experiences, and help your audience.
To do all of that, you need to create a solid social media content strategy.
Pros:
- Allows for direct interaction with your audience
- Helps with customer support
- Opportunity to tap into a massive audience
- Can increase brand loyalty
Cons:
- Building an audience takes time
- Organic reach is in decline
- You might need to field negative comments and trolls
3. Post on YouTube
With over two billion users worldwide, YouTube is the world’s most popular video platform.
Lots of companies are using this platform to connect with their target audience.
Take ClickUp, a project management tool, as an example.
Some of their videos have racked up millions of views.
That's because they're entertaining and use fun skits to captivate viewers' attention.
This approach can be successful. But it may not be for everyone.
So another option is to create educational content (e.g., tutorials, how-to videos, etc.).
Many companies have seen great success and acquired lots of customers by putting out educational videos.
Semrush is a great example of this.
We post lots of educational videos on our YouTube channel. Like our video about social media marketing strategies:

If you haven’t yet pulled the trigger when it comes to YouTube, read our guide on how to create a YouTube channel. And learn about the benefits of YouTube keyword research.
Pros:
- Watching a video is an interactive experience for people
- Videos can be repurposed on various platforms
- Videos can make your brand become popular very quickly if they go viral
Cons:
- Can be quite resource-heavy (equipment, people, dedicated studio, etc.)
- For newcomers, it will take a while to get traction and build an audience
4. Work with Influencers
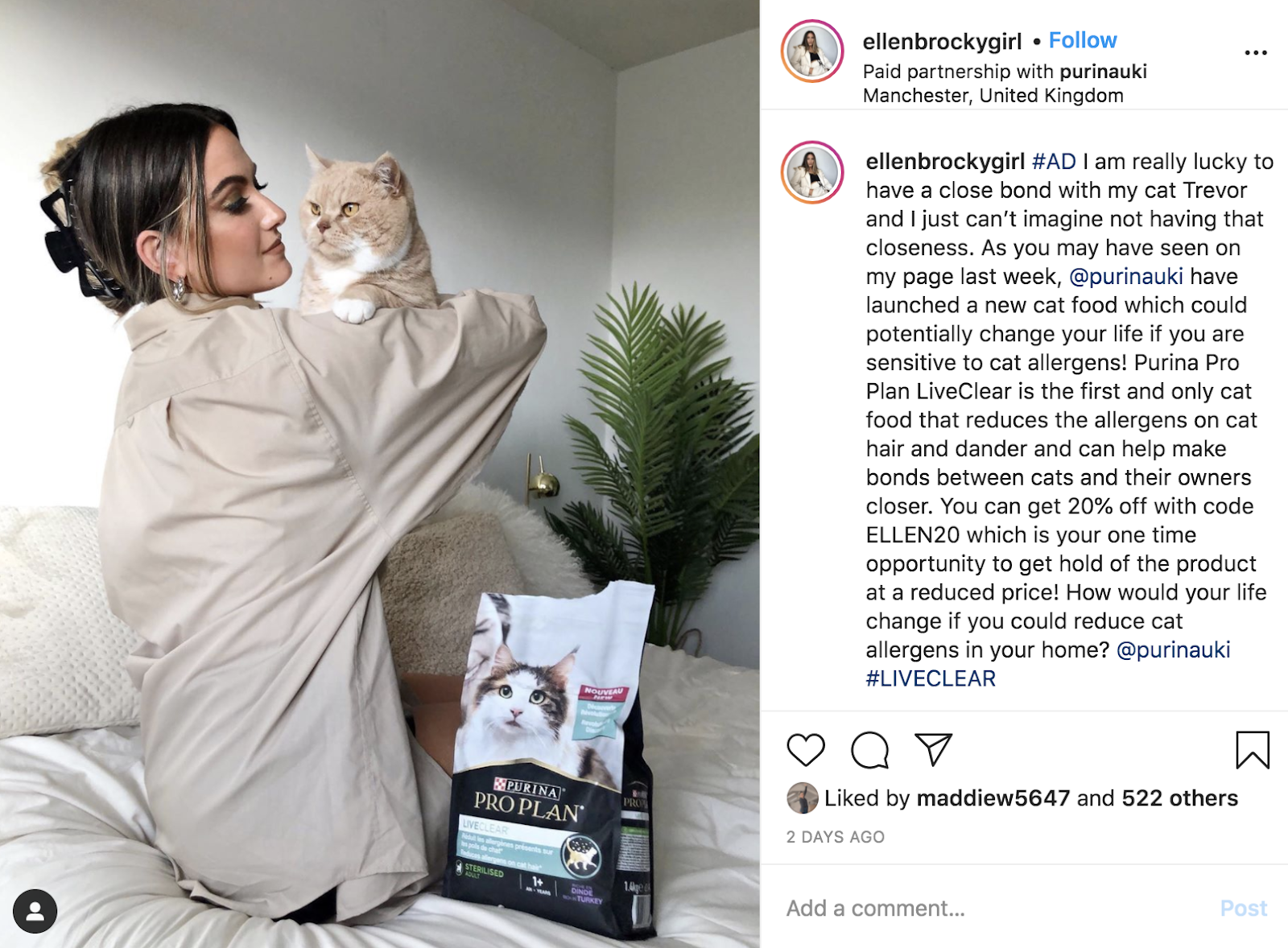
Influencer marketing is paying relevant influencers (like bloggers or YouTubers) to promote your products, services, or content.
