What Are Toxic Backlinks?
Toxic backlinks (or bad backlinks) are incoming links that can negatively affect a website’s visibility in search engine results pages. These links often violate Google’s link spam guidelines because someone placed them for SEO purposes rather than for user benefit.
Google analyzes your backlinks to determine your website’s prominence and trustworthiness. Certain types of links from external sites can benefit your SEO.
Google’s policies and systems discourage manipulative link building, so links acquired through questionable practices are often ignored or “devalued.”
However, a large number of toxic backlinks can trigger a manual action (or Google penalty). This penalty suggests that your site engaged in systematic spamming.
A penalty can cause your site to be suppressed or removed from search results.
Google’s stance on links intended to manipulate rankings is clear:
Links obtained primarily for artificial manipulation of Search rankings are link spam. Our algorithms and manual actions aim to nullify these unnatural links at scale, and we will continue to improve our coverage.
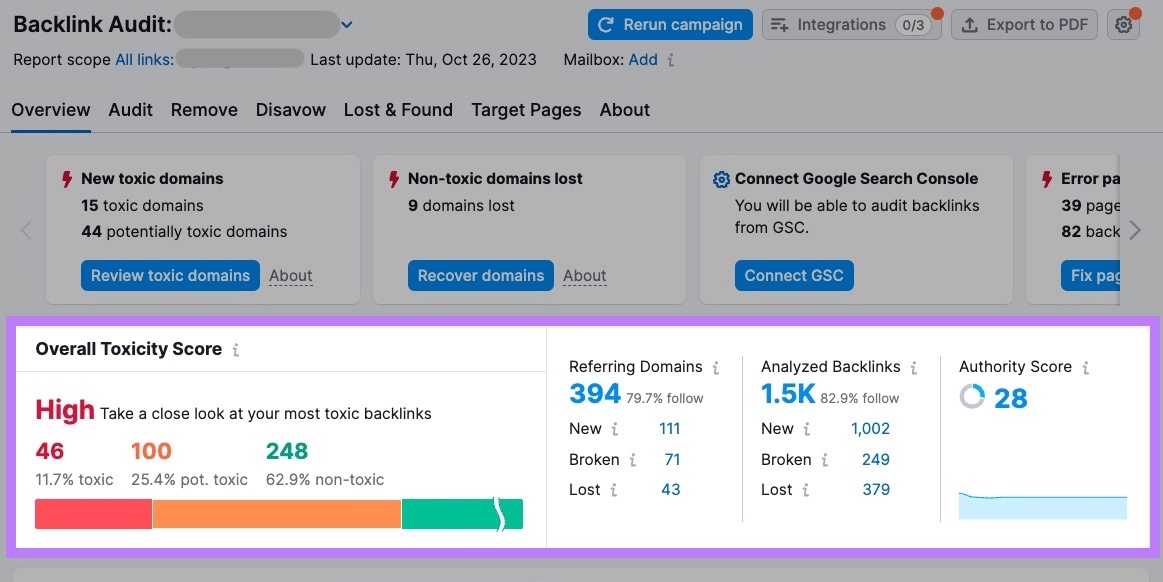
You can evaluate your backlink profile’s health with the Toxicity Score metric in Semrush’s Backlink Audit tool.
9 Causes of Toxic Backlinks
This section explains nine practices that can generate toxic backlinks.
1. Paying for Links
Never pay or receive other compensation for standard follow links that can pass SEO value (PageRank).
If you pay for a link in some way, the site owner should add a nofollow attribute like one of the below options to the link’s HTML code:
- rel="nofollow": Asks Google to ignore the link for ranking
- rel="sponsored": Tells Google the link was bought and shouldn’t count for ranking
A nofollow link looks like the below code:
<a href="https://example.com/" rel="nofollow">Anchor Text Here</a>Ensure your backlinks are nofollow when using link building activities like:
- Placing digital advertisements
- Gifting products in exchange for reviews
- Working with influencers
- Paying for directory listings
Check your “follow” links using Semrush’s Backlink Analytics tool.
Enter your domain and click “Analyze.”
Go to the “Backlinks” tab, apply the “Follow” filter, and review whether any links were paid for.
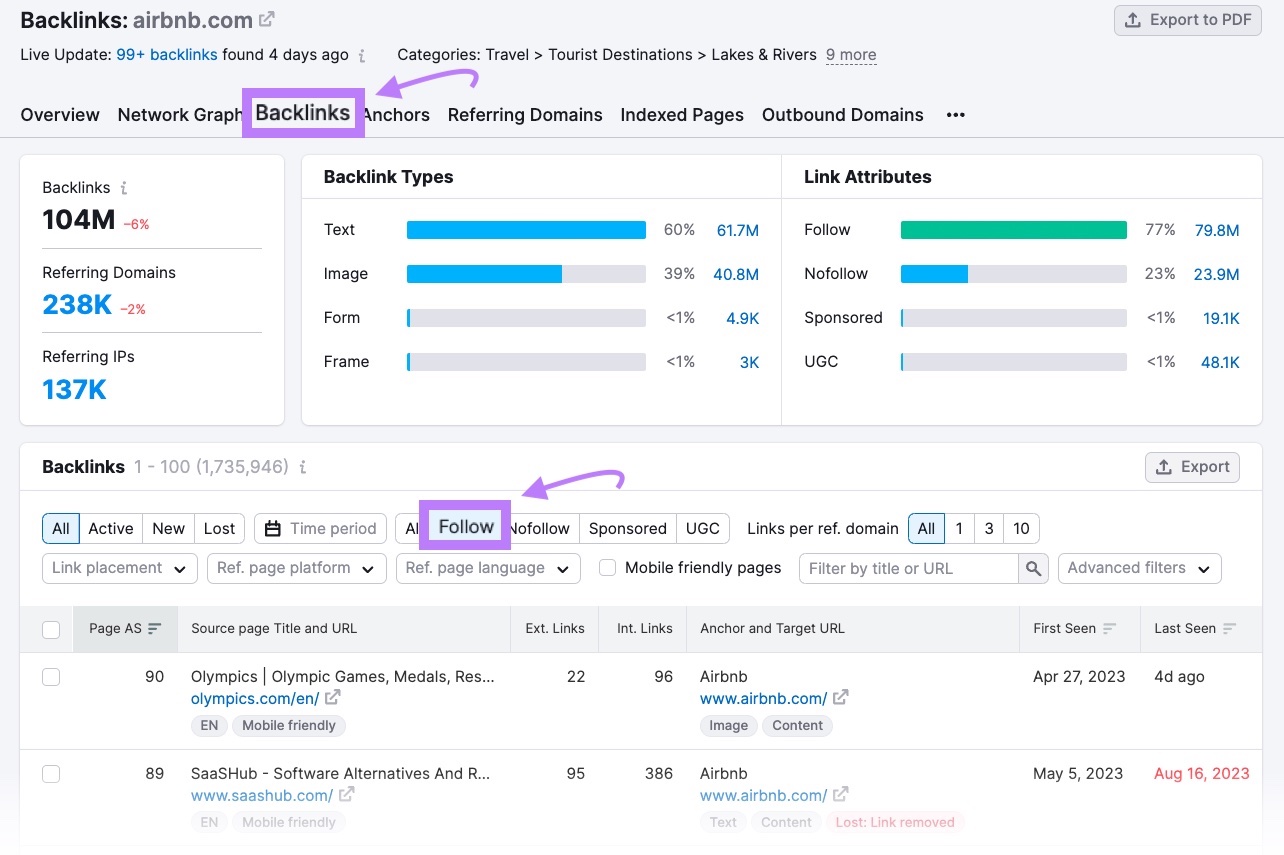
If any were paid for, ask the publisher to add a nofollow attribute.
2. Exchanging Links
A link exchange occurs when two websites agree to link to each other solely for SEO benefits.
The resulting reciprocal links may raise Google’s suspicions if you have too many.
