A good user experience (UX) is when website visitors’ interactions with your website are positive.
And good UX isn't just nice to have—it’s crucial for ranking highly in Google.
This is because many of the actions you take to improve UX help with search engine optimization (SEO)—a set of techniques that help improve your visibility in search engines.
After reading this post, you’ll understand exactly how UX and SEO work together. And how applying UX optimization techniques can improve your SEO performance.
Let’s dive in.
What’s the Relationship Between UX and SEO?
User experience and search engine optimization share a common goal of achieving user satisfaction.
UX and SEO also complement each other.
You must have good UX to be successful in SEO. Especially when you consider that the Google documents leaked in March of 2024 reveal numerous UX elements that may directly influence search rankings.
What UX Factors Affect SEO Performance?
User experience elements related to speed and ease of use can significantly affect SEO performance.
Here are some broad areas of user experience that matter the most:
- Performance: Making sure your pages load quickly and are responsive is a must. Generally speaking, Google wants to prioritize those pages.
- Mobile experience: With Google's move to mobile-first indexing, having a site that works well on mobile devices is extremely important. Good mobile UX could help improve your rankings on Google.
- Design and layout: Arranging information logically, using good formatting, and featuring content that’s easy to read makes users’ time on your site more enjoyable. And that could translate to better SEO performance.
- Usability: Ensuring you have intuitive navigation, clear buttons, and an accessible site that all users can easily interact with goes a long way toward improving your UX
How to Optimize UX to Improve SEO Results
Let’s see how to optimize the user experience to boost your SEO performance.
1. Create Content that Meets Search Intent
Your SEO-focused content needs to meet search intent (the purpose behind a user’s search query) to make sure users find what they’re looking for and to encourage them to stay on your site longer.
There are four main types of search intent:
- Informational: Users want to learn something (e.g., "how to make sourdough bread" or "what is cryptocurrency")
- Navigational: Users want to find a specific website or page (e.g., "facebook login" or "amazon prime")
- Commercial: Users are researching before making a purchase (e.g., "best gaming laptops 2024" or "iphone vs android")
- Transactional: Users are ready to take action, typically to buy something (e.g., "buy macbook pro" or "nike air max sale")
When your site delivers exactly what users are interested in, they’ll stay longer, engage more, and might even share your content.
These positive user behavior signals may help Google understand your page is worth recommending to others searching for similar information.
So, it's crucial to align your content with search intent.
To do that, start by analyzing the current top-ranking pages for your target keyword to understand what type of content users expect.
The top results for the below query include listicles and videos that feature follow-along workouts.
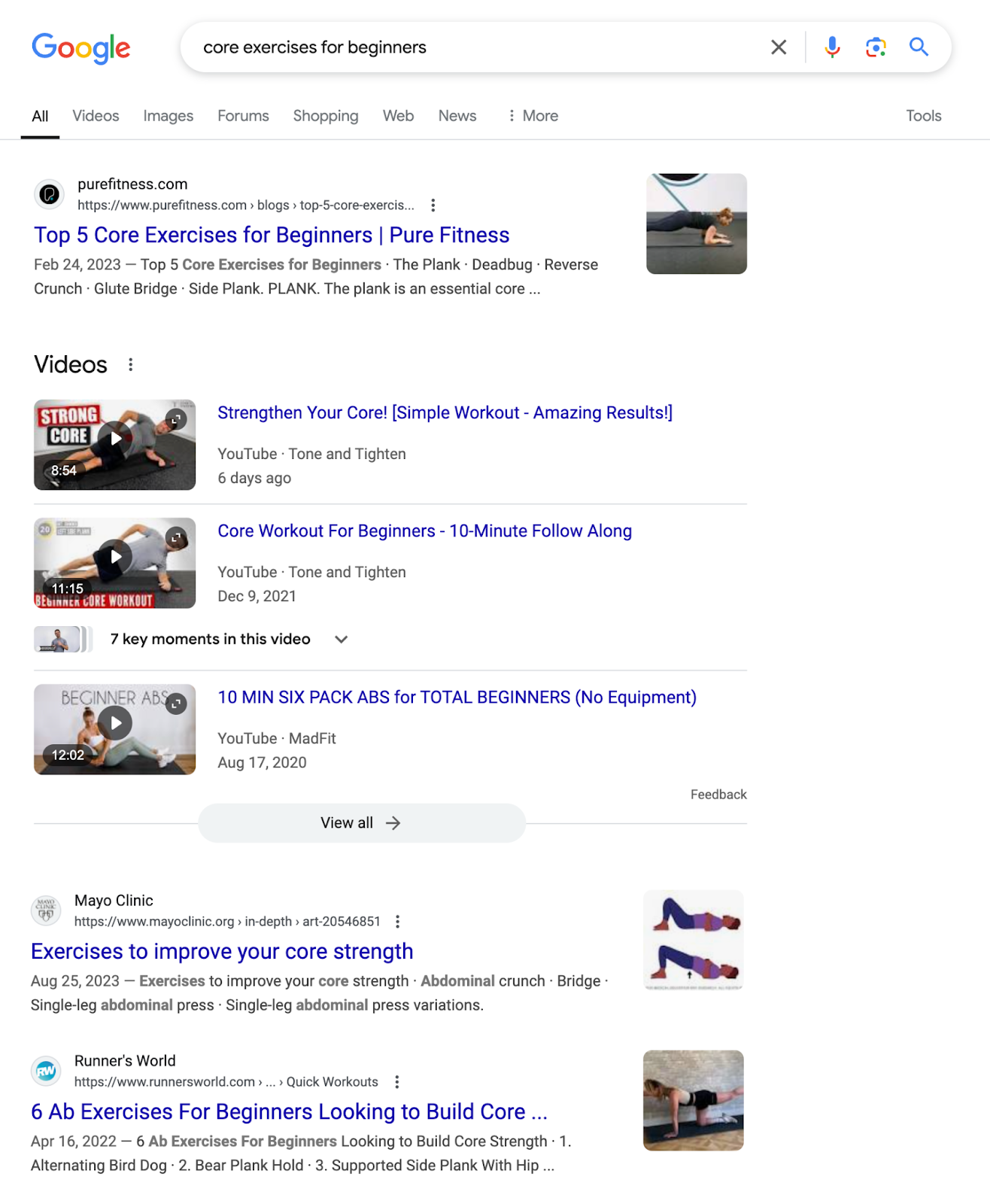
You should structure your content to match the dominant format.
Next, visit the top results to see what information is covered. Because you want to make your content thorough enough to satisfy users.