For example, Purina paid Instagram creator @ellenbrockygirl to promote its cat food:
Influencer marketing can take a lot of work. But Influencer Analytics makes it more accessible.
The app can help you find influencers, analyze competitors, manage campaigns, and monitor performance.
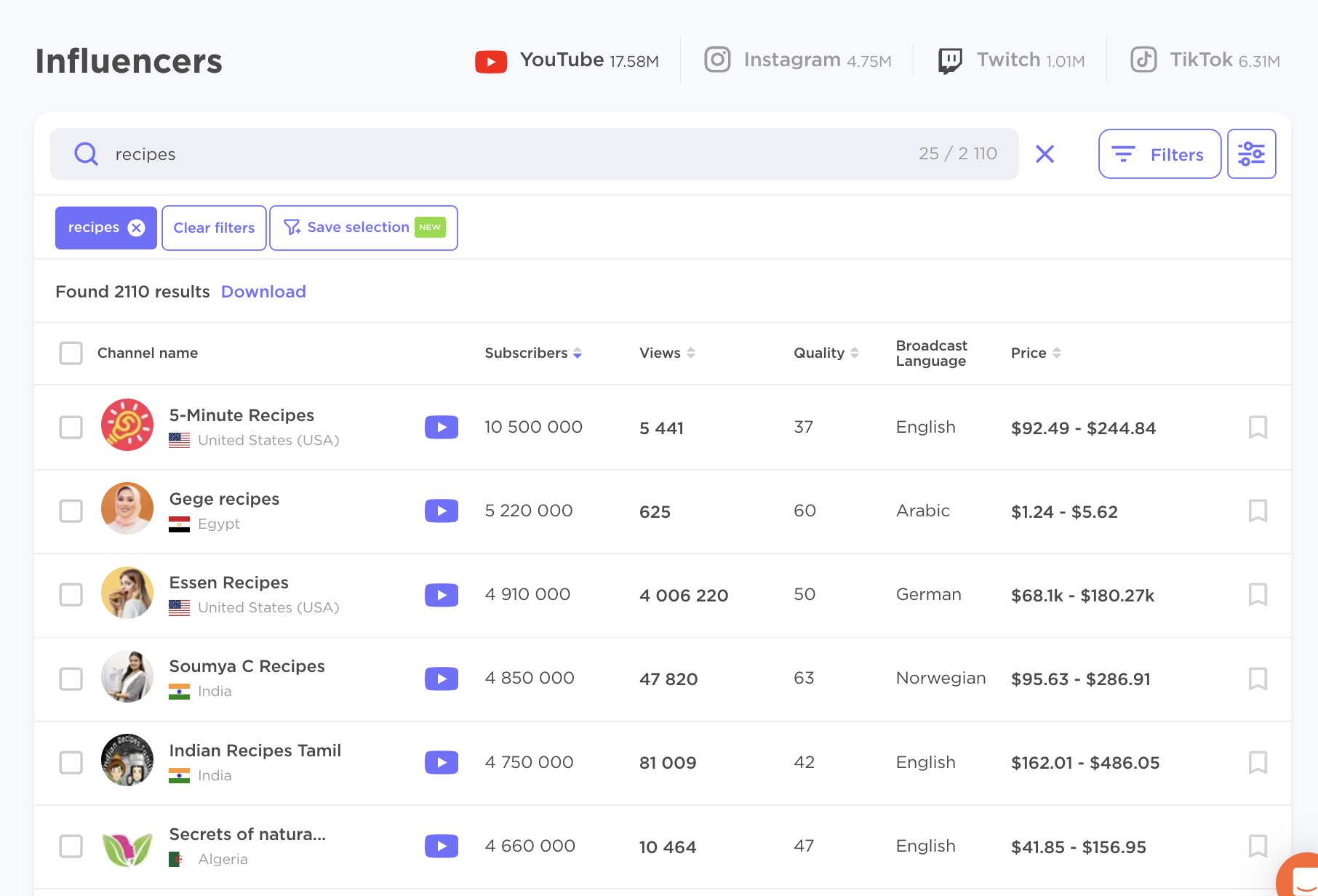
Pros:
- Build trust with target audiences
- Tap into niche communities
Cons:
- Bigger influencers can request high fees
- Attribution can be difficult
- Risk of the creator misrepresenting your brand
5. Set up an Affiliate Program
Affiliate marketing is when brands pay publishers a commission in exchange for referring a customer to their site.