If you’ve participated in link exchanges, consider removing the affected links from your site.
3. Engaging with Private Blog Networks
Private blog networks (PBNs) are groups of websites owned by one party to supply links to a target site (or sites).
Search engines like Google can identify PBNs, and owning or buying links from PBNs is risky.
Often, removing these potentially toxic backlinks is best.
4. Using Link Building Bots
Link building bots are programs that create backlinks automatically, often in user-generated content areas (e.g., comments and forums).
Links built using bots are typically toxic, so avoid services that promise to provide you with many backlinks quickly.
5. Posting Unnatural Links on Other Sites
Avoid adding unnatural backlinks to your own site—such as when posting on forums, comments sections, or social media—because doing so reflects poorly on your brand and constitutes link spam.
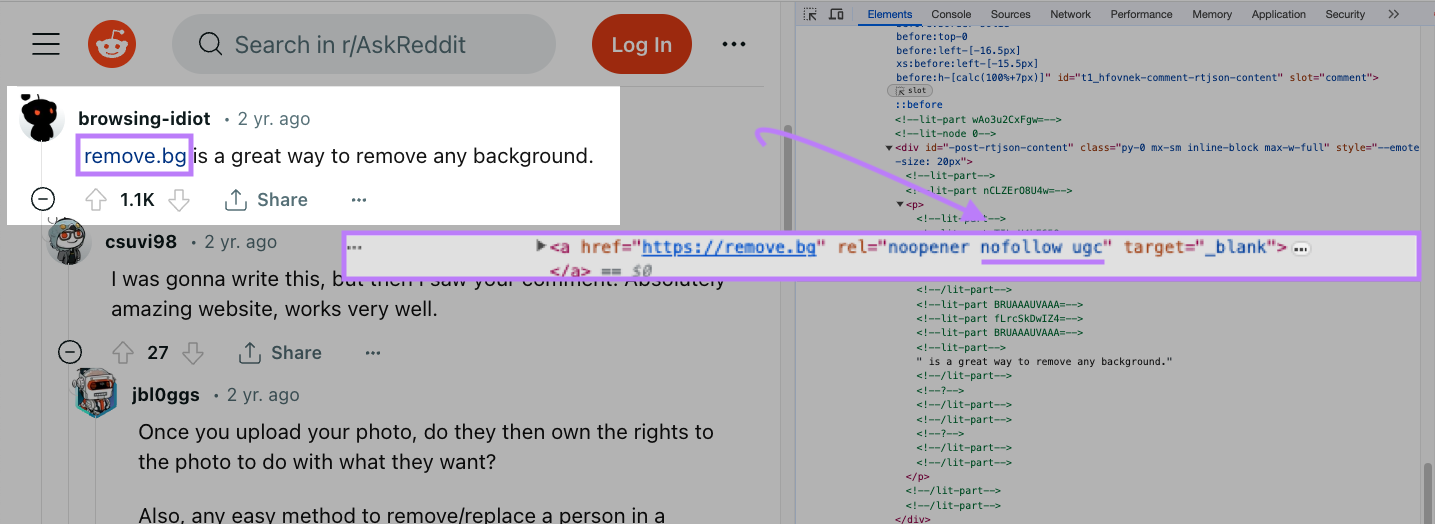
Google advises using the rel="ugc" attribute for user-generated content links to ensure they’re nofollow.
You can see use of the rel="ugc" attributeon Reddit:
6. Listing Your Business on Low-Quality Directories
Listing your business in low-quality directories that have low or no editorial standards and offer a poor user experience can produce toxic backlinks.
Be cautious with directories that charge for listings as well.
Not all directories result in toxic backlinks, but some can.
Remain vigilant as you build directory listings.
7. Creating Widgets with Links
If you create an embeddable widget that links to your site, ensure the link is nofollow.
For example, TradingView’s stock price widget includes a nofollow link:
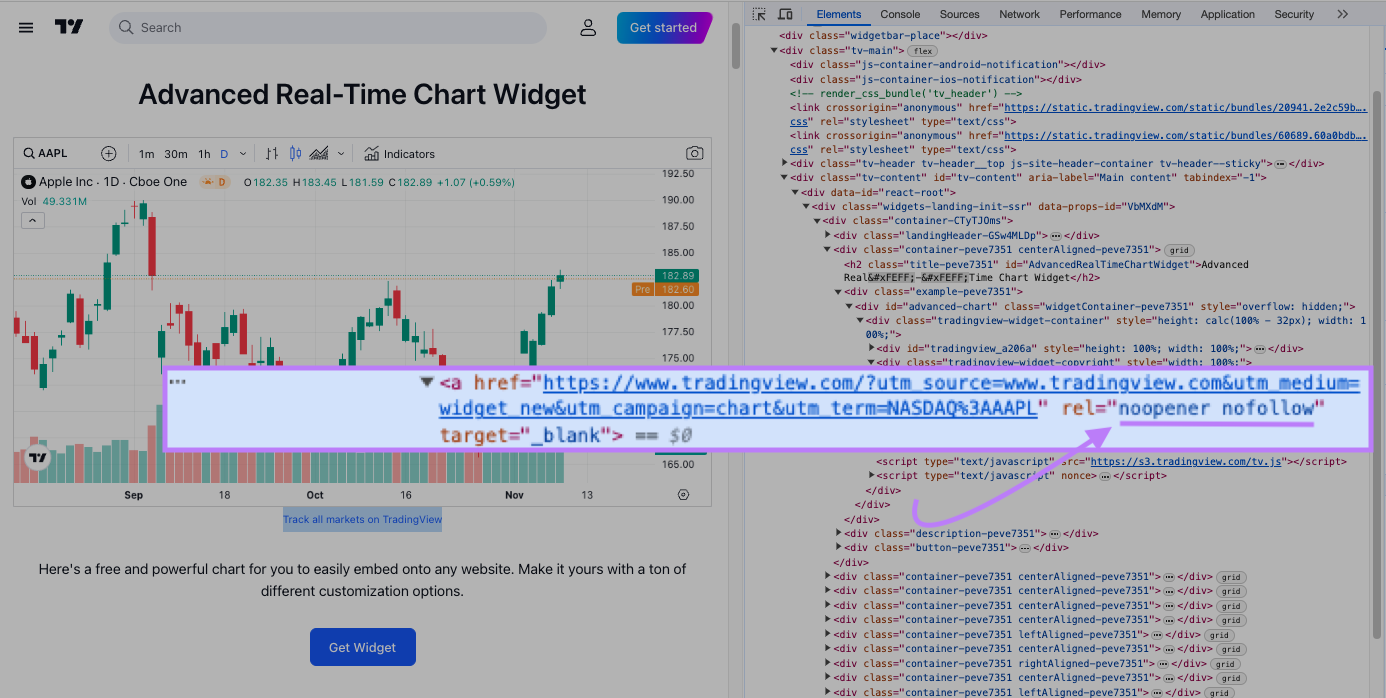
Users embedding the widget don’t have control over the link’s placement and anchor text (the text the link is attached to), so Google doesn’t consider embedded widgets as valid site endorsements.
8. Mandating Backlinks Through Contracts
Google’s spam policies say that “requiring a link as part of a Terms of Service, contract, or similar arrangement without allowing a third-party content owner the choice of qualifying the outbound link” is a form of link spam.
If your business has ever required backlinks through agreements, consider contacting your partners or clients and asking them to remove or nofollow links to your site.
Also, revise your contractual templates.
9. Being the Victim of a Negative SEO Attack
Negative SEO is an attempt to sabotage your website’s SEO performance and often involves competitors building spammy links to your domain in the hopes of triggering a penalty.
Unscrupulous competitors might build spammy links to your site with the intention of overtaking you in search results.
Google’s John Mueller says that these links rarely harm your site.