In this case, it seems important to get to the point and prominently feature at least five exercises.

When you start creating, use clear headings (or chapters if you’re creating a video) and formatting that make it easy for users to find what they're looking for.
And include relevant supplementary content (images, videos, charts, etc.) that enhances understanding.
2. Make Content Easy to Read
Making your content more readable helps to deliver a great user experience that keeps visitors on your site and can also help search engines better understand your content.
Here's how to make your content more readable:
- Use short paragraphs and sentences. Break up your text into two- to three-sentence paragraphs and keep sentences themselves short when possible. Large blocks of text are intimidating and hard to read.
- Include plenty of headings. Use heading tags (like H2 and H3) to add headings and subheadings that create a clear content hierarchy. This helps readers scan and find exactly what they're looking for.
- Add relevant images. Break up text with helpful images, charts, and/or diagrams. These make your content more engaging and easier to understand.
- Format for scannability. Use bullet points, numbered lists, and bold text to highlight key information. Many users scan content before reading in detail.
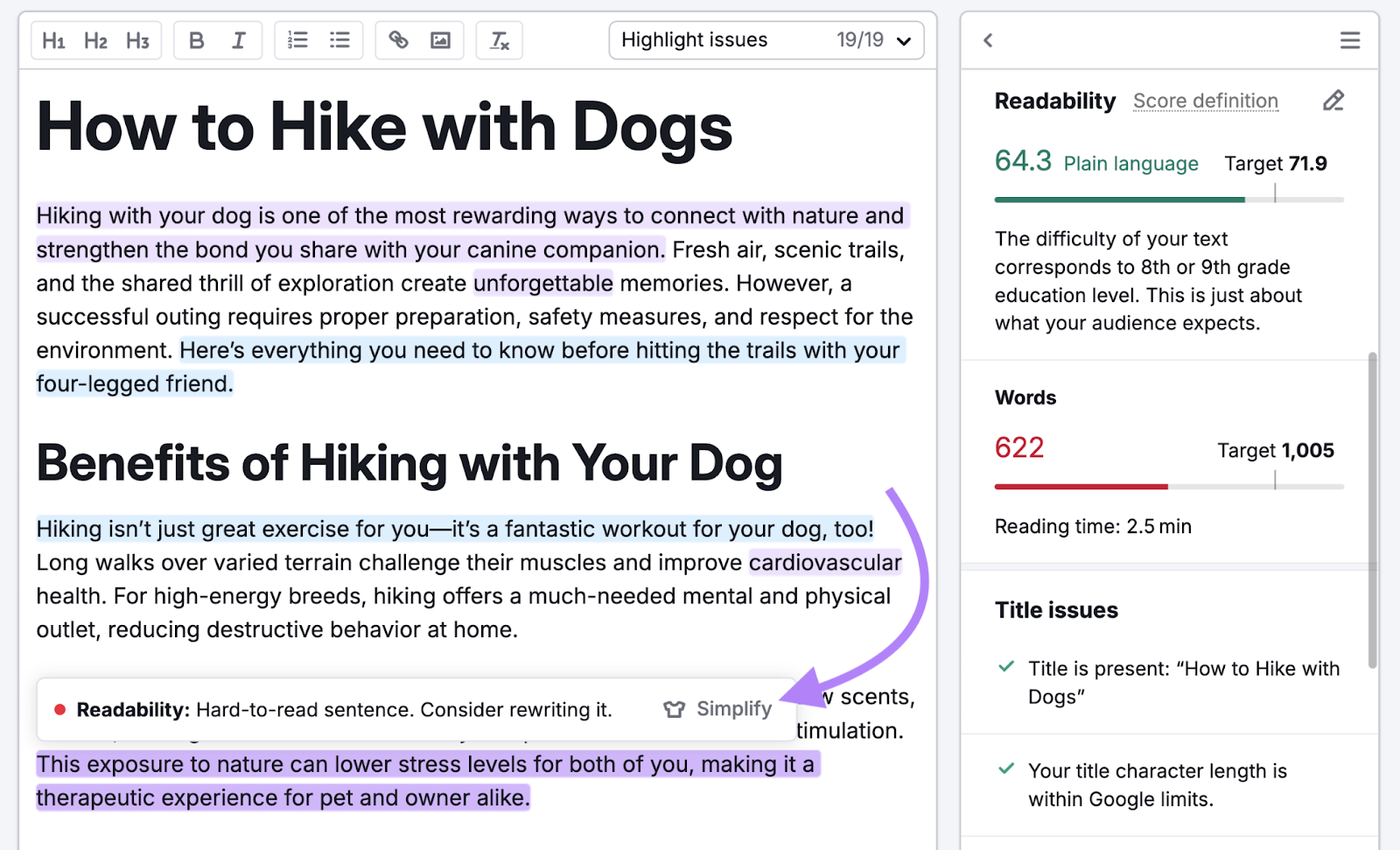
- Use simple language. Unless you're writing for a technical audience, aim for somewhere around an eighth-grade reading level (this can vary a bit depending on your niche). Use tools like Hemingway Editor or SEO Writing Assistant to check your content’s readability.
3. Aim for an Accessible & Visually Appealing Website
A visually appealing website that can be accessed by everyone—including users with disabilities—can help your SEO by sending positive user interaction signals about your website to search engines.
Here’s how to create a visually appealing and accessible website:
- Use a clean, modern design. Avoid cluttered layouts and choose simple, professional designs that prioritize readability.
- Maintain consistent branding. Keep colors, fonts, and design elements consistent across your site to create a cohesive brand experience that always looks good.
- Use legible fonts. Choose fonts that are easy to read and use appropriate font sizes to make sure users have no problem reading the content.
- Add alt text to images. Alt text is HTML that describes images, and it helps both search engines and readers with visual impairments better understand your content.
- Ensure keyboard navigability. Make sure users can navigate your site using a keyboard, which is essential for accessibility.
Many website builders and content management system (CMS) options make it easy to follow these best practices.
Here’s a taste of the WordPress theme options that were created with accessibility in mind:
4. Improve Site Structure and Navigation
A well-structured website with clear navigation makes it easy for users to find what they’re looking for and for search engines to crawl and index (find and store pages) your site more effectively.
To improve site structure, organize your pages into a logical hierarchy.
Your homepage should link to the category pages. And then those categories should link to individual pages on your site.