For example, this article from the New York Times (NYT) contains an affiliate link to Nest Bedding. If a reader clicks this link and makes a purchase, NYT should earn a commission.
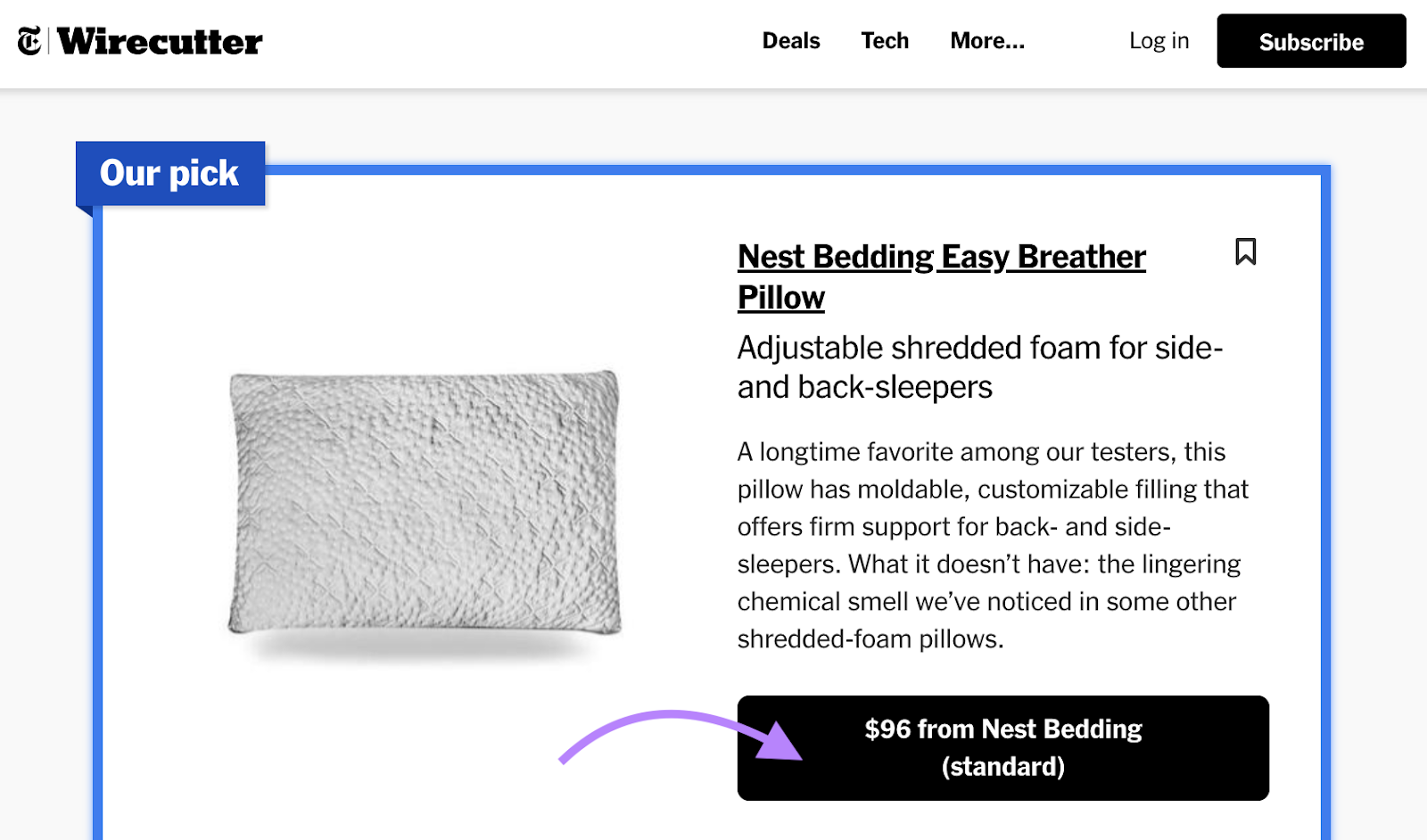
If we look at the article’s stats in Semrush’s Domain Overview tool, we see that it receives an estimated 33.1K monthly organic visits. So there’s a lot of potential for Nest Bedding to acquire customers.