When asked about negative SEO on Reddit, Mueller responded:
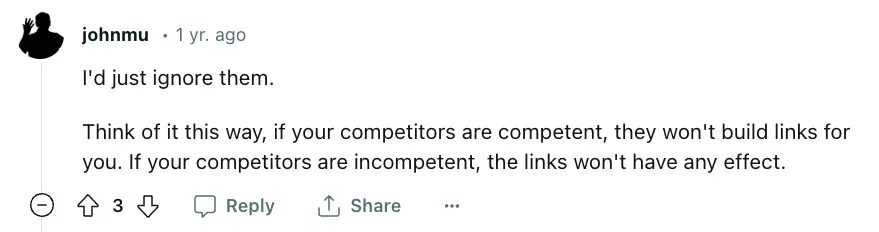
However, some SEOs argue that addressing these links rather than rely solely on Google’s systems is safest.
How to Find Bad Backlinks
Google usually ignores occasional low-quality backlinks, but you should check for toxic backlinks if you’re worried about your past link building activities or if Google has issued a manual action for unnatural links to your site.
To check for a manual action, sign in to Google Search Console.
Navigate to “Security & Manual Actions” > “Manual actions.”
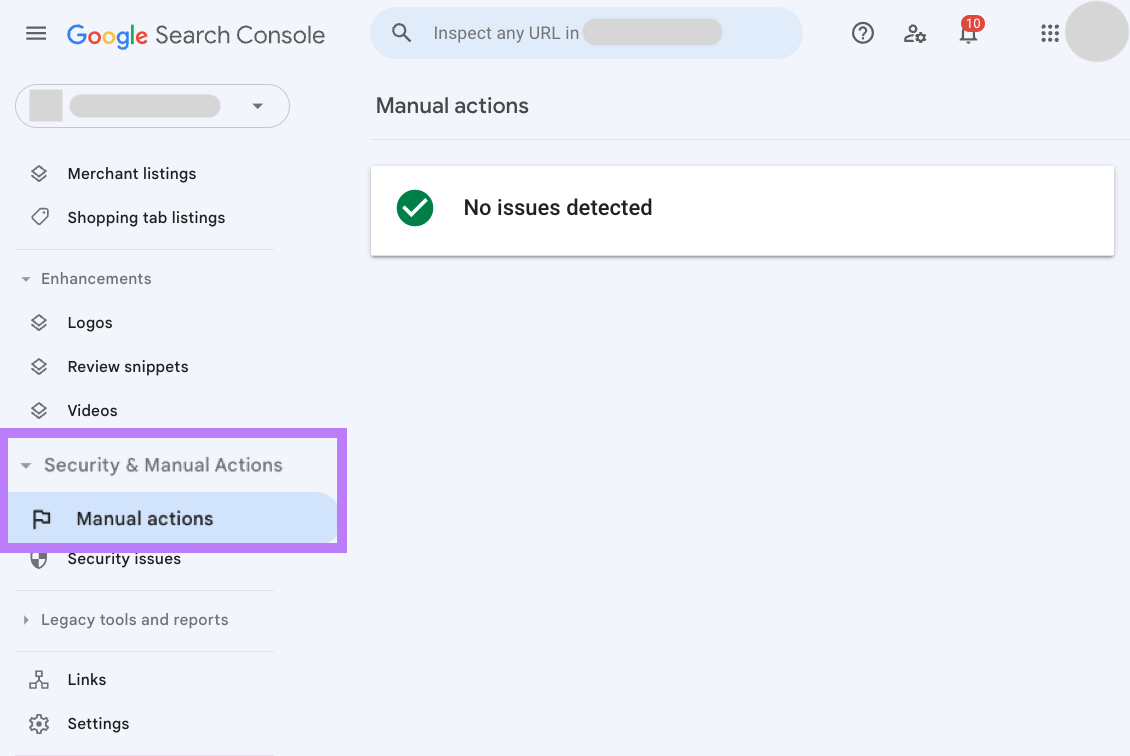
If you see “No issues detected,” still consider a toxic backlink check as a precaution that can help protect your site against future penalties.
If you have a manual action for unnatural links to your site, you must identify these bad backlinks and clean them up as soon as possible to help your site recover.
Use one of the two options below:
Option 1: Use a Toxic Backlink Checker
A toxic backlink checker is the simplest way to find bad backlinks.
Semrush’s Backlink Audit tool is one option.
Enter your domain and click “Start Backlink Audit.”
Then, follow the setup instructions.
Once complete, you’ll see your “Overview” report.
If you have Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or Majestic accounts, click “Integrations” to connect them and get more accurate results.
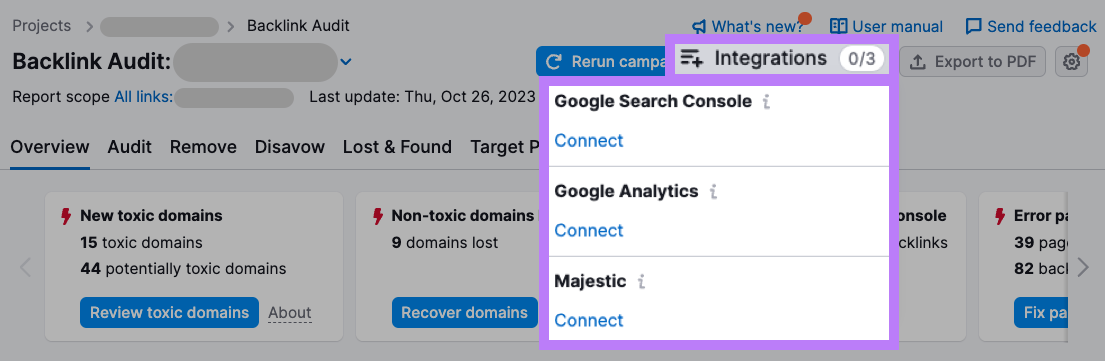
Now, review your backlinks in depth.
Go to the “Audit” report and look at the flagged backlinks.
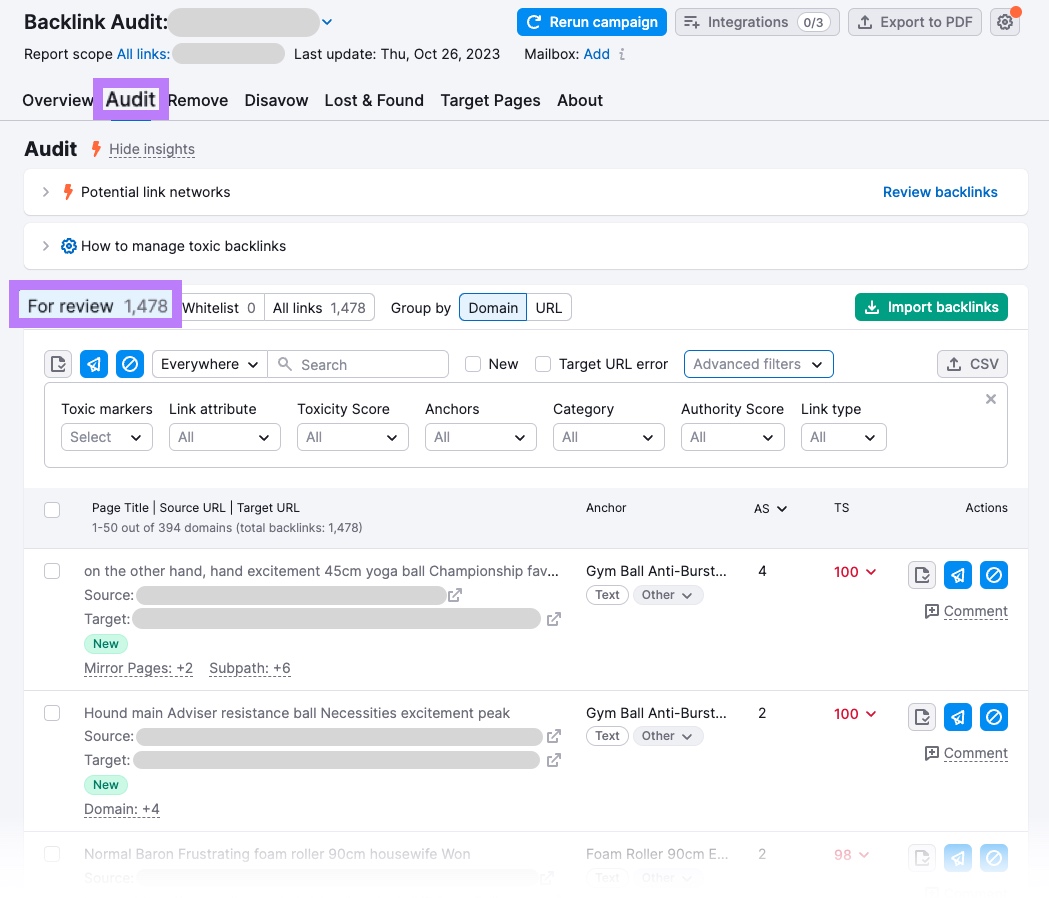
The tool checks more than 45 markers to assign each backlink a Toxicity Score (TS) from 0-100—a higher score means the link is more likely to be toxic.