Like this:
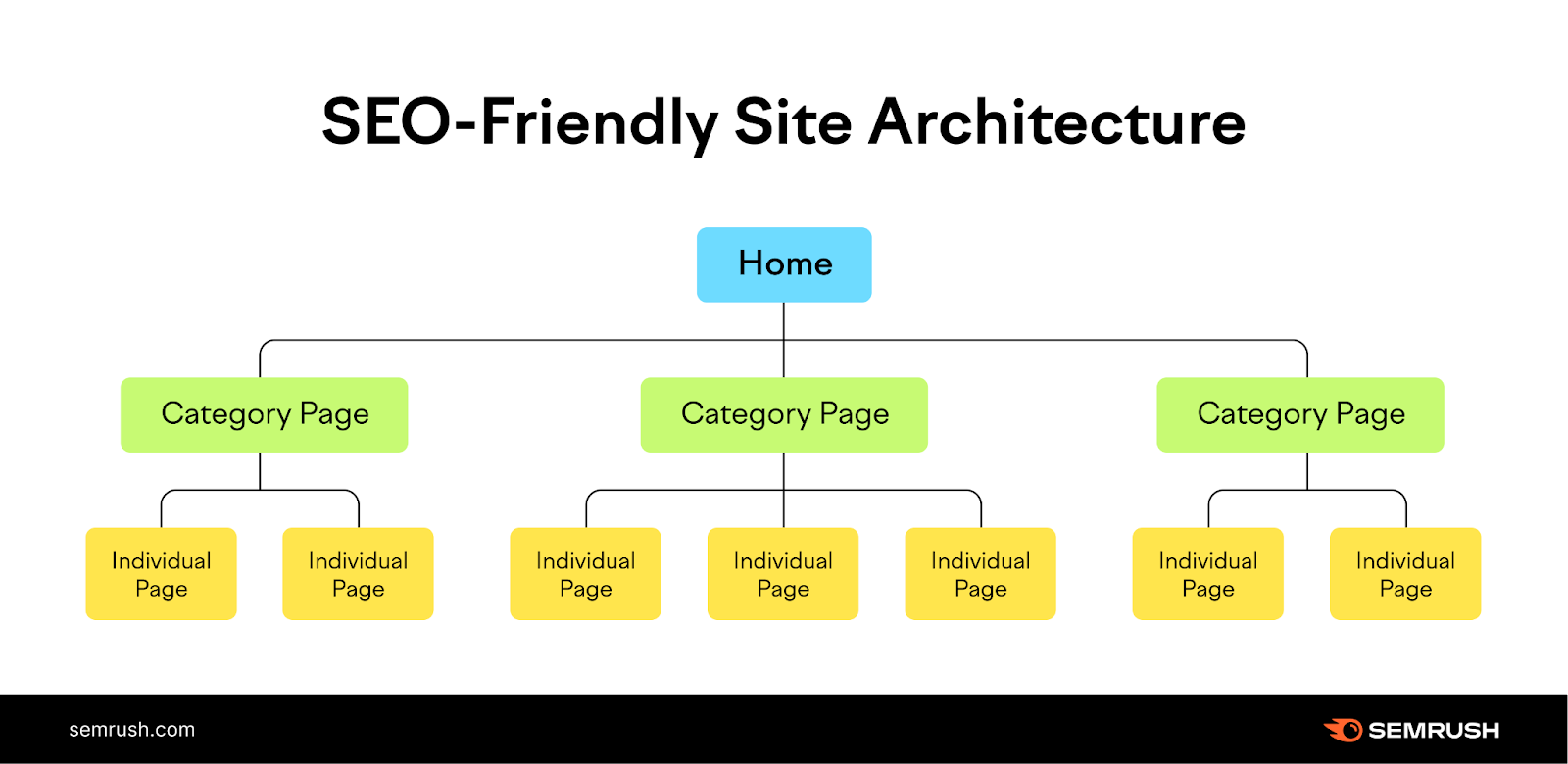
Ideally, your URLs should follow this structure as well:
- Homepage: “yourwebsite.com”
- Category page: “yourwebsite.com/first-category”
- Individual page: “yourwebsite.com/first-category/first-individual-page”
5. Improve Page Performance
Ensuring strong page performance broadly means keeping your pages responsive and fast, which can directly influence search engine rankings
To check the performance of any page on your site, use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool.
Simply enter a URL, and you’ll see whether there’s room for improvement. Along with a list of action items.

To get a better understanding of how your performance is across a larger sample of your website, try Semrush’s Site Audit tool.
Follow the prompts to configure your audit.
Once the tool is ready, go to “View details” under “Site Performance.”
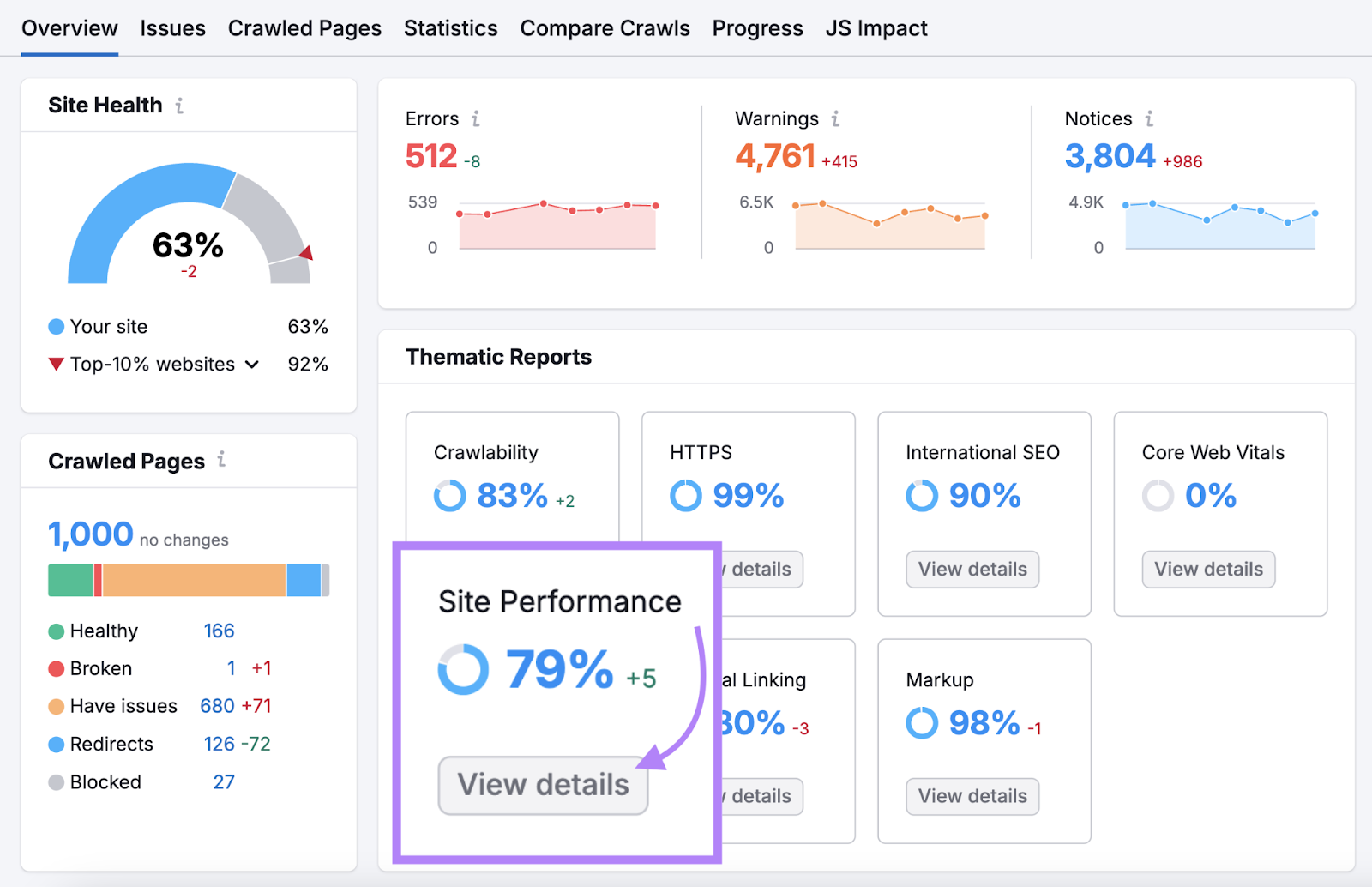
You’ll get an overall score out of 100% (the higher the better) indicating how good your performance is. And a list of issues you can address to further improve.