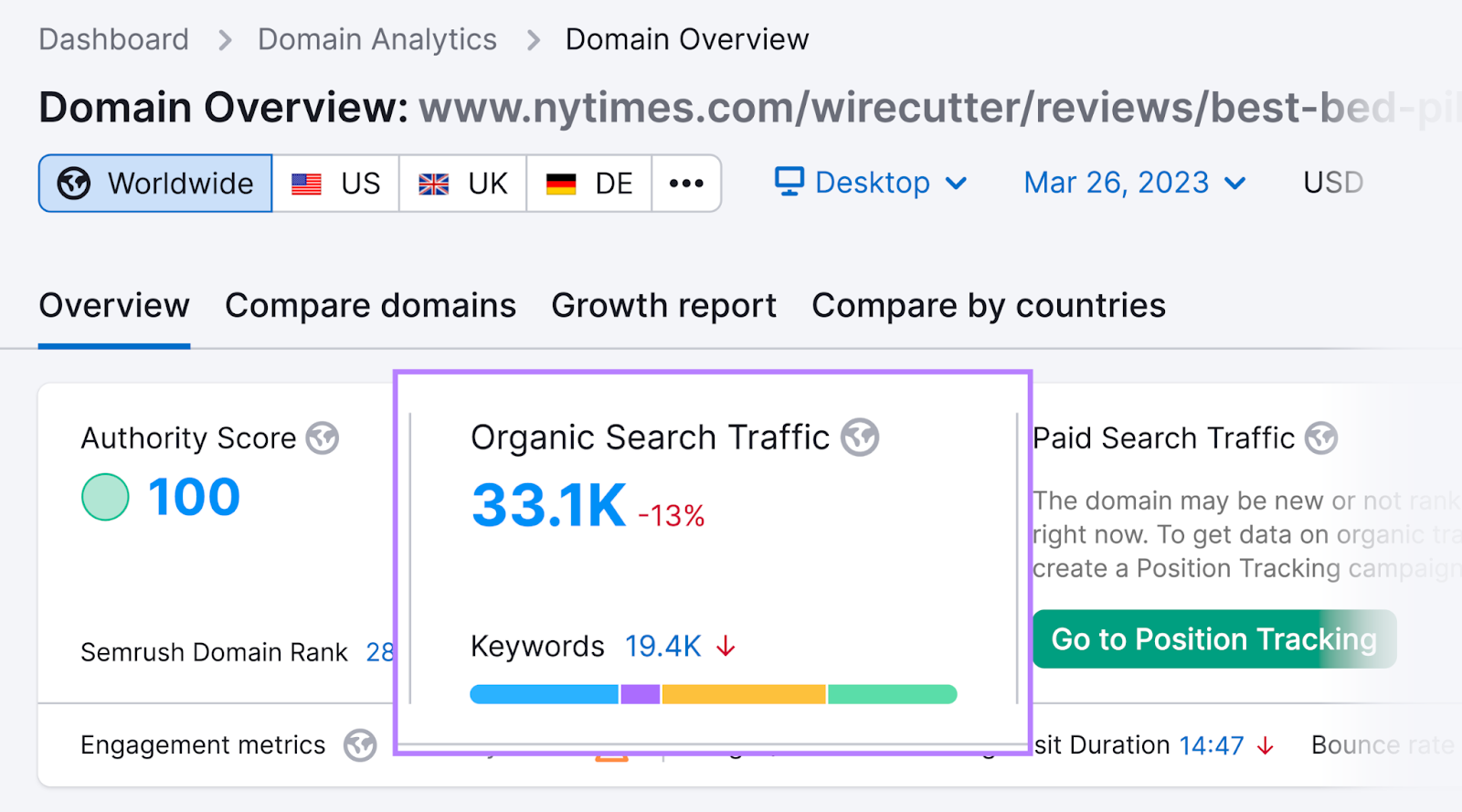
To get started with affiliate marketing, you can register with affiliate networks like ShareASale, GiddyUp, and ClickBank.