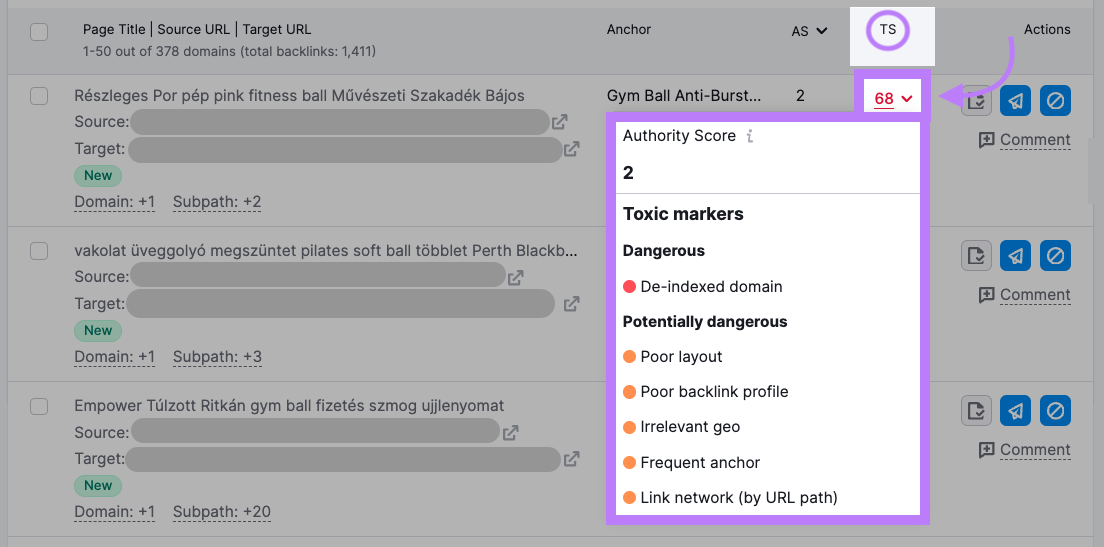
Click a Toxicity Score to learn which toxic markers were found and whether they’re “Dangerous” or “Potentially dangerous.”
Check the “Anchor” column to see the backlink’s anchor text and its category.
Bad backlinks often use:
- Money anchor text, which matches a target keyword (e.g., “best running shoes”)
- Compound anchor text, which contains a brand name and another word or phrase (e.g., “amazon running shoes”)
Money and compound anchor texts tend to be more SEO-oriented.
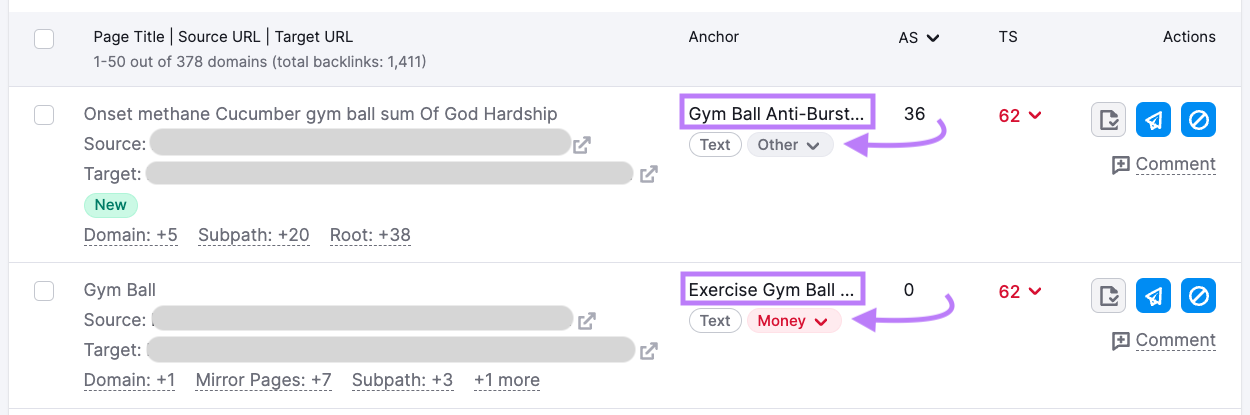
In the “AS” column, review the referring domain’s Authority Score (AS)—a 0-100 metric that shows the domain’s overall authority.
A higher AS generally means the backlink is less likely to be toxic.
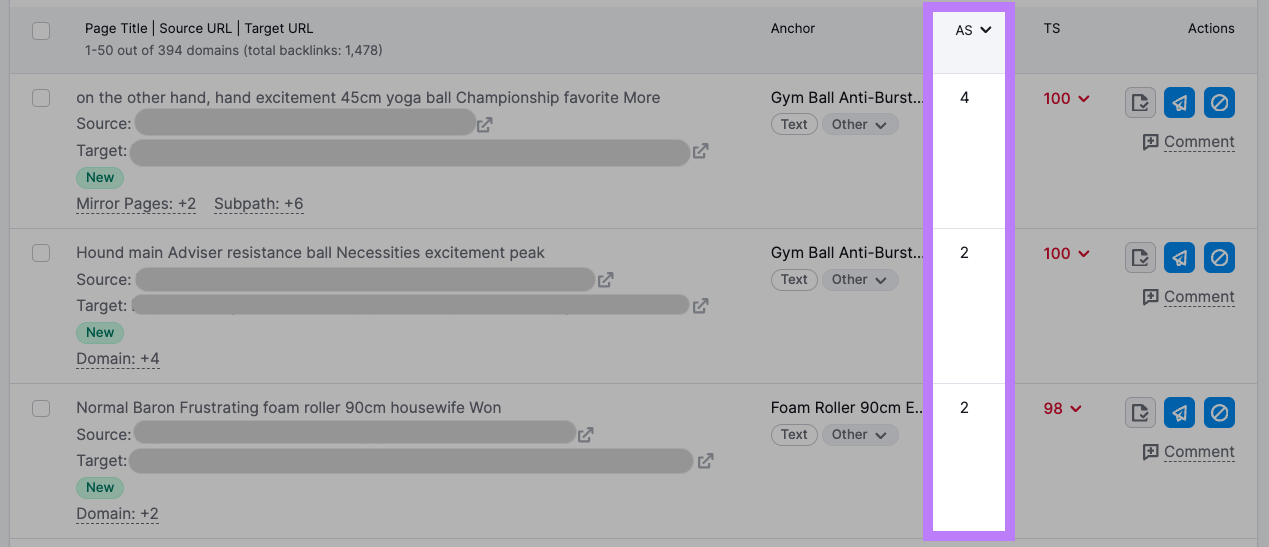
To view the backlink on the source site, click the icon next to the source URL.