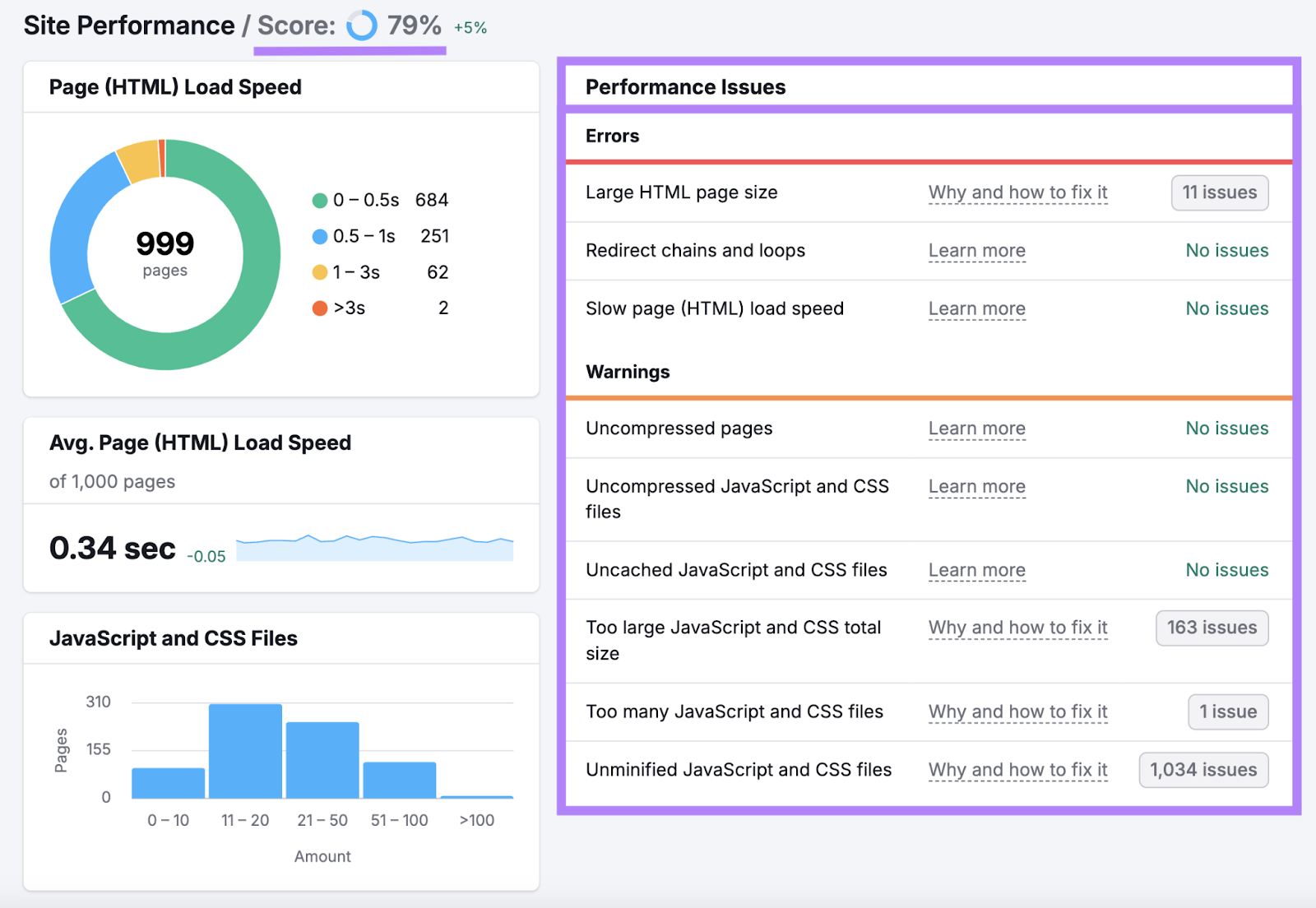
The specific actions you should take to improve performance will depend on your website/page, here are some of the most important to know about:
- Optimize images. Choose modern image formats like WebP that allow for smaller file sizes without losing quality. You can also compress images using a tool like TinyPNG.
- Minify code. Make your code files smaller without impacting the way they work. Work with a developer for help.
- Minimize redirects. Eliminate any unnecessary redirects (especially chains and loops). Too many redirects can slow down your site.
- Choose a good hosting provider. Opt for a hosting option that offers good performance. Cloud hosting (which involves multiple servers hosting a group of sites) is often a good choice.
6. Ensure Your Site Is Mobile-Friendly
Making your website mobile-friendly is a must because more than half of all web traffic comes from mobile devices—and because Google uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking.