These networks act as middlemen. They connect you with relevant publishers so you can partner with them.
Pros:
- Performance-based; no upfront costs involved
- Can bring people who are interested in your products or services to your site
Cons:
- Can damage your brand’s reputation if you partner with the wrong affiliate sites
- Limited control over quality and tone of publisher’s content, which can impact your brand image
6. Get Involved with Podcasts
There are over 464 million podcast listeners worldwide. And three main ways to reach your target audience with podcasts:
- Create your own podcast
- Sponsor a popular podcast whose audience is relevant to your business
- Get interviewed on popular podcasts in your niche
If you create a brand new podcast, growing an audience from scratch can take a while.
So, if you have a budget, it’s probably best to sponsor someone else’s podcast.
That’s what Shopify and others did on The Tim Ferriss Show.
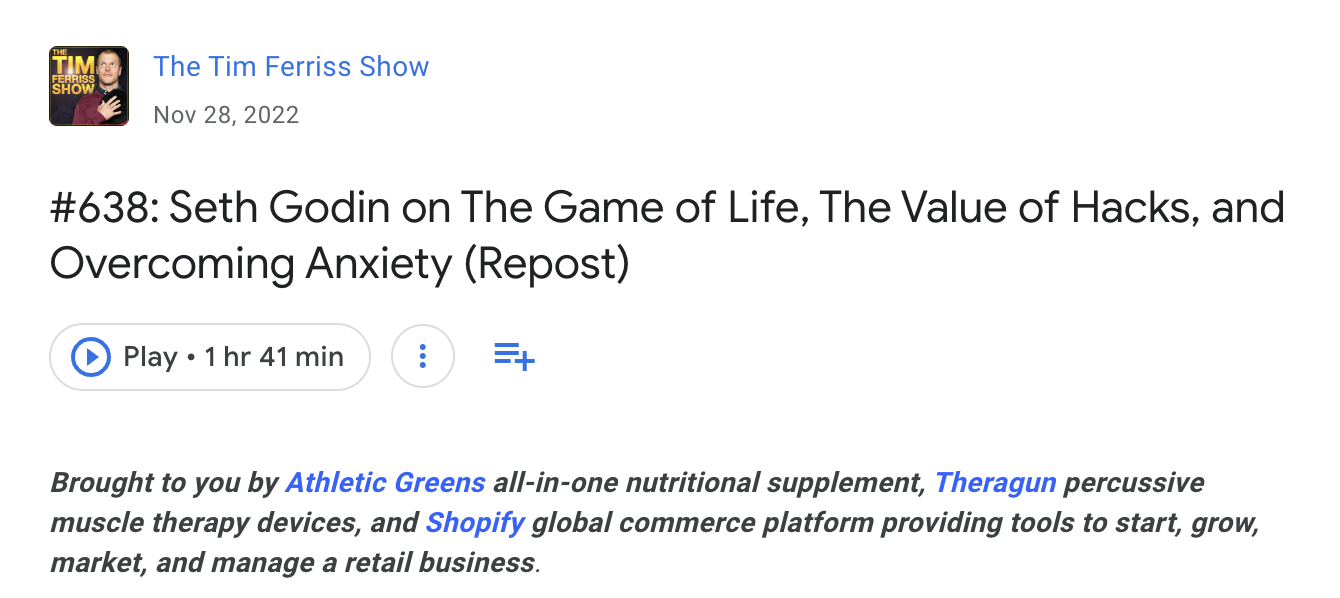
Plus, podcasters are always on the lookout for interesting people to interview.
But you don’t need to be a celebrity for this.