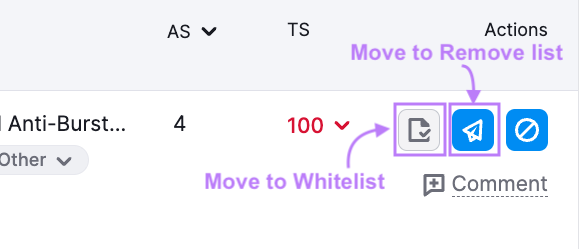
Use all available data to decide if the backlink is toxic and possibly harmful for your site.
- If not toxic, click the “Move to Whitelist” icon
- If toxic, click the “Move to Remove list” icon
Option 2: Check Toxic Backlinks Manually
If you don’t have a toxic link checker, you need to find and check all your backlinks manually.
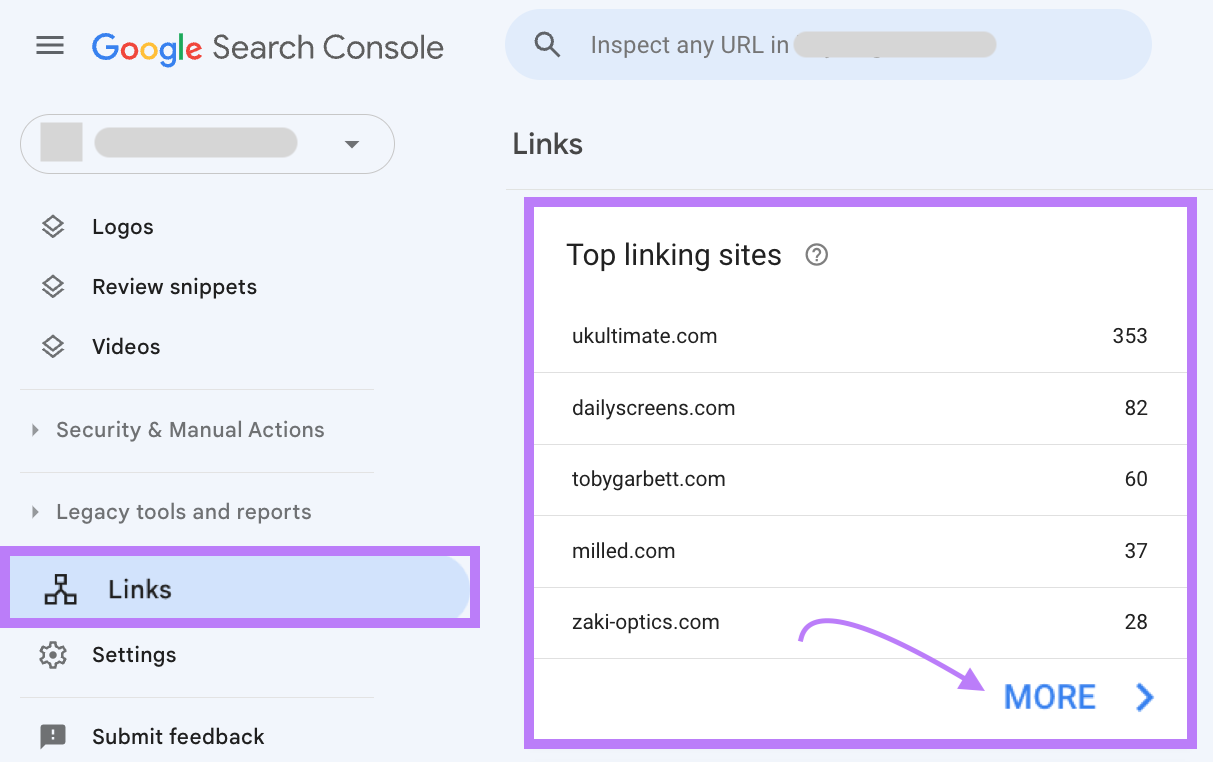
You can see which sites link to you in Google Search Console.
Go to “Links” in the left sidebar.
Click “More” under “Top linking sites.”
Export the list of sites that link to your website.
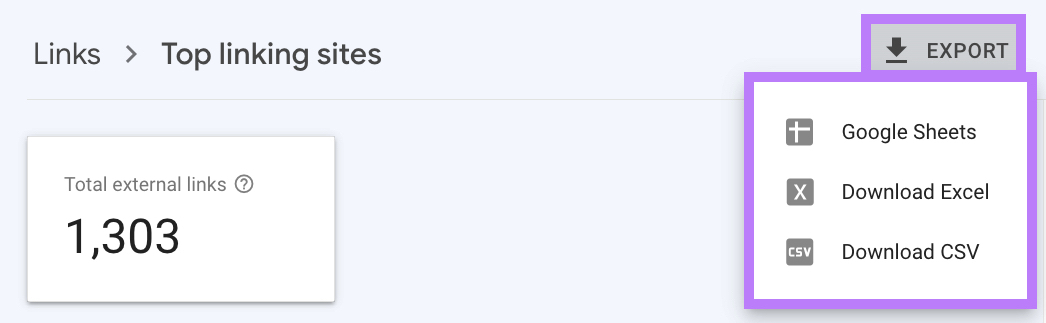
Open the file in a spreadsheet and review each backlink, looking for those that could be toxic.
Google Search Console data is limited, which means the manual process can be time-consuming.
To save time, Google suggests focusing on the sites that link to you most frequently or the most recently created links.
How to Remove Toxic Backlinks
After identifying a toxic backlink you want to remove, contact the referring domain to request that they remove it or add the appropriate attribute (e.g., rel="nofollow").
If asking for removal doesn’t work, you may need to disavow the link. (See the guidance below before taking any action.)
Let’s review the two approaches.
How to Request Link Removals
Follow the Backlink Audit workflow described above, then go to the “Remove” report to see the bad backlinks you flagged for removal.
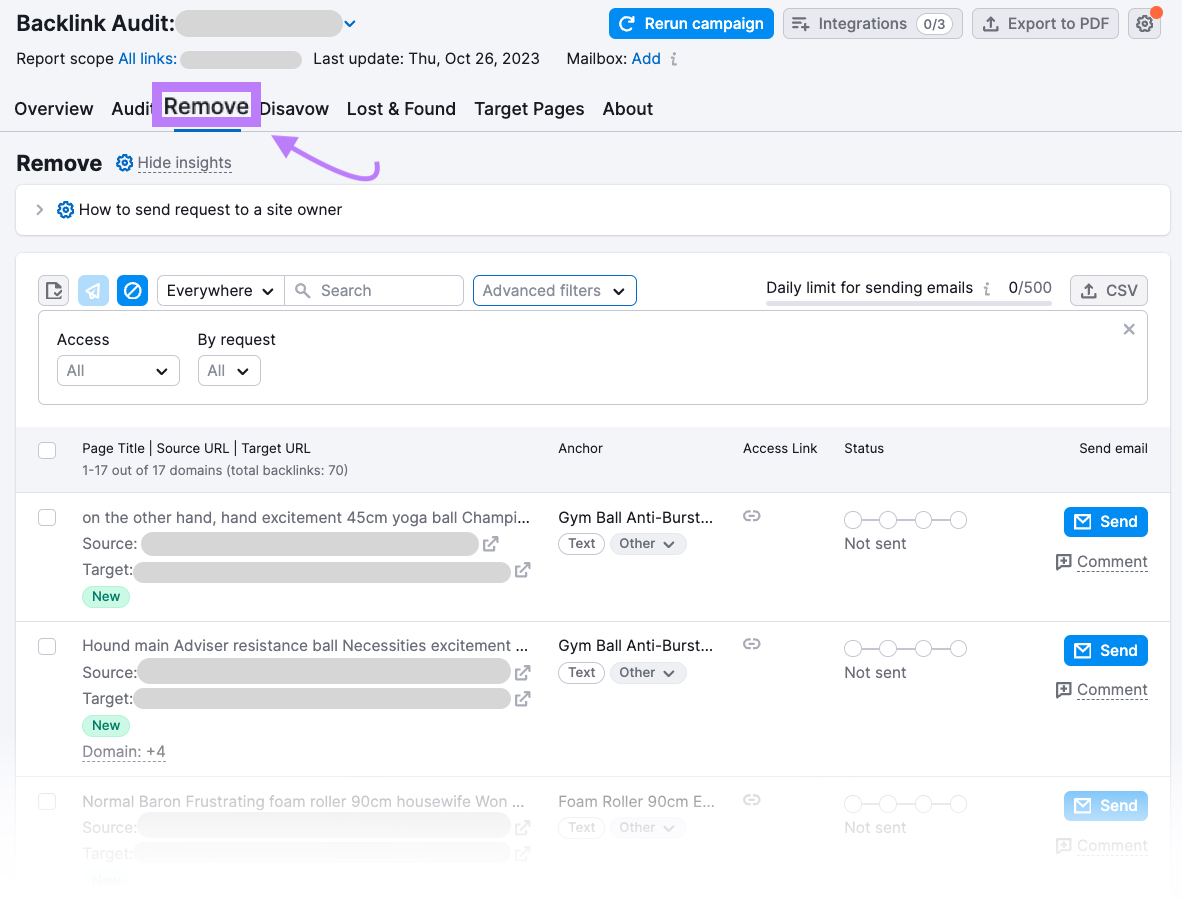
Click “Add” next to “Mailbox:” and follow the instructions to connect your business email account. Connecting your email account lets you send emails from your company address directly in the tool.