Here's how to ensure your site is mobile-friendly:
- Use responsive design. Your website should automatically adjust to small screen sizes, from smartphones to tablets. This ensures a seamless experience for all users.
- Optimize tap targets. Make buttons and links large enough and well-spaced to prevent accidental clicks.
- Minimize intrusive pop-ups. Avoid pop-ups that take up a user’s full mobile screen as soon as the page loads. If you do use pop-ups, ensure they don’t take up too much space and that they serve a purpose.
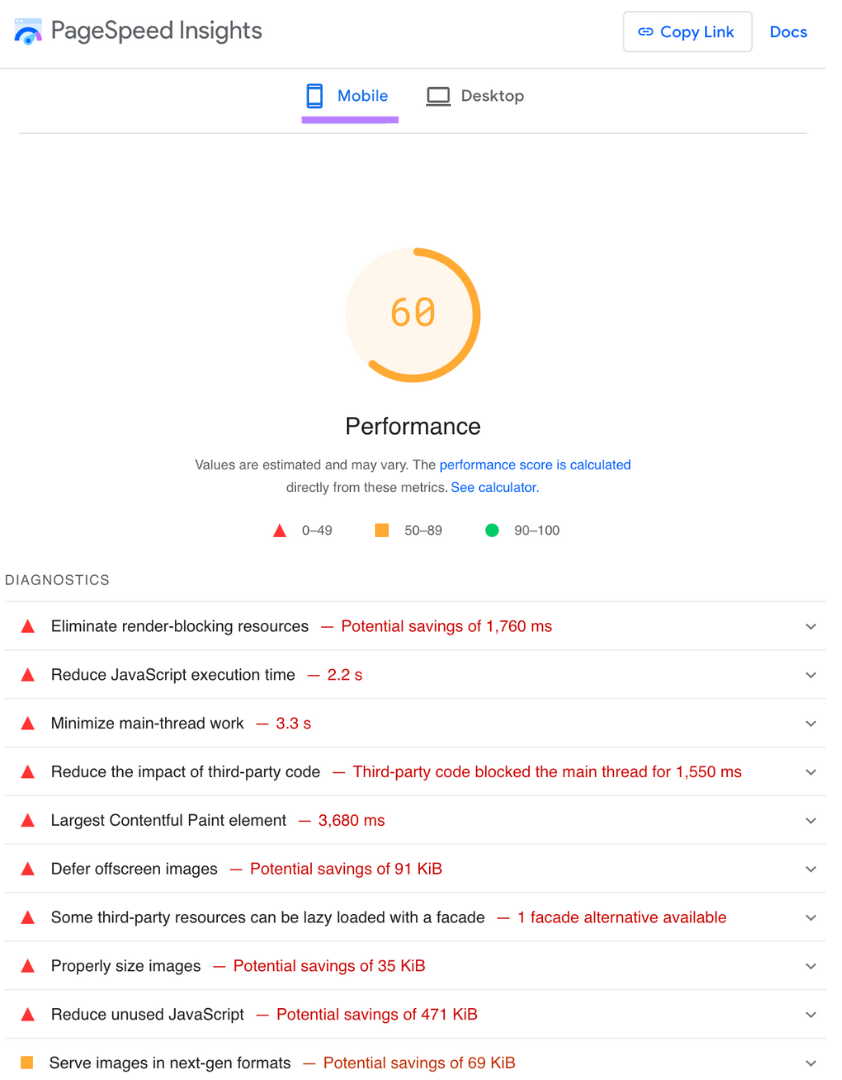
Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to check how well your site works on mobile devices.
Simply enter your URL, and you’ll get a feel for your site’s mobile performance.
Important UX Metrics to Track for SEO
Improving your numbers for these metrics indicates happier users, which may lead to better search rankings.
1. Bounce Rate
Bounce rate is the percentage of unengaged sessions on your site, and a low number may signal to Google that your content is valuable.
(Many marketers think the “badClicks” attribute referenced in the Google API document leak may include bounce rate.)
In Google Analytics, a session counts as unengaged when a user leaves before meeting any of the following criteria:
- Staying for more than 10 seconds
- Viewing at least two pages
- Taking a conversion action (like signing up for a newsletter or making a purchase)
To see your bounce rates for different pages in GA4, go to “Reports” > “Lifecycle” > “Engagement” > “Pages and screens.”
You’ll need to click the pencil icon in the top right corner to add the bounce rate metric to this table.
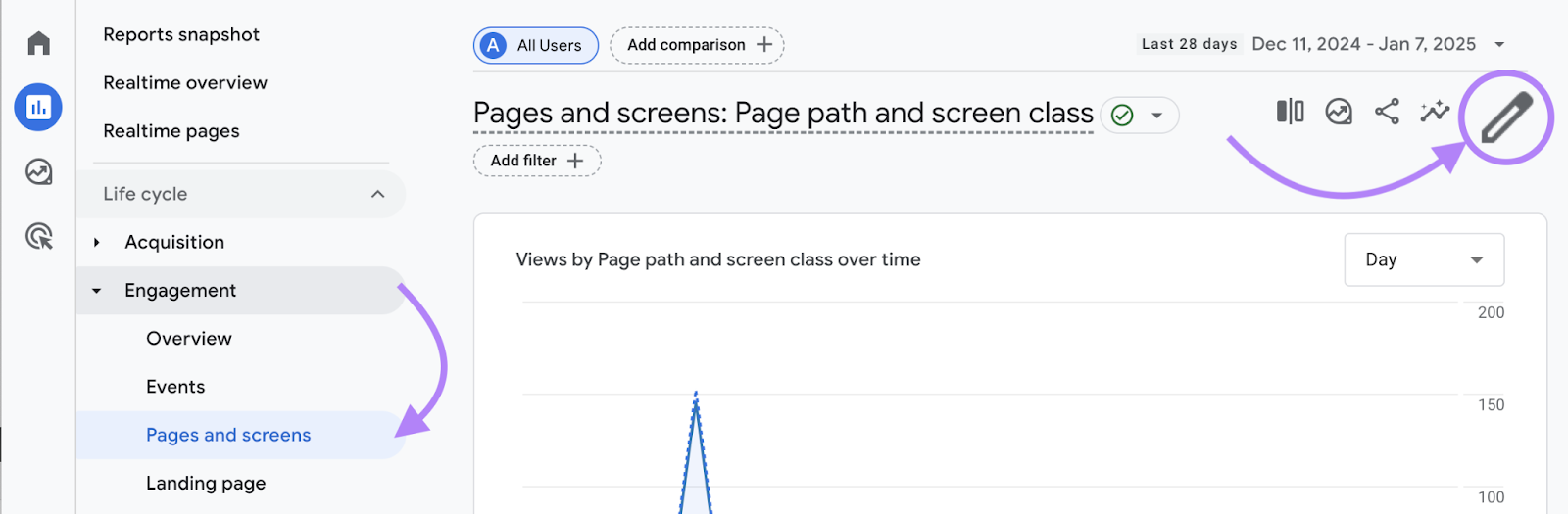
Once you do, you’ll be able to see each page’s bounce rate.