Do you have extensive experience in a particular field? And are willing to provide value in an interview? Then you’ve got what it takes.
All you have to do is reach out to podcasters and pitch yourself as a guest.
Pros:
- Great for brand awareness
- Can be more engaging than written content
- Can enhance your brand’s image by associating it with the content and values of the podcast, which can help build trust and credibility with your audience
Cons:
- ROI may be hard to measure
- Risk of unwanted brand associations if you sponsor the wrong podcasts
- For newcomers creating their own podcasts, it takes time to get traction and build an audience
7. Use Email Marketing
Email marketing helps you reach your target audience directly in their inbox.
Semrush is living proof that email marketing works.
We regularly send newsletters and promotional emails to our subscribers. And we get thousands of visitors to our website that way.
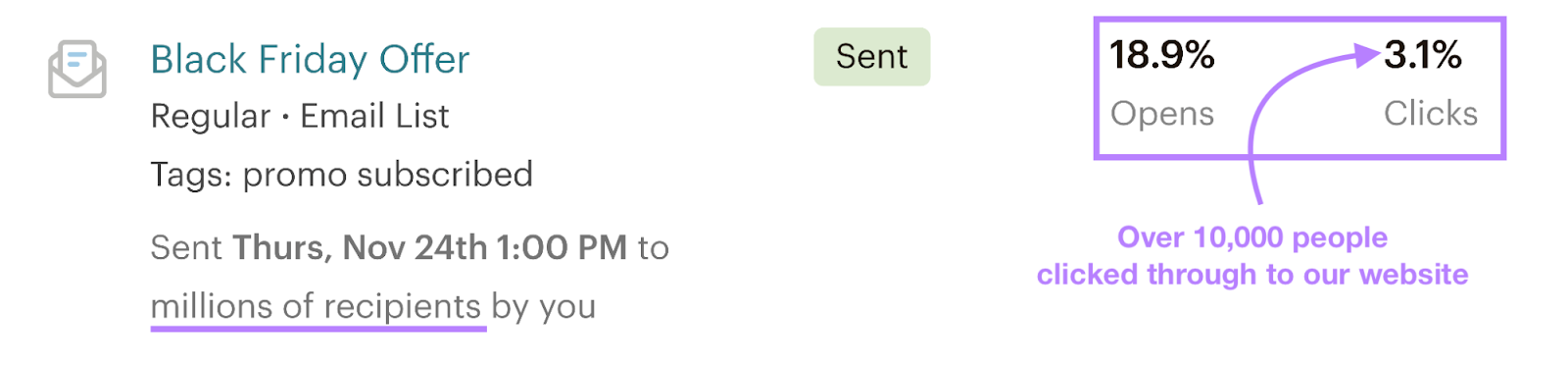
But building an email list takes time.
To get started, start using email opt-in forms offering lead magnets like ebooks, case studies, and free templates on your website.
Or collect your customers’ emails when they make a purchase. With their permission, of course.
We’ve spent years growing our email list, and now have tens of thousands of subscribers who look forward to reading our newsletter.
If you haven’t yet run any email marketing campaigns, the best time to start is right now.
Pros:
- Emails can be personalized
- Can reach large number of people instantly
- Can be cost-effective
- Easy to measure
Cons:
8. Try Online Advertising
Online advertising involves paying for digital ads to reach and attract your target audience.
Search engines, websites in ad networks, and social media channels all represent a great opportunity to get exposure with ads.
Online advertising typically has two main goals: brand awareness and conversions.
But you can’t just blindly throw money into ads and expect to generate sales.
A lot of factors go into running successful ad campaigns. But the key is to always ask yourself: Who is the target audience?
Pros:
- Can cover every stage of the marketing funnel
- Low barrier to entry
- Easy to measure
- Allows for precise targeting
- Easy to scale
Cons:
- Ads can be expensive
- Lots of competition
- People often get tired of seeing the same advertisement repeatedly
Find and Reach Your Target Audience with Semrush
By identifying target audiences, you can focus your marketing efforts on the right people.
For the best results, you’ll need data and target audience insights.
That’s where Semrush comes in.
Semrush offers a suite of online marketing tools that give you both data and insights about your target audience. Including:
- One2Target: Analyze your competitors’ audiences
- Audience Intelligence: Gather in-depth insights about social followers
- Market Explorer: Find opportunities in your target market