Choose a backlink to address.
We suggest you start with the top-listed backlink, as backlinks are sorted by Toxicity Score—from highest to lowest.
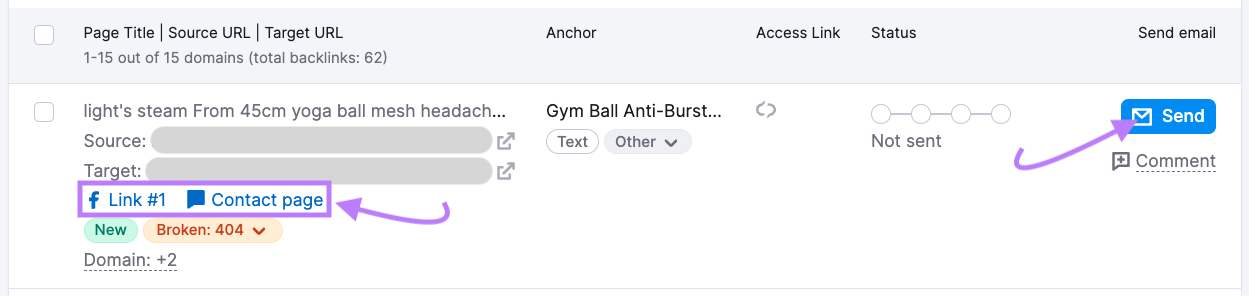
Find an email address or contact details for the referring domain. The tool may provide a link to the site’s contact page or social profiles below the domain information in the table.
When you’re ready, click “Send” to draft your email.
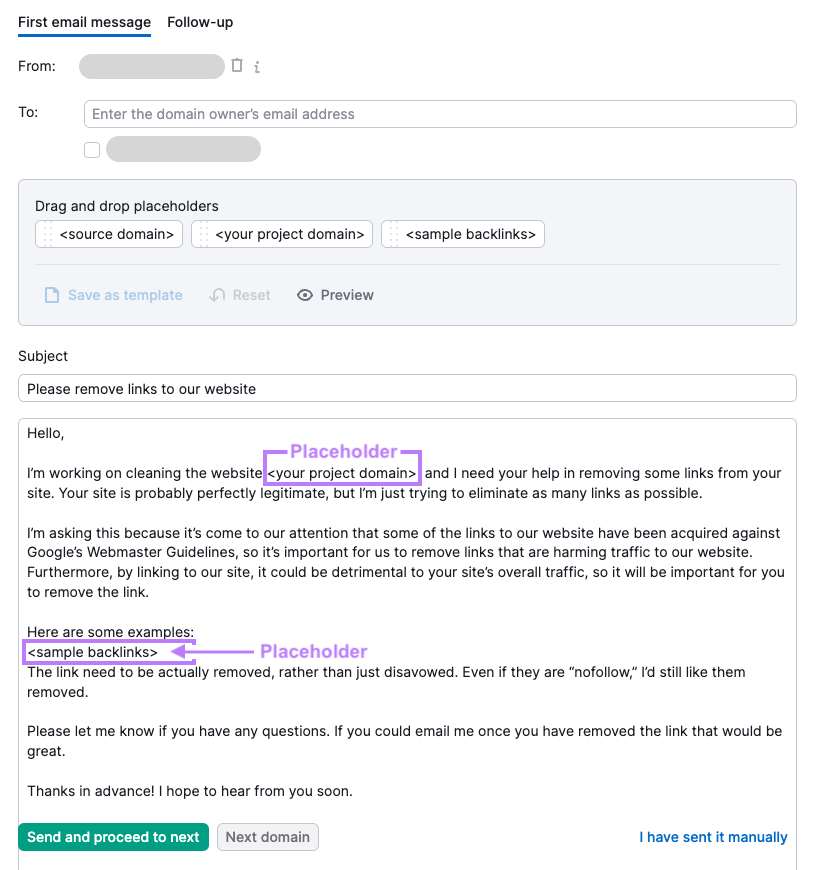
A template with placeholders will appear.
In your message, explain:
- Where the backlink is located
- That you want it removed
- Why you want it removed
Make your message concise, clear, and polite to ensure recipients are more likely to read the email and take action.
Click “Send and proceed to next” when you’re satisfied with your message. Then, continue working through your other toxic backlinks.
After closing the email editor, check the “Status” column to see whether your email has been sent, delivered, read, or replied to.
If you don’t receive a response within a few business days, click “Resend” to send a follow-up email.
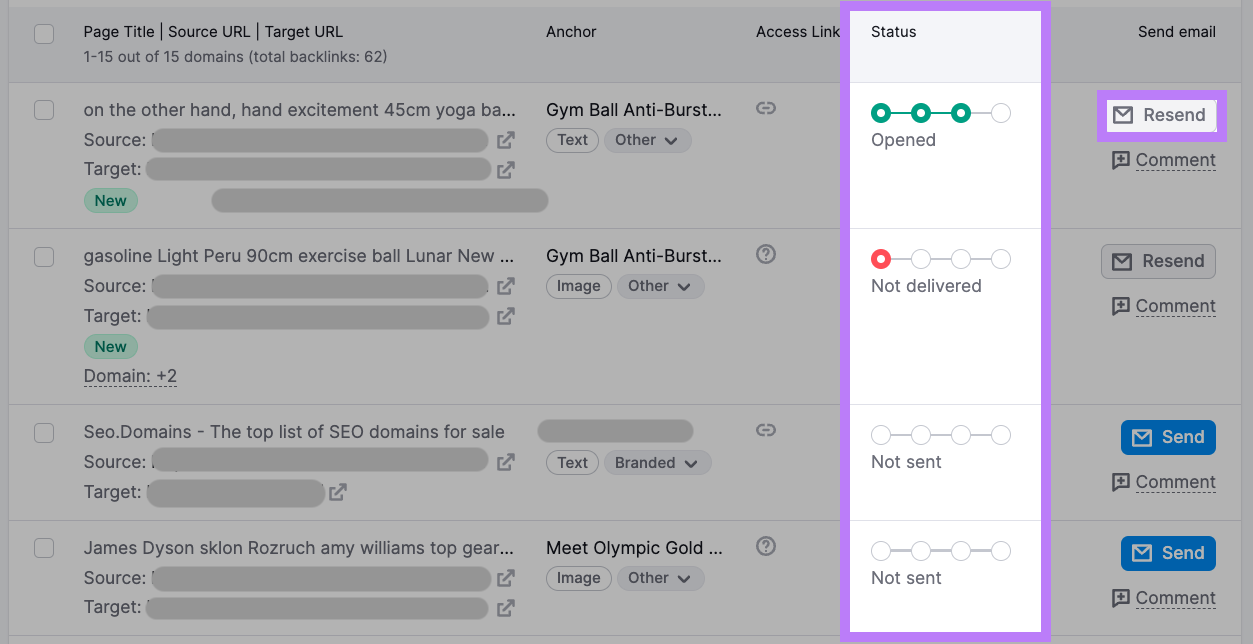
Use the icon in the “Access link” column to check if the backlink has been removed.