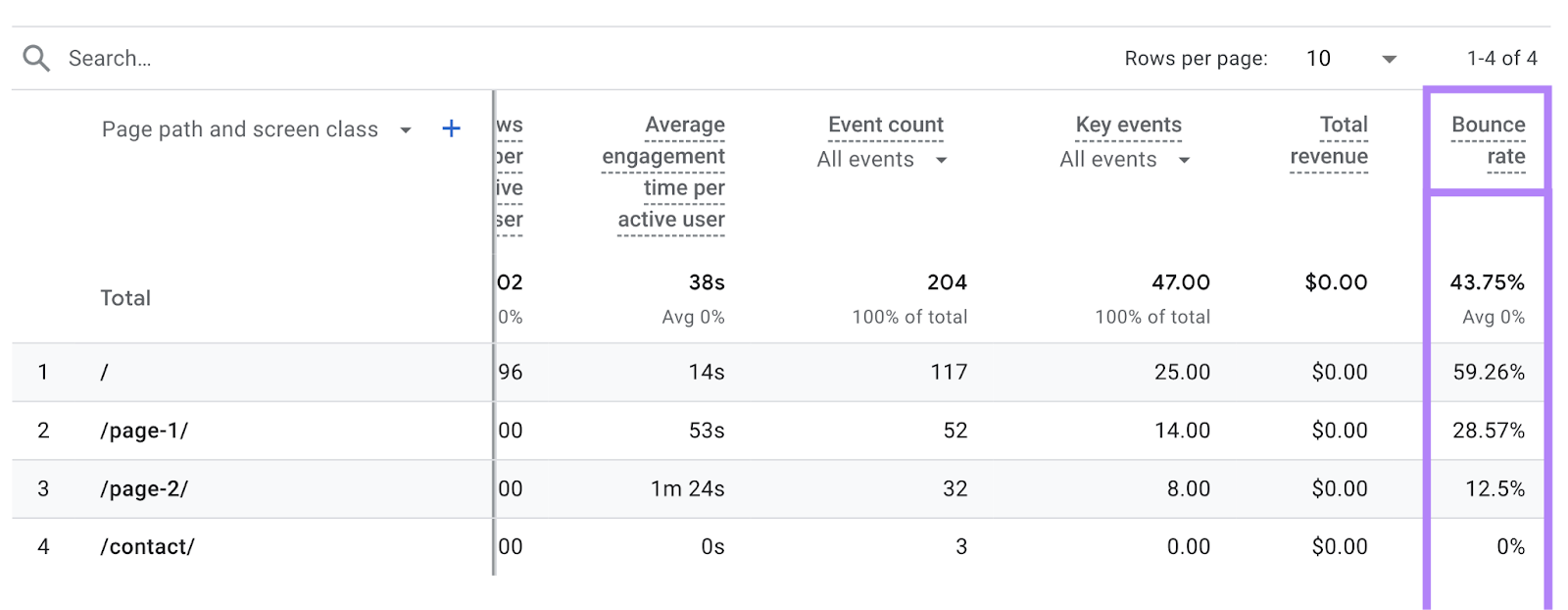
A bounce rate under 40% is generally considered good.
If you see any pages significantly higher than that, it’s worth revisiting them to see what improvements you can make.
2. Average Engagement Time
Average engagement time measures the average amount of time your website was users’ main focus—longer times may signal that your content is valuable and worthy of being ranked highly.
You can find your average engagement time in GA4 by going to “Reports” > “Lifecycle” > “Engagement” > “Pages and screens.”
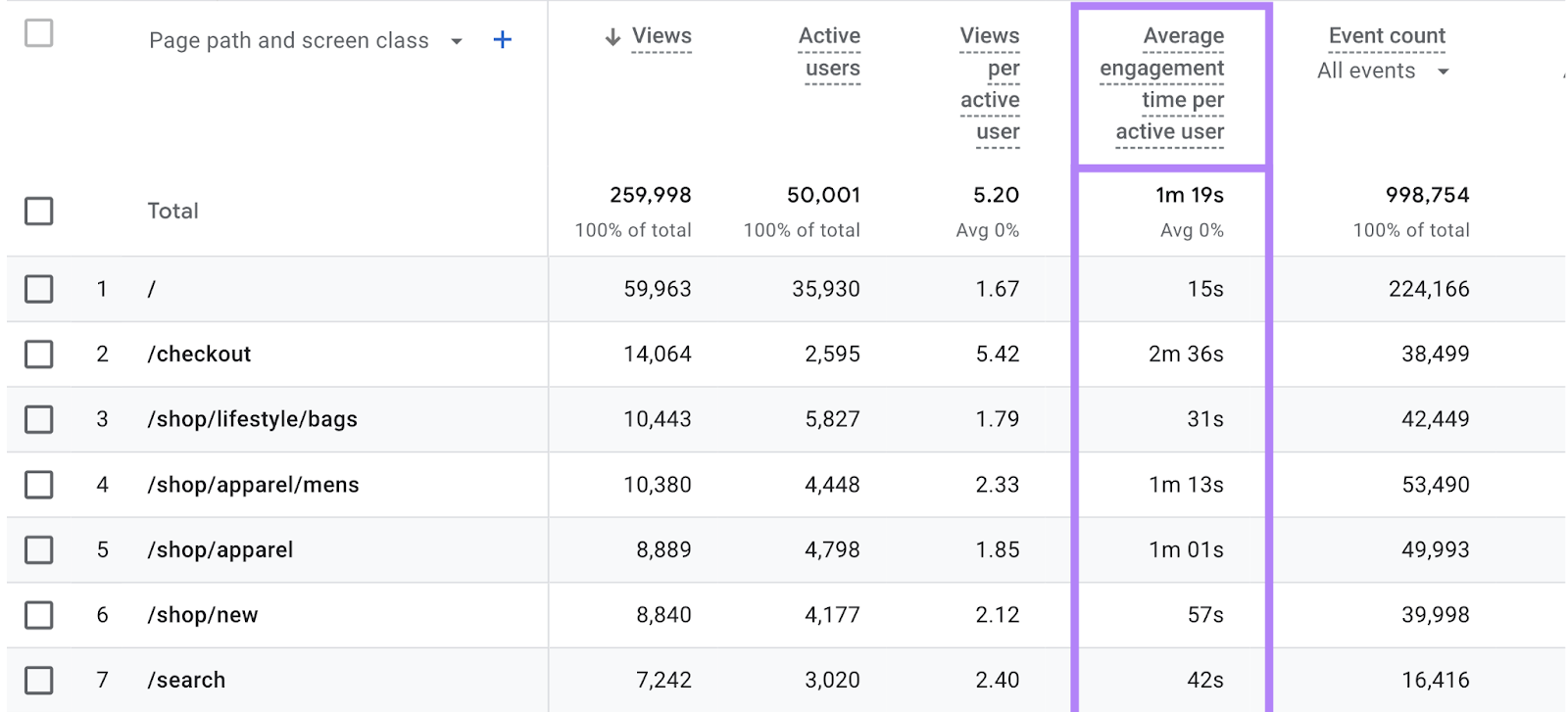
What good engagement time looks like can vary by content type and your niche. But aim for at least several minutes for content pages like blog posts.
3. Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals (CWV) are a collection of three metrics that measure the technical aspects of user experience and are used as ranking factors.
These metrics include:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how long it takes for the largest visible content on the page to load. Your LCP score should be 2.5 seconds or less.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures how quickly your page responds to user interactions like clicks, taps, and key presses. Your INP should be 200 milliseconds or less.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures the visual stability of the page, tracking how much elements shift unexpectedly as the page loads. Your score should be 0.1 or less.
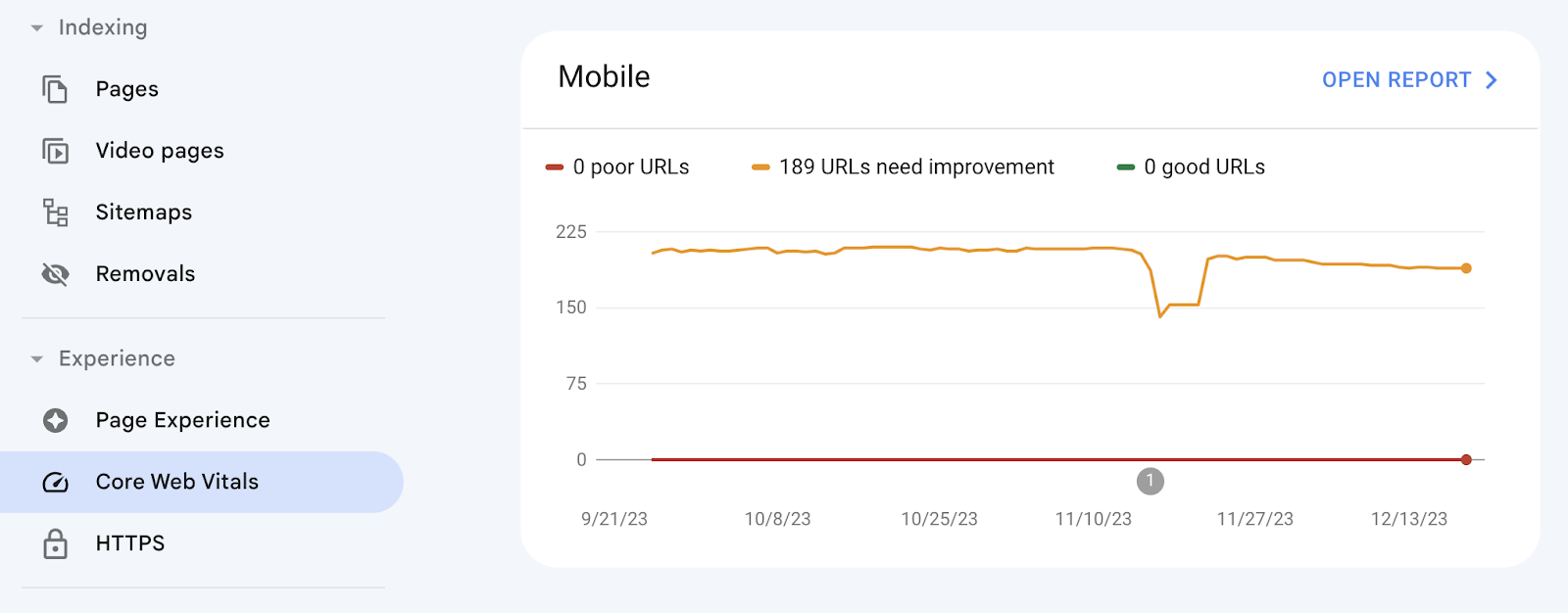
You can monitor your website’s current performance for the CWV metrics in Google Search Console.
Just go to the “Core Web Vitals” report.