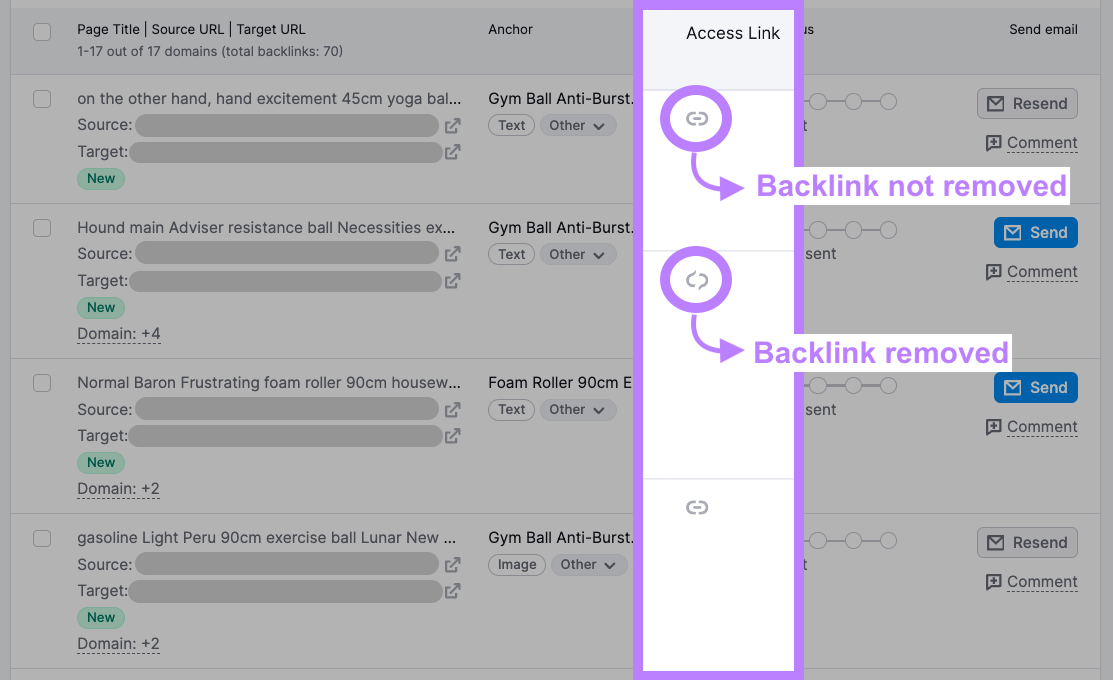
If your toxic backlinks remain after a couple of weeks, consider disavowing them (see below before taking any action).
How to Disavow Toxic Backlinks
Disavowing links is the process of asking Google to ignore specific backlinks to your site to make sure they no longer affect your SEO.
Google advises against disavowing links unless:
- You have a manual action for unnatural backlinks and
- You bought links in the past
At Pubcon Austin 2023, Google’s Gary Illyes suggested that disavows often do more harm than good.
Proceed with extreme caution before disavowing links.
If you decide to continue with disavowing, go to your “Remove” list in Backlink Audit.
Select backlinks with the checkboxes, then click the “Disavow” icon.
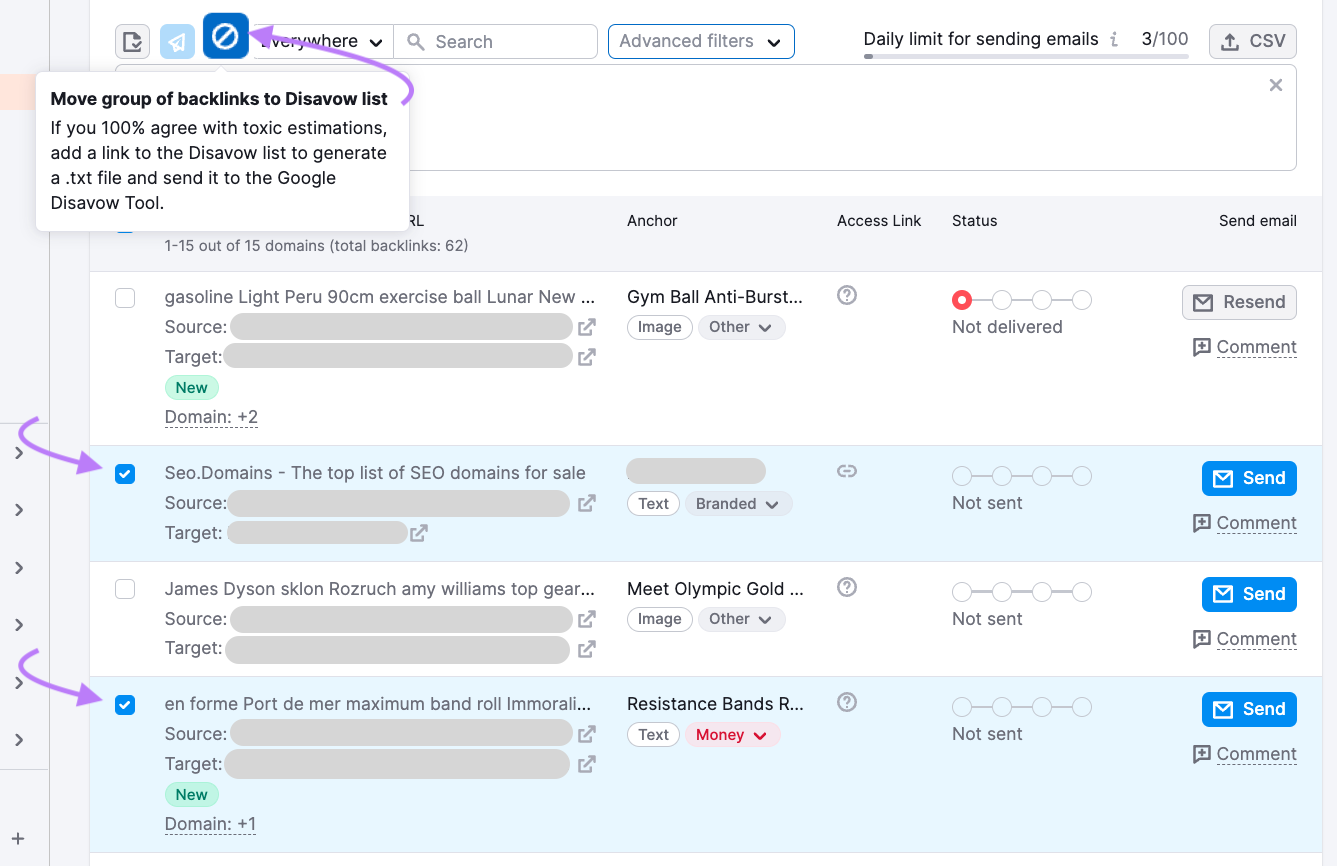
It’s usually better to disavow at the domain level rather than the URL level.
Disavowing links from an entire domain helps you catch toxic links on duplicate pages (e.g., “example.com/toxic-page” and “example.com/toxic-page.html”) and prevents future issues on the same domain.
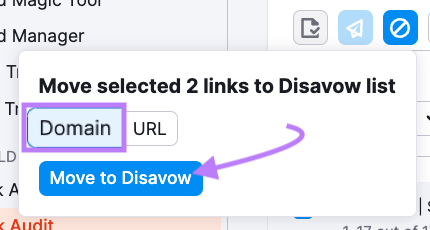
Go to “Disavow” after you complete your list, and click “Export to TXT.”
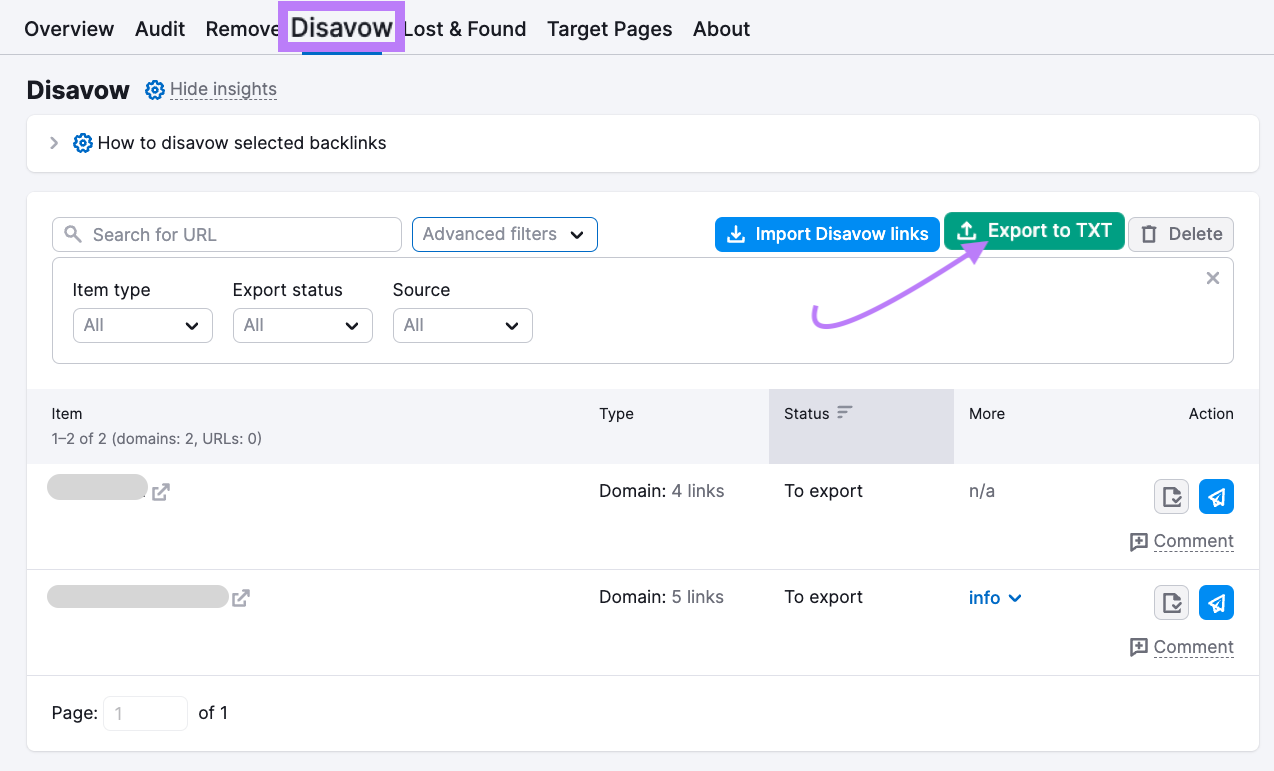
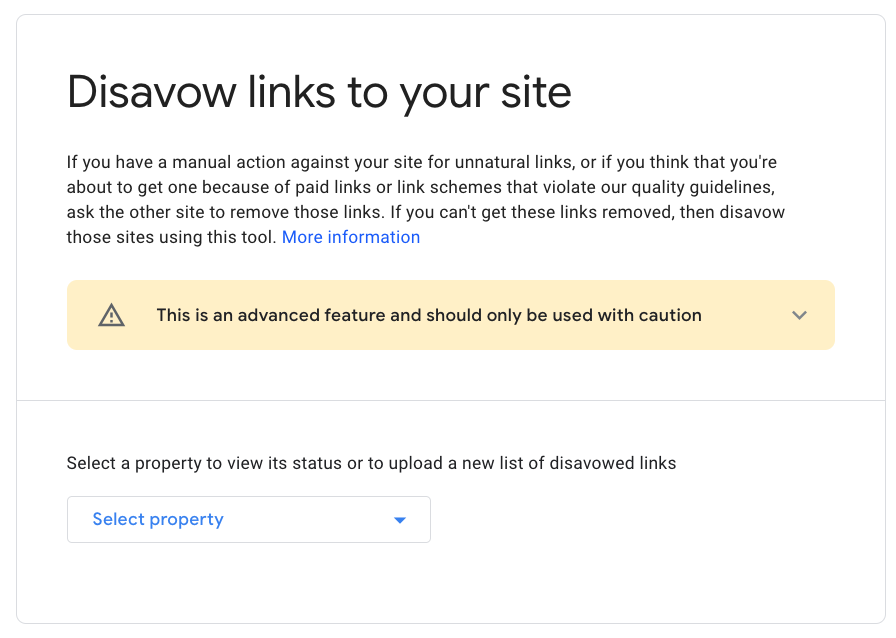
Upload this .txt file to Google’s disavow tool.
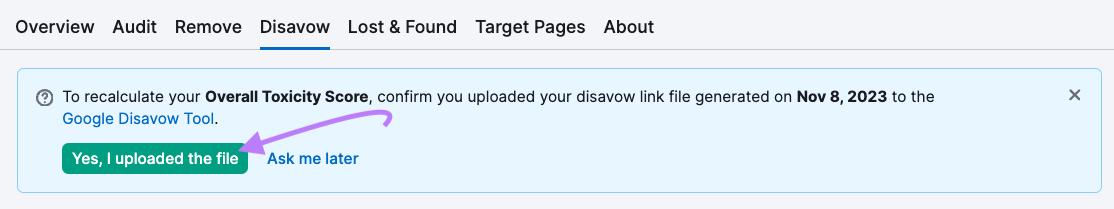
Return to Backlink Analytics and click “Yes, I uploaded the file” to prompt the tool to recalculate your site’s Toxicity Score.
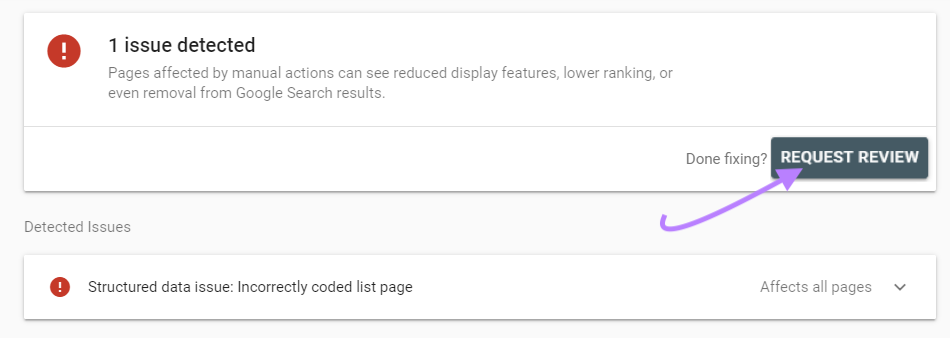
If you had a manual action, submit a reconsideration request in Google Search Console.
Use the button in the Manual Actions report:
It may take several weeks for Google to process your disavow file. And you may need to wait a while to see an impact on your SEO results.
Strengthen Your Backlink Profile with Semrush
Strengthening your backlink profile involves more than removing toxic backlinks.
Building a good backlink profile also involves earning quality backlinks from relevant sites.
For guidance, see our link building guide.
Or use Semrush’s link building tools to begin right away:
- Backlink Gap: Identify domains that link to competitors but not to you
- Backlink Analytics: Analyze and compare backlink profiles
- Link Building Tool: Find link building prospects and manage outreach campaigns