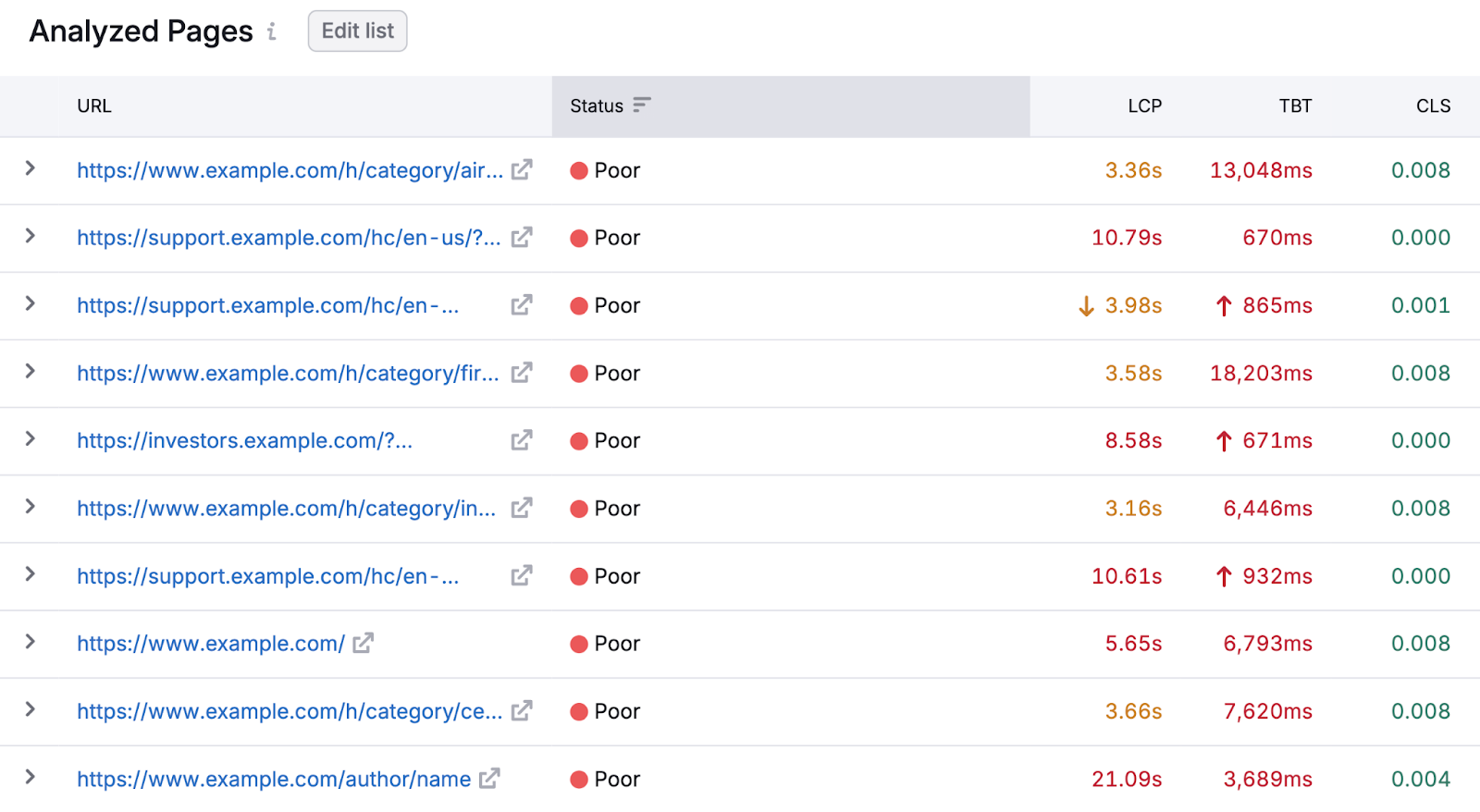
Alternatively, you can use Semrush’s Site Audit tool to monitor your CWV performance.
Set up a project and run an audit of your website.
Once the audit is complete, go to the “Core Web Vitals” report by clicking “View details.”
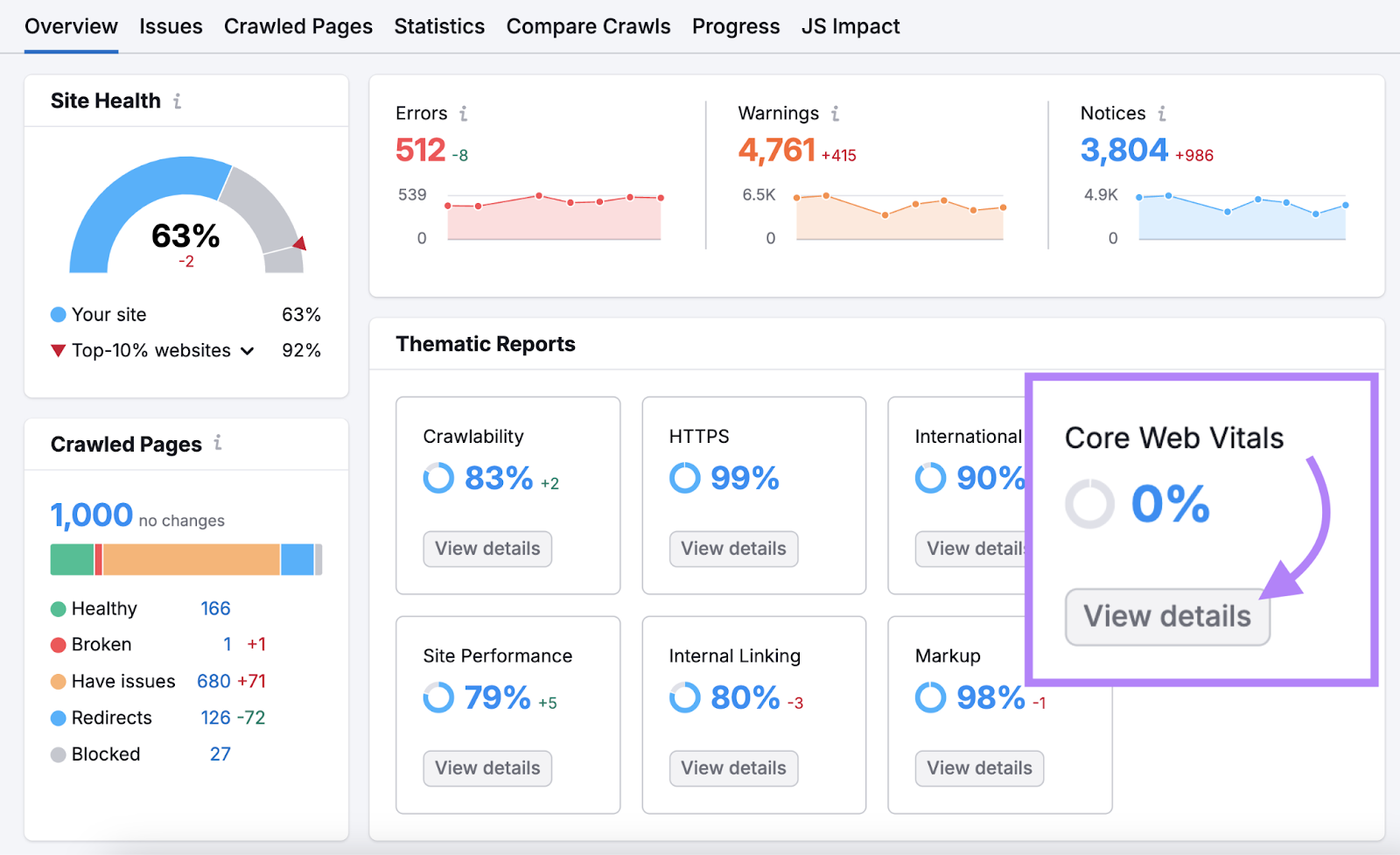
You'll see a list of pages on your website and their CWV performance (you can edit the list if you want to investigate other pages).
Start Optimizing for User Experience
Providing a good user experience is essential for SEO success—and it can help you reach your business goals.
Now that you know how to optimize your site’s UX, it’s time to get started.
Semrush offers tools that help you in your optimization journey.
Try them today with a free trial.
